This is part one of a six-part series developed by the Data Analytics Team at Allgeier Schweiz. The original implementation was part of a workshop for the Swiss Data Science Conference of 2024.
You can also find the series in the Allgeier Schweiz GitHub repository.
The following series showcases how to use the Azure OpenAI Service in Python by calling the Azure OpenAI REST API.
- Part 1: (this page) provides readers with an overview of the workshop use case, what Azure OpenAI Service is, the language models used, the different techniques to enhance these models and the differences between Azure OpenAI and OpenAI.
- Part 2 will show readers the preparations required to start using the Azure OpenAI API in Python using GitHub Codespaces.
- Part 3 will show readers how to start using the Azure OpenAI API. Model enhancement techniques will be implemented, such as prompt engineering, zero-shot, one-shot, and few-shot learning.
- Part 4 will show readers how to implement a retrieval strategy such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) using the Azure OpenAI API together with LangChain and ChromaDB as the vector database. Additionally, the implementation of the Azure OpenAI Assistant API for data pre-processing of the data for RAG will also be showcased.
- Part 5 will show readers how to use a fine-tuned model using the Azure OpenAI API and explore the implementation of RAG together with a fine-tuned model. Additionally, the implementation of the Azure OpenAI Assistant API for data pre-processing for fine-tuning will also be showcased.
- Part 6 will show readers how to translate images into text using the new GPT-4o model through the Azure OpenAI API.
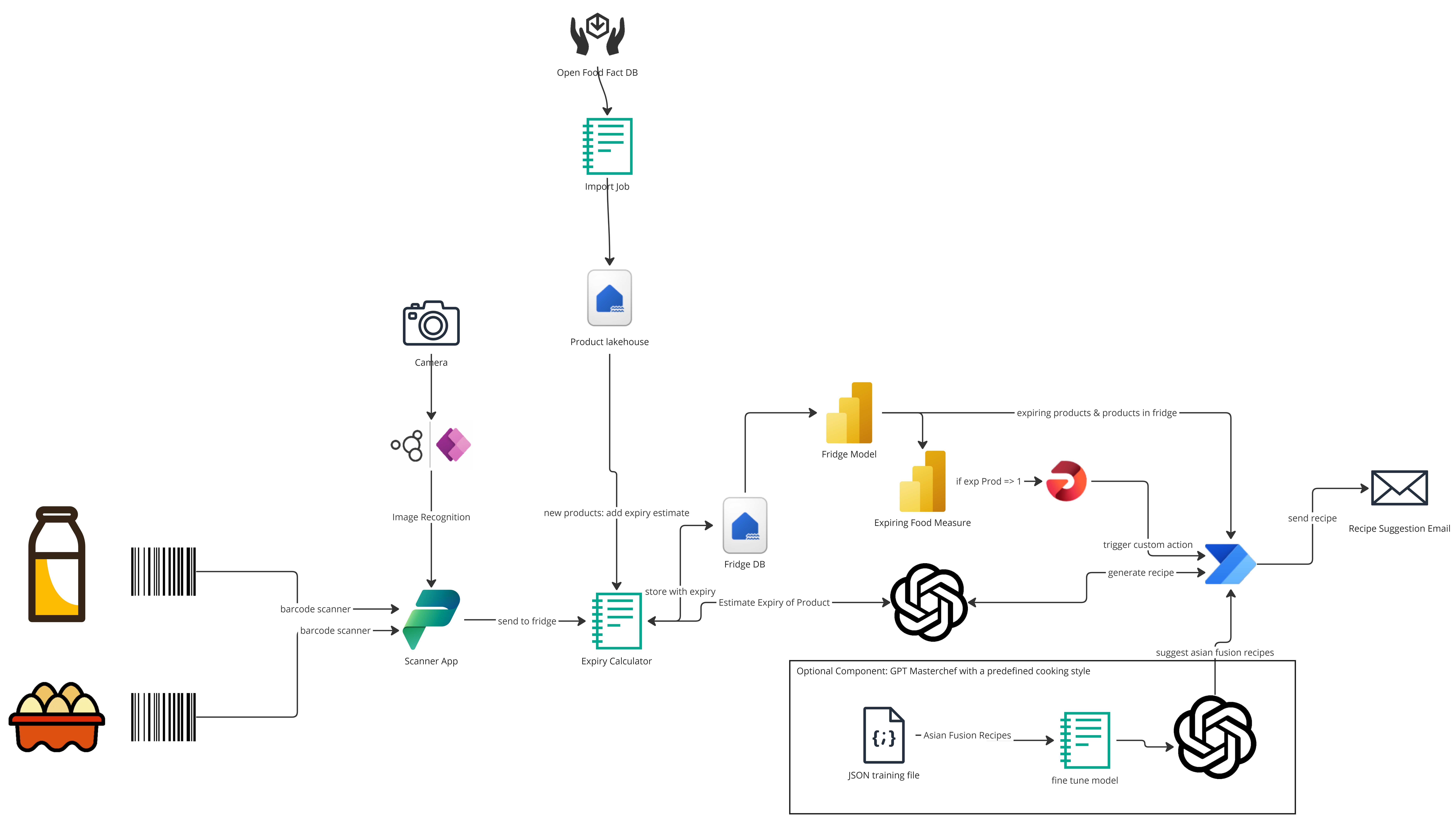
The use case of this series revolves around the Food Fighters concept created for The Microsoft Fabric Global AI Hack of 2024.
The solution aims to combat food waste by empowering users to effortlessly manage their food inventory, track food expiration dates, and receive personalized recipe suggestions via email, all with a simple product scan.
Unfortunately, we don't have time to build the entire architecture of this solution, for this reason, we will focus on creating the personalized recipe suggestions aspect using the Azure OpenAI Service.
- We want the language model to create recipes from a list of ingredients we pass as the model input.
- To improve the recipes created by the model we will implement model enhancement techniques such as prompt engineering with zero-shot, one-shot and few-shot learning.
- To further improve the recipes created by the model, specifically creating vegan recipes in JSON format, we will implement a retrieval strategy called Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) using a CSV file of vegan recipes as our data foundation.
