forked from facebook/react-native
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
[README] New README co-authored with @brentvatne
This new README talks more about the react-native project, repository, and contribution process (the old one was more focused on technical details). @brentvatne and I want people to get help and file issues & PRs more effectively. Here's a first draft that we believe helps with that.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
50 additions
and
206 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,219 +1,63 @@ | ||
| # React Native [](https://travis-ci.org/facebook/react-native) [](http://badge.fury.io/js/react-native) | ||
|
|
||
| React Native enables you to build world-class application experiences on native platforms using a consistent developer experience based on JavaScript and | ||
| [React](http://facebook.github.io/react). The focus of React Native is on developer efficiency across all the platforms you care about - learn once, write anywhere. Facebook uses React Native in multiple production apps and will continue investing in React Native. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Native iOS Components | ||
|
|
||
| With React Native, you can use the standard platform components such as `UITabBar` and `UINavigationController` on iOS. This gives your app a consistent look and feel with the rest of the platform ecosystem, and keeps the quality bar high. These components are easily incorporated into your app using their React component counterparts, such as _TabBarIOS_ and _NavigatorIOS_. | ||
|
|
||
| ```javascript | ||
| var React = require('react-native'); | ||
| var { TabBarIOS, NavigatorIOS } = React; | ||
|
|
||
| var App = React.createClass({ | ||
| render: function() { | ||
| return ( | ||
| <TabBarIOS> | ||
| <TabBarIOS.Item title="React Native" selected={true}> | ||
| <NavigatorIOS initialRoute={{ title: 'React Native' }} /> | ||
| </TabBarIOS.Item> | ||
| </TabBarIOS> | ||
| ); | ||
| }, | ||
| }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Asynchronous Execution | ||
|
|
||
| All operations between the JavaScript application code and the native platform are performed asynchronously, and the native modules can also make use of additional threads as well. This means we can decode images off of the main thread, save to disk in the background, measure text and compute layouts without blocking the UI, and more. As a result, React Native apps are naturally fluid and responsive. The communication is also fully serializable, which allows us to leverage Chrome Developer Tools to debug the JavaScript while running the complete app, either in the simulator or on a physical device. | ||
|
|
||
| 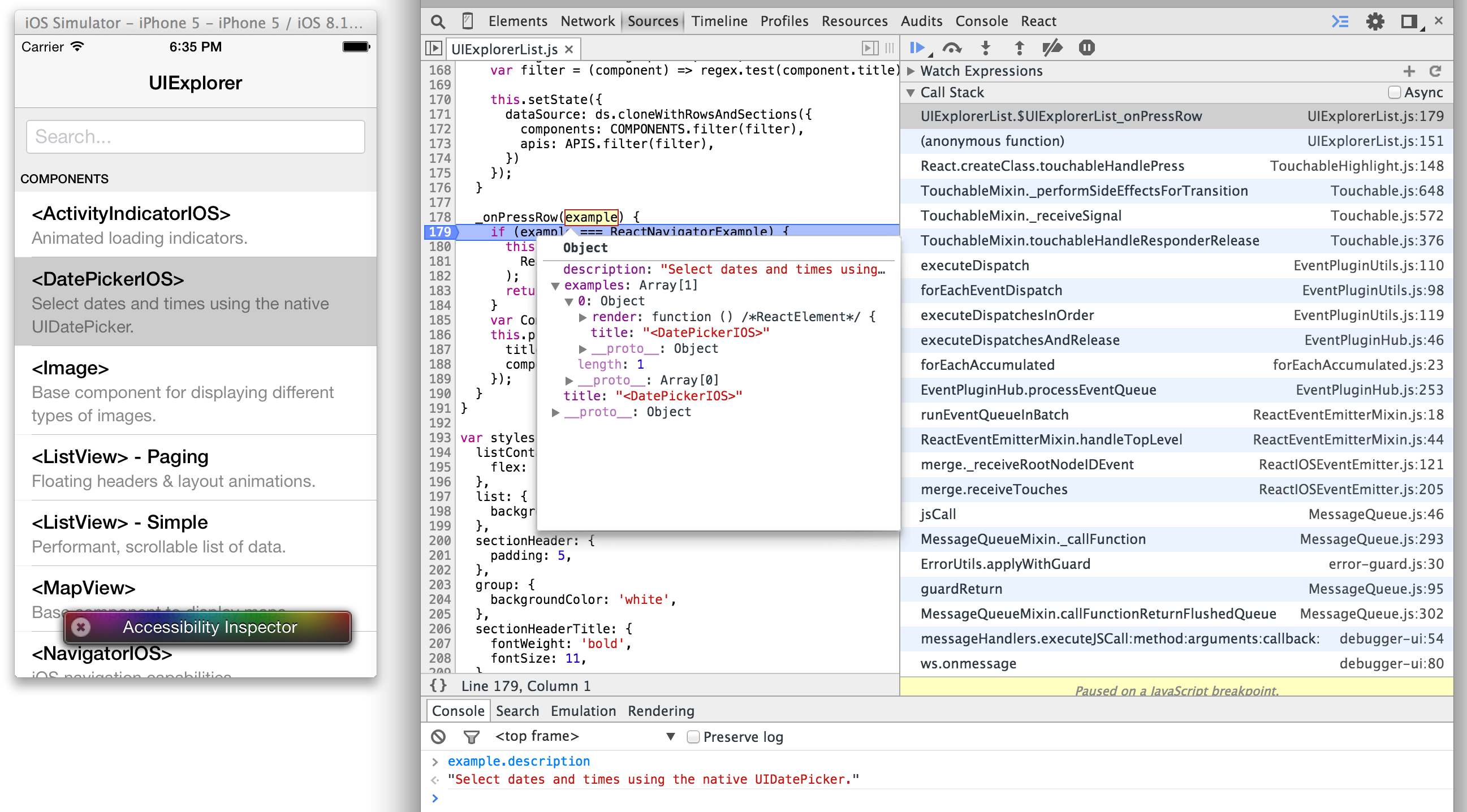 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Touch Handling | ||
|
|
||
| iOS has a very powerful system called the Responder Chain to negotiate touches in complex view hierarchies which does not have a universal analog on the web. React Native implements a similar responder system and provides high level components such as TouchableHighlight that integrate properly with scroll views and other elements without any additional configuration. | ||
|
|
||
| ```javascript | ||
| var React = require('react-native'); | ||
| var { ScrollView, TouchableHighlight, Text } = React; | ||
|
|
||
| var TouchDemo = React.createClass({ | ||
| render: function() { | ||
| return ( | ||
| <ScrollView> | ||
| <TouchableHighlight onPress={() => console.log('pressed')}> | ||
| <Text>Proper Touch Handling</Text> | ||
| </TouchableHighlight> | ||
| </ScrollView> | ||
| ); | ||
| }, | ||
| }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Flexbox and Styling | ||
