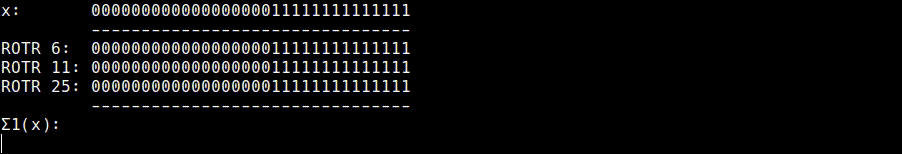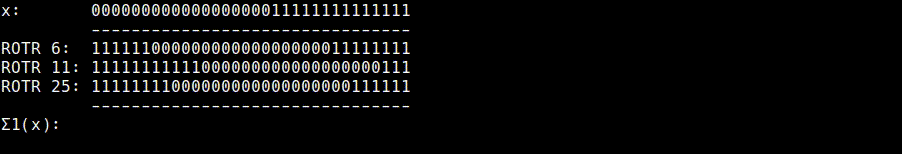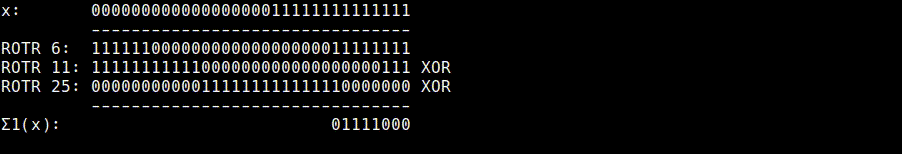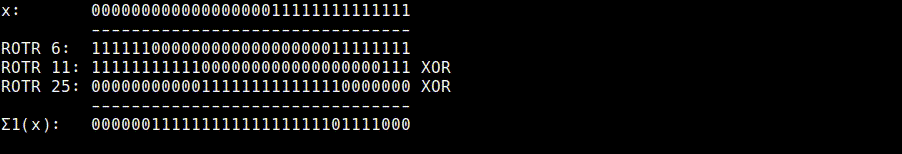An animation of the SHA-256 hash function in your terminal.
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f9EbD6iY9zI
Just run the sha256.rb script with the data you want to see hashed.
# simple
ruby sha256.rb abc
# hash binary or hex data by using `0b` or `0x` prefixes
ruby sha256.rb 0b01100001
ruby sha256.rb 0xaabbccdd
# speed up or step through the animation (optional)
ruby sha256.rb abc normal # default
ruby sha256.rb abc fast
ruby sha256.rb abc enter
You can also run the individual functions used in SHA-256 by passing in binary strings as arguments:
ruby shr.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000 22
ruby rotr.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000 22
ruby sigma0.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000
ruby sigma1.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000
ruby usigma0.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000
ruby usigma1.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000
ruby ch.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000 11110000111100001111000011110000 00000000000000001111111111111111
ruby maj.rb 11111111111111110000000000000000 11110000111100001111000011110000 00000000000000001111111111111111
You can do double-SHA256 (e.g. Bitcoin) by using hash256.rb. This script accepts hex data (e.g. block headers, transaction data) by default.
ruby hash256.rb 0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003ba3edfd7a7b12b27ac72c3e67768f617fc81bc3888a51323a9fb8aa4b1e5e4a29ab5f49ffff001d1dac2b7c # genesis block header
The NIST specification contains a precise explanation of SHA-256. The following is essentially a visualised summary of that document.
The official specification begins with a number of definitions, but seeing as this is a simplified explanation, all I want you to know is:
bit=0or1(the smallest unit of storage on a computer)word= 32 bits
Also, bitwise operations use the following symbols:
OR = |
XOR = ^
AND = &
NOT = ~
SHA-256 uses four basic bitwise operations on words.
Right Shift (shr.rb)
SHRn(x) = x >> n
Move bits a number of positions to the right. The bits shifted off the right-hand side are lost.
Rotate Right (rotr.rb)
ROTRn(x) = (x >> n) | (x << 32-n)
Move bits a number of positions to the right, and place the shifted bits on the left-hand side. This can also be referred to as a circular right shift.
Exclusive Or (xor.rb)
x ^ y ^ z
The XOR bitwise operator takes two input bits, and outputs a 1 if only one of them is a 1. This is useful for getting a balanced representation of multiple bits when merging them together via multiple XOR operations.
Addition (add.rb)
(v + w + x + y + z) % 232
This is standard integer addition, but we constrain the result to a 32 bit number by taking the result modulus 232.
The operations above can be combined to create functions.
The first four functions are named using the Greek symbol Sigma (lowercase σ and uppercase Σ). This is for no particular reason, it's just so we can give names to some combined operations.
I like to think of these as the "rotational" functions.