- To further improve the recipes created by the model we will implement an enhancement technique called Fine-Tuning to re-train the base language model using a CSV file of vegan recipes as our training data. Furthermore, we will explore the implementation of RAG together with a fine-tuned model.
- Before implementing the enhancement techniques listed in steps 3 and 4, we need to perform data preparation steps on the CSV file. To achieve this, we will use the Azure OpenAI Assistant API with the code interpreter functionality. This will allow us to conduct data-wrangling steps on the data based on our natural language inputs.
- We want to create a list of ingredients from a set of food product images that can be used to generate recipes. To achieve this, we will utilize the multimodal GPT-4o model, which enables the translation of images into text.
The Azure OpenAI Service offers access to various large language models (LLMs), including GPT-4o, GPT-4, GPT-4 Turbo with Vision, GPT-3.5-Turbo, and Embeddings model series. These are the same language models made available by OpenAI.
These models allow us to create written, image, and audio-based content, summarize information, perform semantic searches, and use natural language to code translations.
Users can utilize the Azure OpenAI Service through REST APIs, Python SDK, or the web-based interface provided in the Azure OpenAI Studio.
In our case, we will use the language models GPT-4o, GPT-4, GPT-3.5-Turbo, and Embeddings. Each one will be called using the Azure OpenAI API. Additionally, we will use the Azure OpenAI Assistants API to perform data pre-processing operations using the code interpreter functionality.
An assistant is an AI agent that is designed for a specific purpose. It augments the functionality of the Azure OpenAI models. The assistant facilitates the integration of third-party tools through custom functions and provides access to a coding environment through the Code Interpreter functionality. The exceptional performance of these AI agents is achieved through the utilisation of Threads, which facilitates the management and storage of message history.
In our case, we will use this agent to perform data pre-processing steps using the code interpreter functionality. This functionality grants the model a Python environment to run the Python code it generates to perform data transformation steps.
NOTE: It is important to note that Azure OpenAI Assistants are not the only agents that offer these functionalities. LangChain presented their own approach with the introduction of LangChain Agents.