| Laying out views should be easy, which is why we brought the flexbox layout model from the web to React Native. Flexbox makes it simple to build the most common UI layouts, such as stacked and nested boxes with margin and padding. React Native also supports common web styles, such as `fontWeight`, and the `StyleSheet` abstraction provides an optimized mechanism to declare all your styles and layout right along with the components that use them and apply them inline. | ||
|
|
||
| ```javascript | ||
| var React = require('react-native'); | ||
| var { Image, StyleSheet, Text, View } = React; | ||
|
|
||
| var ReactNative = React.createClass({ | ||
| render: function() { | ||
| return ( | ||
| <View style={styles.row}> | ||
| <Image | ||
| source={{uri: 'http://facebook.github.io/react/img/logo_og.png'}} | ||
| style={styles.image} | ||
| /> | ||
| <View style={styles.text}> | ||
| <Text style={styles.title}> | ||
| React Native | ||
| </Text> | ||
| <Text style={styles.subtitle}> | ||
| Build high quality mobile apps using React | ||
| </Text> | ||
| </View> | ||
| </View> | ||
| ); | ||
| }, | ||
| }); | ||
| var styles = StyleSheet.create({ | ||
| row: { flexDirection: 'row', margin: 40 }, | ||
| image: { width: 40, height: 40, marginRight: 10 }, | ||
| text: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center'}, | ||
| title: { fontSize: 11, fontWeight: 'bold' }, | ||
| subtitle: { fontSize: 10 }, | ||
| }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Polyfills | ||
|
|
||
| React Native is focused on changing the way view code is written. For the rest, we look to the web for universal standards and polyfill those APIs where appropriate. You can use npm to install JavaScript libraries that work on top of the functionality baked into React Native, such as `XMLHttpRequest`, `window.requestAnimationFrame`, and `navigator.geolocation`. We are working on expanding the available APIs, and are excited for the Open Source community to contribute as well. | ||
|
|
||
| ```javascript | ||
| var React = require('react-native'); | ||
| var { Text } = React; | ||
|
|
||
| var GeoInfo = React.createClass({ | ||
| getInitialState: function() { | ||
| return { position: 'unknown' }; | ||
| }, | ||
| componentDidMount: function() { | ||
| navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition( | ||
| (position) => this.setState({position}), | ||
| (error) => console.error(error) | ||
| ); | ||
| }, | ||
| render: function() { | ||
| return ( | ||
| <Text> | ||
| Position: {JSON.stringify(this.state.position)} | ||
| </Text> | ||
| ); | ||
| }, | ||
| }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Extensibility | ||
|
|
||
| It is certainly possible to create a great app using React Native without writing a single line of native code, but React Native is also designed to be easily extended with custom native views and modules - that means you can reuse anything you've already built, and can import and use your favorite native libraries. To create a simple module in iOS, create a new class that implements the `RCTBridgeModule` protocol, and wrap the function that you want to make available to JavaScript in `RCT_EXPORT_METHOD`. Additionally, the class itself must be explicitly exported with `RCT_EXPORT_MODULE();`. | ||
|
|
||
| ```objc | ||
| // Objective-C | ||
|
|
||
| #import "RCTBridgeModule.h" | ||
|
|
||
| @interface MyCustomModule : NSObject <RCTBridgeModule> | ||
| @end | ||
|
|
||
| @implementation MyCustomModule | ||
|
|
||
| RCT_EXPORT_MODULE(); | ||
|
|
||
| // Available as NativeModules.MyCustomModule.processString | ||
| RCT_EXPORT_METHOD(processString:(NSString *)input callback:(RCTResponseSenderBlock)callback) | ||
| { | ||
| callback(@[[input stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"Goodbye" withString:@"Hello"]]); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| @end | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ```javascript | ||
| // JavaScript | ||
|
|
||
| var React = require('react-native'); | ||
| var { NativeModules, Text } = React; | ||
|
|
||
| var Message = React.createClass({ | ||
| getInitialState() { | ||