σ0 (sigma0.rb)
σ0(x) = ROTR7(x) ^ ROTR18(x) ^ SHR3(x)
σ1 (sigma1.rb)
σ1(x) = ROTR17(x) ^ ROTR19(x) ^ SHR10(x)
Σ0 (usigma0.rb)
Σ0(x) = ROTR2(x) ^ ROTR13(x) ^ ROTR22(x)
Σ1 (usigma1.rb)
Σ1(x) = ROTR6(x) ^ ROTR11(x) ^ ROTR25(x)
The last two functions of Choice and Majority accept three different inputs.
Choice (ch.rb)
This function uses the x bit to choose between the y and z bits. It chooses the y bit if x=1, and chooses the z bit if x=0.
Ch(x, y, z) = (x & y) ^ (~x & z)
Majority (maj.rb)
This function returns the majority of the three bits.
Maj(x, y, z) = (x & y) ^ (x & z) ^ (y & z)
4. Constants (constants.rb)
Kt = ∛primes (first 32 bits of fractional part)
SHA-256 uses sixty four constants Kt to help with mixing up the bits during the main hash computation. These constants are generated by taking the cube root of the first sixty four prime numbers.
The fractional parts of these cube roots are irrational (they go on forever), so they make for a good selection of random bits to use at constants. This is better than using specifically chosen constants, as this makes it less likely that the hash function has been designed with a back-door.
Anyway, to get 32 bits from these numbers, we take the fractional part and multiply it by 232, and use the resulting integer as the constant.
Now that we've defined the functions and constants we're going to use, the next step is to prepare the message for hashing.
5. Message (message.rb)
As you may have noticed, SHA-256 operates on the individual bits of data. So we before we can hash any data, we first of all need to convert it to its binary representation (1s and 0s).
For example when hashing a string, we convert each character to its corresponding number in the ASCII table. These numbers are converted to binary, and it's this binary data that we use as the input to the hash function.
6. Padding (padding.rb)
The SHA-256 hash function works on data in 512-bit chunks, so all messages need to be padded with zeros up to the nearest multiple of 512 bits.
Furthermore, to prevent similar inputs from hashing to the same result, we separate the message from the zeros with a 1 bit, and also include the size of the message in the last 64 bits of the padding.
NOTE: This method of separating the message with a 1 and including the message size in the padding is known as Merkle–Damgård strengthening (MD strengthening).
7. Message Blocks (blocks.rb)
After the message has been padded, we cut it in to equal 512-bit message blocks Mi to be processed by the hash function. (There is only one message block for this example message, so the animation above isn't very interesting.)
Each of these message blocks can also be further split in to 16 words Mij (512 / 32 = 16 words), which will come in handy in just a moment.
Now that we have padded our message and cut it in to equal chunks, we put each of the message blocks through the main hash function.
8. Message Schedule (schedule.rb, expansion.rb)
For each message block we create a sixty-four word message schedule Wt.
The first sixteen words of this message schedule are constructed from the message block.
Wt = Mit (for 0 ≤ t ≤ 15)
This is then expanded to a total of sixty four words by applying rotational functions to some of the words already in the schedule.
Wt = σ1(Wt-2) + Wt-7 + σ0(Wt-15) + Wt-16 (for 16 ≤ t ≤ 63)
9. Initial Hash Value (initial.rb)
The hash function begins by setting the initial hash value H0 in the state registers (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h).
H0 = √primes (first 32 bits of fractional part)
Like the constants, the initial hash value uses the fractional part of the square root of the first eight prime numbers. This gives us a random set of bits that we can use as a platform to begin the hash computation.
This is the heart of the hash function.
For each word in the message schedule, we use the current values in the state registers to calculate two new temporary words (T1 and T2).
Temporary Word 1 (t1.rb)
T1 = Σ1(e) + Ch(e, f, g) + h + Kt + Wt
This temporary word takes the next word in the message schedule along with the next constant from the list. These values added to a Σ1 rotation of the fifth value in the state register, the choice of the values in the last three registers, and the value of the last register on its own.
Temporary Word 2 (t2.rb)
T2 = Σ0(a) + Maj(a, b, c)
This temporary word is calculated by adding a Σ0 rotation of the first value in the state register to a majority of the values in the first three registers.
Compression (compression.rb)
After calculating the two temporary words, we shift each value in the state registers down one position, and update the following registers:
- The first value in the state register becomes
T1+T2. - The fifth value in the state register has
T1added to it.
This is one "round" of compression, and is repeated for every word in the message schedule.
After we have compressed the entire message schedule, we add the resulting hash value to the initial hash value we started with. This gives us the final hash value for this message block.
If there are further message blocks to be processed, the current hash value will be used as the initial hash value in the next compression.
