ISO 28258:2013 describes how to digitally exchange soil-related data. It aims to facilitate the exchange of valid, clearly described and specified soil-related data between individuals and organizations via digital systems, and enables any soil data producer, holder or user to find and transfer data in an unambiguous way. Read more
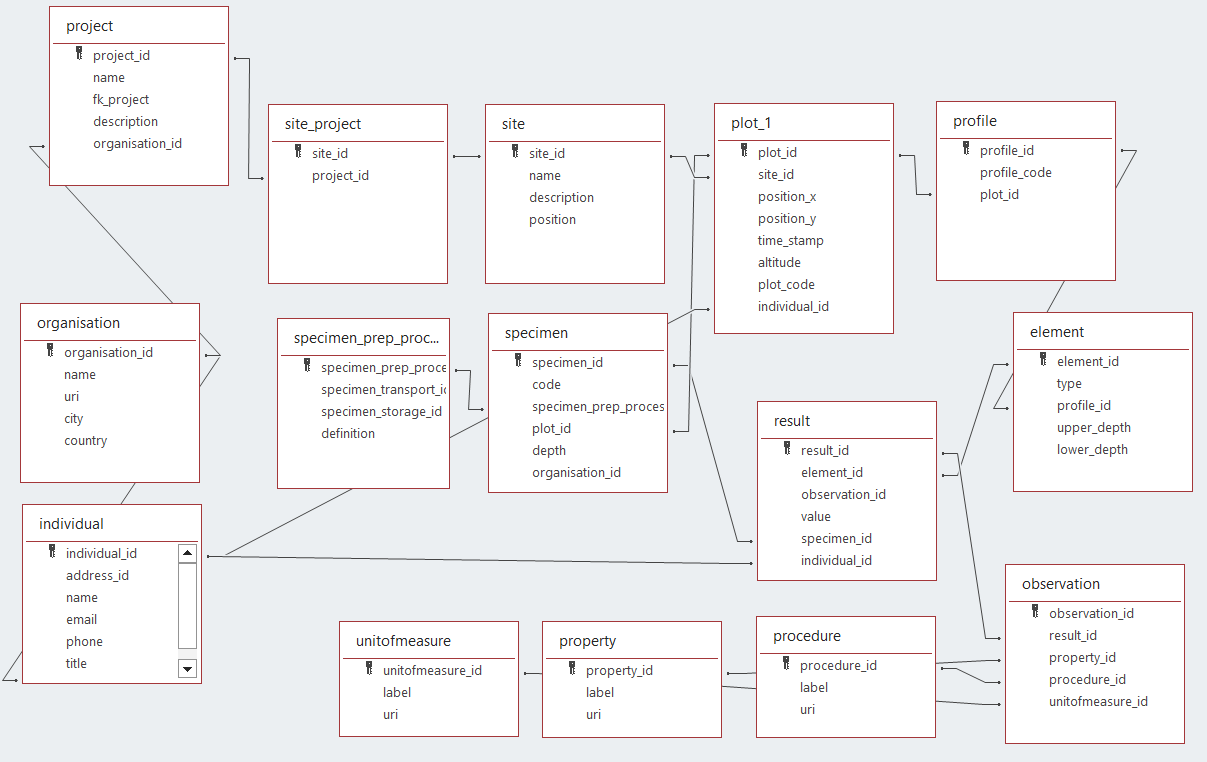
ISO28258 is implemented as a UML model. The UML model has been used to create a relational database model able to capture the entities from the UML model and their relations in a database. Initial development started in MS Access and is ported to other formats, such as GeoPackage (SQLite) and PostGreSQL. The benefit of the latter is that they can store positions as actual geometries.
This work builds on the work of Sousa et al, which implemented a postgres version of ISO28258. A simplification has been applied to the model suggested by Sousa et al, the observation and result types are not split out by type (physio chemical, descriptive, biological, ...) but all stored in a single results table. The result.value column is currently of type string, which allows both string and numeric values, but can not enforce numeric if numeric is expected. One could even supply a xml or json snippet in that field, if the result has a complex value. Results are either linked to a element (of type layer or horizon) via element_id, or to a specimen via specimen_id.
The lookup tables (code lists) properties, procedures and unit of measure are populated from the Glosis ontology.
The project is currently in beta state, welcoming your suggestions.