| return { text: 'Goodbye World.' }; | ||
| }, | ||
| componentDidMount() { | ||
| NativeModules.MyCustomModule.processString(this.state.text, (text) => { | ||
| this.setState({text}); | ||
| }); | ||
| }, | ||
| render: function() { | ||
| return ( | ||
| <Text>{this.state.text}</Text> | ||
| ); | ||
| }, | ||
| }); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Custom iOS views can be exposed by subclassing `RCTViewManager`, implementing a `-view` method, and exporting properties with the `RCT_EXPORT_VIEW_PROPERTY` macro. Then use `requireNativeComponent` in JavaScript to use the component in your app. | ||
|
|
||
| ```objc | ||
| // Objective-C | ||
|
|
||
| #import "RCTViewManager.h" | ||
|
|
||
| @interface MyCustomViewManager : RCTViewManager | ||
| @end | ||
|
|
||
| @implementation MyCustomViewManager | ||
|
|
||
| RCT_EXPORT_MODULE() | ||
|
|
||
| - (UIView *)view | ||
| { | ||
| return [[MyCustomView alloc] init]; | ||
| } | ||
| React Native enables you to build world-class application experiences on native platforms using a consistent developer experience based on JavaScript and [React](http://facebook.github.io/react). The focus of React Native is on developer efficiency across all the platforms you care about - learn once, write anywhere. Facebook uses React Native in multiple production apps and will continue investing in React Native. | ||
|
|
||
| RCT_EXPORT_VIEW_PROPERTY(myCustomProperty, NSString); | ||
| ## Getting Started | ||
|
|
||
| @end | ||
| ``` | ||
| - Follow the [Getting Started guide](http://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/getting-started.html) to install React Native and its dependencies. | ||
| - Check out this [tutorial](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/tutorial.html) to walk through your first project that fetches real data and displays it in a list. | ||
| - [Open the UIExplorer example project](#examples) to see a list of components that ship with React Native. | ||
| - Install the [React Developer Tools](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/react-developer-tools/fmkadmapgofadopljbjfkapdkoienihi) for Chrome or Firefox for better debugging [(read more)](http://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/debugging.html). | ||
| - Try out apps from the [Showcase](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/showcase.html) to see what React Native is capable of! | ||
|
|
||
| ```javascript | ||
| // JavaScript | ||
| ## Getting Help | ||
|
|
||
| var React = require('react-native'); | ||
| var { requireNativeComponent } = React; | ||
| class MyCustomView extends React.Component { | ||
| render() { | ||
| return <NativeMyCustomView {...this.props} />; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| MyCustomView.propTypes = { | ||
| myCustomProperty: React.PropTypes.oneOf(['a', 'b']), | ||
| }; | ||
| - Ask a question on [StackOverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/) and tag it with `react-native` | ||
| - Start a thread on the [React Discussion Board](https://discuss.reactjs.org/) | ||
| - Join #reactnative on IRC: chat.freenode.net | ||
| - Slack: Sign up for [Reactiflux](http://reactiflux.com/) and join #react-native | ||
| - If it turns out that you may have found a bug, please [open an issue](#opening-issues) | ||
|
|
||
| var NativeMyCustomView = requireNativeComponent('MyCustomView', MyCustomView); | ||
| module.exports = MyCustomView; | ||
| ``` | ||
| ## Documentation | ||
|
|
||
| ## Running the Examples | ||
| - [The website’s documentation](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/) divided into multiple sections. | ||
| There are **Guides** that discuss topics like [debugging](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/debugging.html), [integrating with existing apps](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/embedded-app-ios.html), and [the gesture responder system](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/gesture-responder-system.html). | ||