- GPT-4o (Version 2024–05–13): This model is used to translate food product images into text i.e. a list of ingredients. GPT-4o models are multimodal, meaning that they integrate text and image processing in a single model, enabling the handling of multiple data types simultaneously. This is also the latest model and offers superior AI capabilities compared to the GPT-4 Turbo model.
- GPT-4 (Version 0125-preview, Version 1106-preview): This model is used to create our assistant for code interpretation. The GPT-4 series is a set of models that improve on the GPT-3.5 and can understand and generate natural language and code. The latest version, 0125-preview, supersedes its predecessor, version 1106-preview, offering enhanced performance in code generation, a reduction in instances of incomplete model tasks and additional enhancements.
- GPT-3.5-Turbo (Version 0125, Version 1106 and Version 0613): This model is used to create recipes based on a list of ingredients as our input prompt. GPT-3.5 models can understand and generate natural language or code. The most capable and cost-effective model in the GPT-3.5 family is the GPT-3.5 Turbo. The latest 0125 version replaces the 1106 and offers higher accuracy at responding in requested formats and general bug fixes. For Fine-Tuning, we will use version 0613.
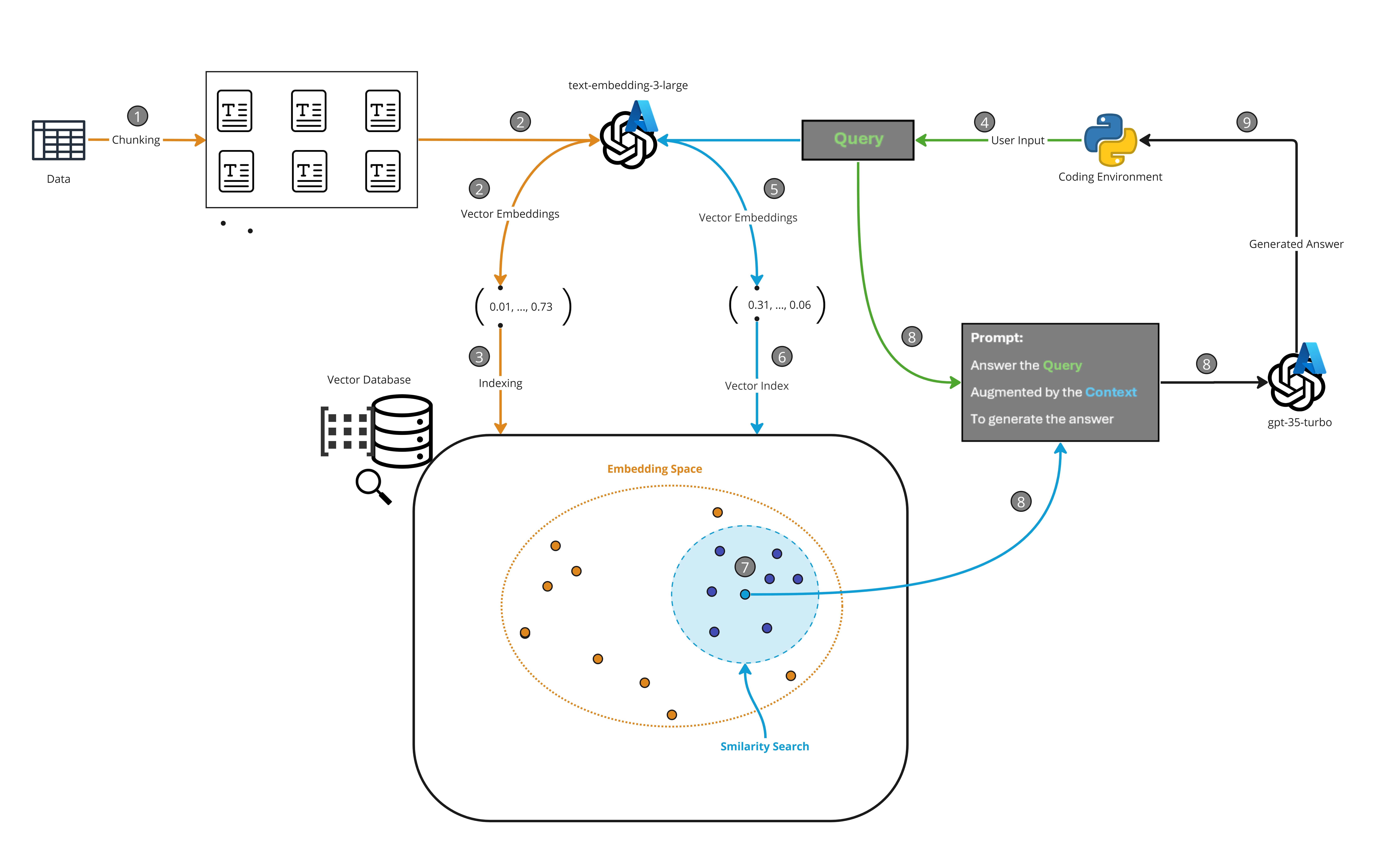
- Embeddings (text-embedding-3-large): This model is used to create an embedding of our recipe data which will be used to enhance our model output using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). An embedding is a compact, organized way to represent text information in numerical format using vectors. They are particularly useful in Artificial Intelligence applications, as it enables the essential meaning of text to be captured and transformed into a format that can be understood by an algorithm.
This workshop will showcase three key techniques for improving the language model's output: prompt engineering, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and Fine-tuning.
