(French version below)
This repository focuses on Infra-As-Code. But a blog post on Medium covers it all, including how to automate the software installation and configuration.
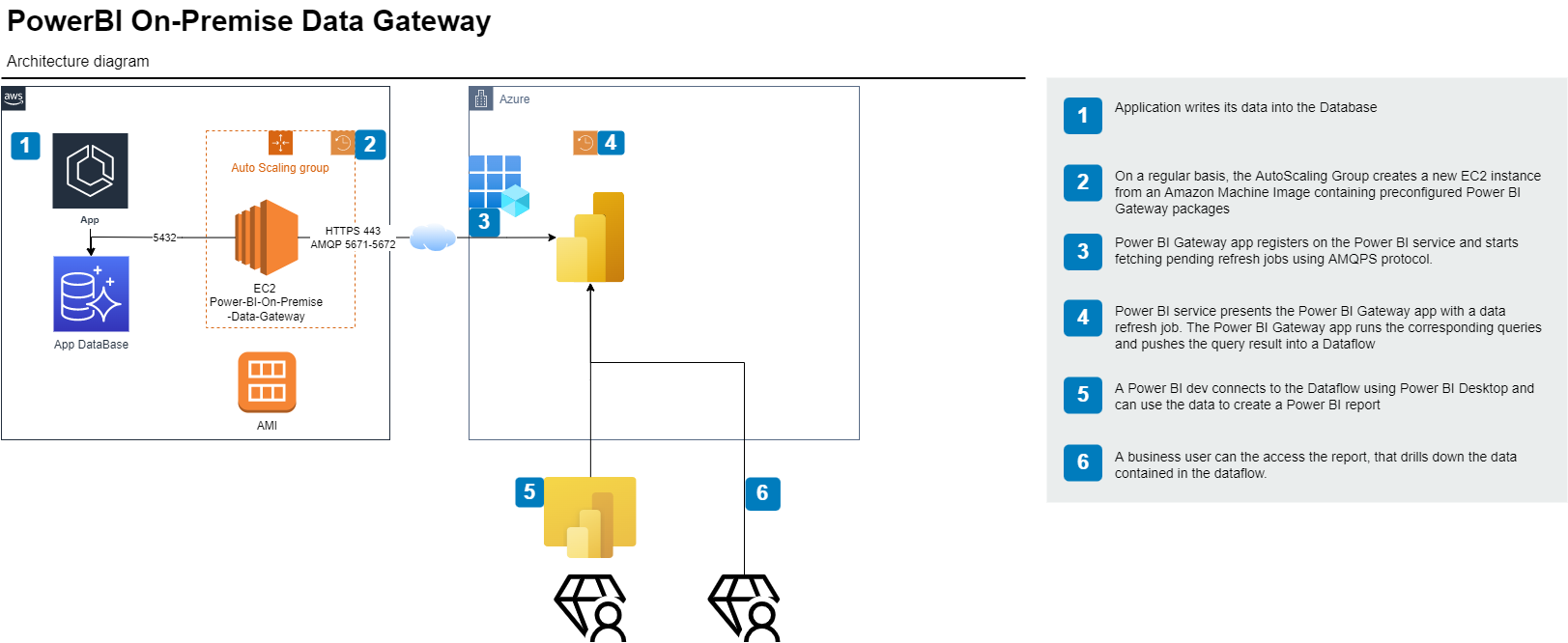
This stack contains an AWS Auto Scaling Group, enabling to
- schedule the periodic creation of an EC2 instance from an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- We start with a blank Windows server image, then once the Gateway is up and running, we replace it with an snapshot of the installed VM.
- schedule the instance termination a short while after (letting Power BI service perform schedule Dataflow refresh in the meantime)
The EC2 instance:
- is sourced on AWS spot market
- belongs to a security group that can access both the (365/Azure hosted) Power BI service as well as the (PostgreSQL) database.
- has the role required to register with SSM, hence enabling console/remote desktop access without the need of any network connectivity
The stack also creates the key pair required to get the admin user password.
La stack comprend essentiellement un Auto Scaling Group, qui permet de :
- programmer la création périodique d'une instance EC2 à partir d'une image machine Windows
- Cette image porte déjà l'ensemble des composants nécessaires : PowerBI On-Premise Gateway + driver Npgsql-4.0.10.
- détruire l'instance EC2 qqs min après sa création, ce qui laisse le temps au service Power BI de faire le rafraichissement périodique de données.
L'instance EC2 :
- est sourcée au prix spot AWS
- appartient à un Security Group qui lui permet d'atteindre les services Power BI et la base de données PostgreSql
- porte le rôle nécessaire pour être accessible (en RDP ou console Powershell) via AWS Systems Manager.
La stack permet enfin la création de la paire de clés permettant de se connecter à la machine.
Nb : la stack s'appuie sur 2 AMIs.
- La première est l'image Win 2019 server AWS à utiliser au premier deploy
- La seconde est l'image de la machine avec la Gateway installée, qui doit être crée à la main après avoir installé la Gateway.
- Gestion Profile
- Soit avec l'attribut de commande Terraform
--profile- exemples :
terraform init --var "profile=<<PROFILE_NAME>" --backend-config=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/backend.tfbackend terraform (plan,apply,destroy) --var "profile=<PROFILE_NAME>" --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars
- exemples :
- Soit en export du profile en variable d'environnement
- Linux/MacOS
ou inline
export AWS_PROFILE=<PROFILE_NAME> terraform (plan,apply,destroy) --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT-FOLDER>/values.tfvarsAWS_PROFILE=<PROFILE_NAME> terraform apply --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT-FOLDER>/values.tfvars - Windows (cmd)
SET AWS_PROFILE="<PROFILE_NAME>" terraform (plan,apply,destroy) --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT-FOLDER>/values.tfvars - Windows (powershell)
$Env:AWS_PROFILE="<PROFILE_NAME>" terraform (plan,apply,destroy) --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT-FOLDER>/values.tfvars
- Linux/MacOS
- Soit avec l'attribut de commande Terraform
- Initialization
terraform init --backend-config=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/backend.tfbackendterraform init --var "profile=<PROFILE_NAME>" --backend-config=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/backend.tfbackend
- Plan
terraform plan --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvarsterraform plan --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/<OTHER_FILE>.tfvarsterraform plan --var "profile=<PROFILE_NAME>" --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars
- Apply
terraform apply --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvarsterraform apply --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/<OTHER_FILE>.tfvarsterraform apply --var "profile=<PROFILE_NAME>" --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars
- Destroy
terraform destroy --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvarsterraform destroy --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/<OTHER_FILE>.tfvarsterraform destroy --var "profile=<PROFILE_NAME>" --var-file=./var/<ACCOUNT_FOLDER>/values.tfvars