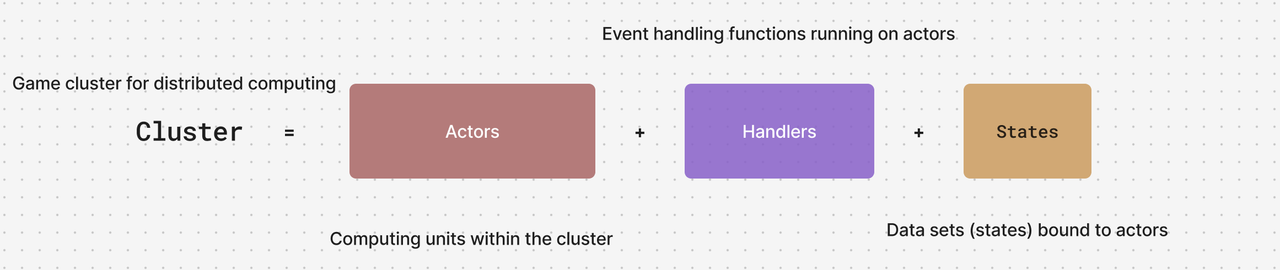
Braid is an innovative serverless game framework powered by the Actor model. It achieves intelligent load management through a unified addressing system, allowing developers to focus on designing and implementing Actors without the need to concern themselves with complex distributed system components.
- Actor-Centric: Built around a pure Actor model, simplifying distributed logic.
- Automatic Load Balancing: Intelligent resource allocation through the addressing system.
- Development Focus: No need to consider underlying architecture like services or clusters; concentrate on game logic.
Install and set up a minimal working game server using the braid-cli tool
# 1. Install CLI Tool
$ go install github.com/pojol/braid-cli@latest
# 2. Generate a New Project
$ braid-cli new "you-project-name" v0.1.4
# 3. Creating .go Files from Actor Template Configurations
$ cd you-project-name/template
$ go generate
# 4. Navigate to the services directory, then try to build and run the demo
$ cd you-project-name/node
$ go run main.goRegister actors to nodes by configuring
node.yaml
actors:
- name: "USER"
id : "user"
unique: false
weight: 100
limit: 10000Create actor constructors and bind them to the factory
type userActor struct {
*actor.Runtime
state *Entity
}
func NewUserActor(p core.IActorBuilder) core.IActor {
return &httpAcceptorActor{
Runtime: &actor.Runtime{Id: p.GetID(), Ty: p.GetType(), Sys: p.GetSystem()},
state: user.NewEntity(p.GetID())
}
}
func (a *userActor) Init(ctx context.Context) {
a.Runtime.Init(ctx)
a.state.Load(ctx) // Load data from cache to local storage
}
// factory.go with node.yaml
case template.USER:
factory.bind("USER", v.Unique, v.Weight, v.Limit, NewUserActor)Note: All handling functions (events, timers) registered in an actor are processed synchronously. Users do not need to concern themselves with asynchronous logic within the actor.
Bind event handler
user.RegisterEvent("use_item", func(ctx core.ActorContext) *actor.DefaultChain {
// use middleware
unpackcfg := &middleware.MsgUnpackCfg[proto.xxx]{}
return &actor.DefaultChain{
Before: []Base.MiddlewareHandler{
middleware.MsgUnpack(unpackcfg),
},
Handler: func(ctx context.Context, msg *router.MsgWrapper) error {
realmsg, ok := unpackcfg.Msg.(*proto.xxx)
// todo ...
return nil
}
}
})Bind timer handler
user.RegisterTimer(0, 1000, func(ctx core.ActorContext) error {
state := ctx.GetValue(xxxStateKey{}).(*xxxState)
if state.State == Init {
// todo & state transitions
state.State = Running
} else if state.State == Running {
}
return nil
})Subscribe to messages and bind event handler
user.SubscriptionEvent(events.EvChatMessageStore, a.Id, func() {
// After successful subscription, bind a handler function for the message
a.RegisterEvent(events.EvChatMessageStore, events.MakeChatStoreMessage)
}, pubsub.WithTTL(time.Hour*24*30))Use the project built with scaffold above
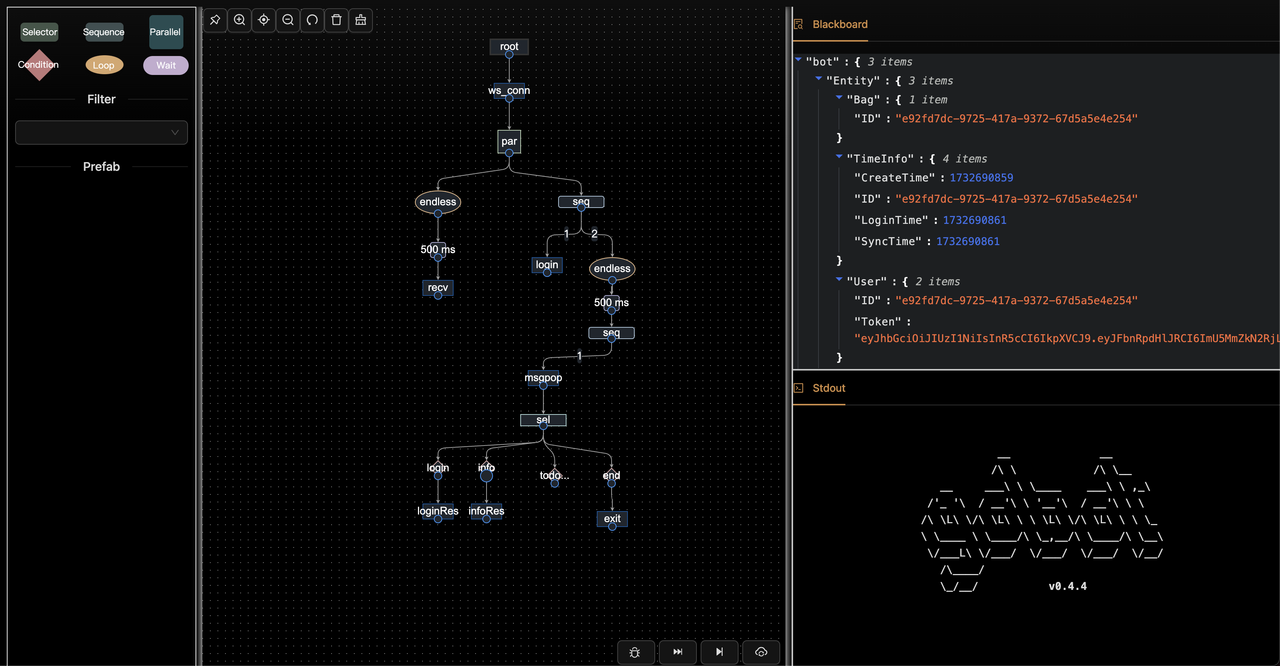
$ cd you-project-name/testbots
# 1. Launch Bot service
$ go run main.go
# 2. Download gobot editor #latest
https://github.com/pojol/gobot/releases
# 3. Launch Bot editor
$ run gobot_editor_[ver].exe or .dmg
# 4. Go to Bots tab
# 5. Click Load button to load the bot
# 6. Drag the testbot.bh file from the testbots directory to the bots page
# 7. Click bottom-left Create Bot button to create instance
# 8. Click Run to the Next button to execute the bot step by step. Monitor the bot-server interaction in the right preview window