Approaches to AI: When to Use Prompt Engineering, Embeddings, or Fine-tuning | Entry Point AI
The model’s used in this workshop are prompt-based. With prompt-based models, the user interacts with the model by entering a text prompt i.e. text input, to which the model responds with a text completion. This completion is the model’s continuation of the input text i.e. text output.
Prompt engineering involves crafting a structurally optimized text prompt to guide and influence the model’s output. It aims to achieve the desired contextual and formatted response that aligns with the user’s model output expectations while minimizing the inherent biases of the underlying language model.
Depending on the objective, prompt engineering can serve as an alternative approach to more complex techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) or Fine-Tuning by providing the model with an example of the desired model output. This is where concepts like one-shot and few-shot learning become relevant. We will learn more about these concepts in Part 3.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a retrieval strategy aimed at enhancing language models by providing them with supplementary information, a process also known as grounding. Rather than solely depending on the model’s existing knowledge, we can add proprietary data into the model prompt to guide it to more precise and domain-specific responses. It’s important to note that the model is not re-trained on the new data. The new data is only used as an additional prompt input, acting similarly to one-shot learning.
In this workshop, we’ll work with a new dataset, a CSV file filled with examples of vegan recipes. By incorporating this particular dataset, our model should more accurately produce vegan recipes. We will learn more about these concepts in Part 4.
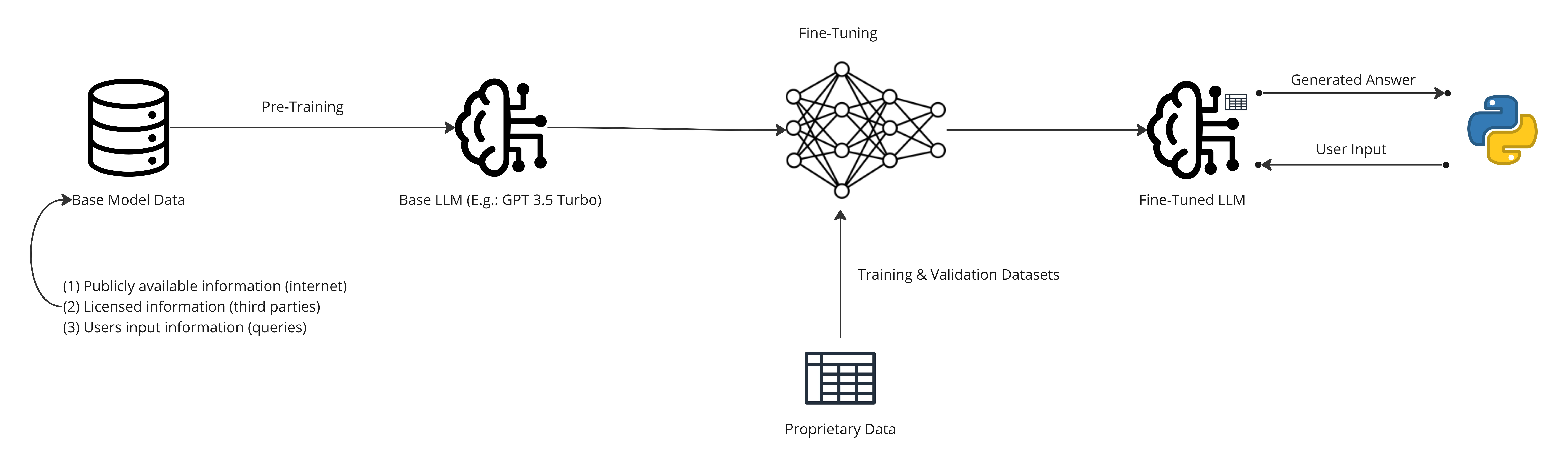
Fine-tuning is a technique used to train a pre-trained base model using a new foundation of information i.e. training data, to suit a specific task.