NOTE: This process of applying a compression function to each message block and using the output as the input for the next compression is known as the Merkle–Damgård construction.
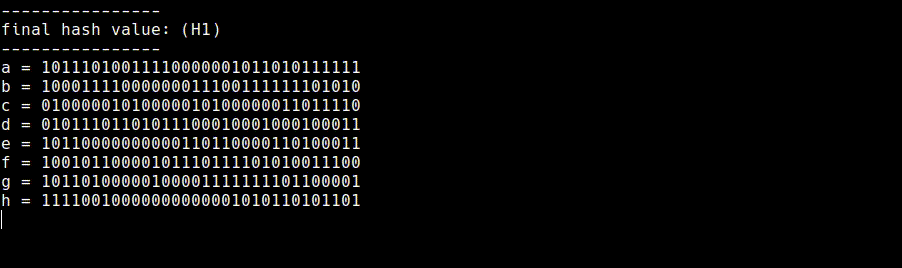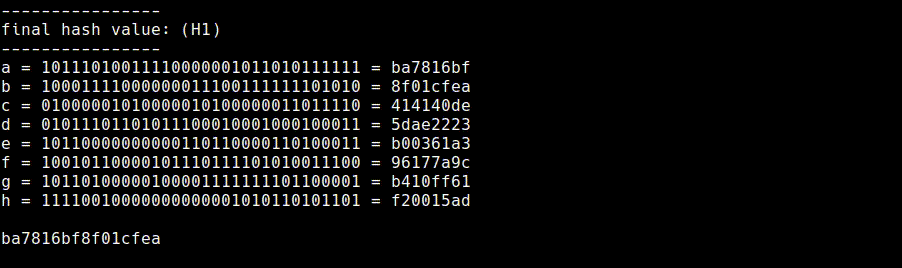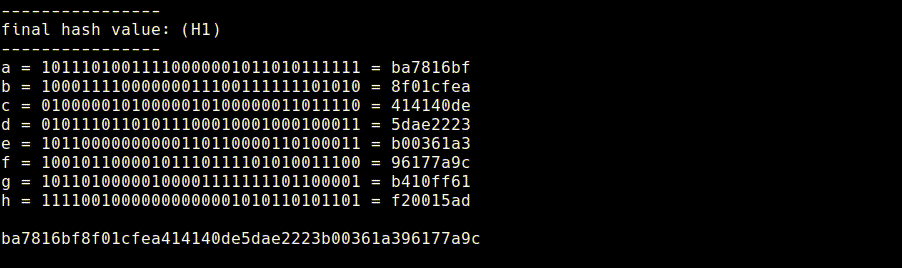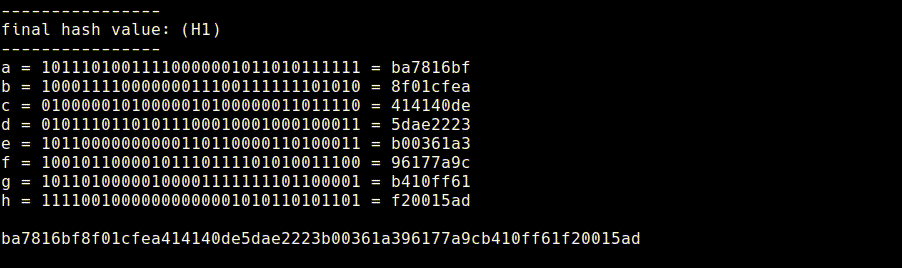
11. Final Hash Value (final.rb)
We will be left with eight 32-bit values in the state registers after applying the compression function to each message block.
The final hash value is just the concatenation of these eight 32-bit values to produce a 256-bit message digest. For compactness this message digest is usually shown in hexadecimal.
- This isn't the prettiest code I've ever written.
- These scripts redraw the entire terminal screen for every frame of the animation, so the display can become disjointed at faster speeds.
- All of the actual code for calculating SHA-256 hashes can be found in
sha256lib.rb, all of the other files are animations. - I decided not to include the individual animations for
expansion.rb,t1.rb,t2.rbin the mainsha256.rbanimation. This is to help speed up the flow of the animation. - In terms of security; I believe the Sigma functions help with the diffusion of bits, and the Choice and Majority functions give the hash function it's one-wayness due to being nonlinear. The addition modulus 232 is also nonlinear.1
that's dope - esky33
- FIPS 180-4 - The official specification for the SHA-2 family of hash functions, including SHA-256.
- SHA-256 Examples - A couple of official hash examples to check your implementation with.
- Security Analysis of SHA-256 and Sisters - A paper by Henri Gilbert and Helena Handschuh explaining some security details about SHA-256.
1: Cryptography For Developers, Simon Johnson (pg. 218)