Azure OpenAI models possess extensive knowledge of diverse topics drawn from different data sources. This enables the model to address a wide array of problems; however, not every business requires a model capable of simultaneously addressing an extensive range of topics. Fine-tuning allows us to counteract this state, making the language model sharper in a specific knowledge domain.
The fine-tuning process requires a careful investment of time and effort. You should first try to get good results with prompt engineering or RAG. As fine-tuning is more time and resource-intensive, requiring us to create datasets and run training jobs, implementing these alternative enhancement techniques should always be pursued first. In cases where fine-tuning is implemented, prompt engineering work is not wasted. The best results are usually obtained by combining good prompt engineering with a fine-tuned model.
In this workshop, we’ll work with a new dataset, a CSV file filled with examples of vegan recipes. By re-training the model with this dataset, our model will be able to generate higher-quality vegan recipes that are finely tailored to the provided prompt input. We will learn more about these concepts in Part 5
Azure OpenAI combines the security features of Microsoft Azure with the various language models developed by OpenAI. This means customers can benefit from Azure’s reliability and safety measures while using OpenAI’s technology. OpenAI is ideal for experimenting and exploring new functionalities. However, when it comes to professional applications, security, and compliance, choose Azure OpenAI.
Additionally, Azure OpenAI collaborates closely with OpenAI to develop the REST APIs. This partnership guarantees compatibility between the services and makes it easy for customers to switch between them with minimal hassle.
Azure OpenAI provides features like data encryption, access control, private networking, availability in different regions, and tools for responsible AI content filtering. In summary, it adds an extra layer of protection to your workload.
Reach out to us! We are happy to answer any questions you might have or use your feedback to optimize this series!
- Nicolas Rehder - [email protected]
- Alex Dean - [email protected]
Download and unzip the file on your local computer.
Have fun!
- Use openai=1.12. Newest version is problematic. Especially with Assistant and Fine-Tuning.
- Embedding with Proxy API does not work. We'll need to fall back on the original Endpoint and API Key.
- Azure OpenAI Assistant API not creating output file from transformation. Token limit needs to be increased.
- P3, P4 and P5 data preprocessing requires models gpt-35-turbo, gpt-4-1106-preview and text-embedding-3-large.
- P5 and P6 requires models gpt-4o, gpt-35-turbo and text-embedding-3-large.
The following documentation was used to source the information contained in this workshop.
[1] What is Azure OpenAI Service? — Azure AI services | Microsoft Learn
[2] Azure OpenAI Service — Features Overview and Key Concepts — Microsoft Community Hub
[3] Azure OpenAI Service models — Azure OpenAI | Microsoft Learn
[4] Azure OpenAI Service deprecated models — Azure OpenAI | Microsoft Learn
[6] Fine-Tuning LLMs: Your Blueprint for Informed AI Choices! (substack.com)
[7] Prompt Engineering Complete Guide | by Fareed Khan | Medium