| - The **Components** section covers React components such as [`View`](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/view.html) and [`Navigator`](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/navigator.html). | ||
| - The **APIs** section covers other libraries like [Animated](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/animated.html) and [StyleSheet](https://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/stylesheet.html) that aren’t React components themselves. | ||
| - Finally, React Native provides a small number of **Polyfills** that offer web-like APIs. | ||
|
|
||
| Another great way to learn more about the components and APIs included with React Native is to read their source. Look under the `Libraries` directory for components like `ScrollView` and `Navigator`, for example. The UIExplorer example is also here to demonstrate some of the ways to use these components. By looking at the source you can get an accurate understanding of each component’s behavior and API. | ||
|
|
||
| The React Native documentation only discusses the components, APIs and topics specific to React Native (React on iOS and Android). For further documentation on the React API that is shared between React Native and React DOM, refer to the [React documentation](http://facebook.github.io/react/). | ||
|
|
||
| ## Examples | ||
|
|
||
| - `git clone https://github.com/facebook/react-native.git` | ||
| - `cd react-native && npm install` | ||
| - `cd Examples` | ||
|
|
||
| Now open any example and hit run in Xcode. | ||
| Now open any example (the `.xcodeproj` file in each of the `Examples` subdirectories) and hit Run in Xcode. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Extending React Native | ||
|
|
||
| - Looking for a component? [react.parts](http://react.parts/) | ||
| - Fellow developers write and publish React Native modules to npm and open source them on GitHub. | ||
| - Making modules helps grow the React Native ecosystem and community. We recommend writing modules for your use cases and sharing them on npm. | ||
| - Read the [Native Modules iOS](http://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/native-modules-ios.html#content) and [Native UI Components iOS](http://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/native-components-ios.html#content) guides in the documentation if you are interested in extending native functionality. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Opening Issues | ||
|
|
||
| If you encounter a bug with React Native we would like to hear about it. Search the [existing issues](https://github.com/facebook/react-native/issues) and try to make sure your problem doesn’t already exist before opening a new issue. It’s helpful if you include the version of React Native and iOS you’re using. Please include a stack trace and reduced repro case when appropriate, too. | ||
|
|
||
| The GitHub issues are intended for bug reports and feature requests. For help and questions with using React Native please make use of the resources listed in the [Getting Help](#getting-help) section. There are limited resources available for handling issues and by keeping the list of open issues lean we can respond in a timely manner. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Contributing | ||
|
|
||
| For more information about contributing, see our [Contribution Guidelines](https://github.com/facebook/react-native/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md). | ||
|
|
||
| ## License | ||
|
|
||
| React is [BSD licensed](./LICENSE). We also provide an additional [patent grant](./PATENTS). | ||
|
|
||
| React documentation is [Creative Commons licensed](./LICENSE-docs). | ||
|
|
||
| Further documentation, tutorials, and more on the [React Native website](http://facebook.github.io/react-native/docs/getting-started.html). | ||
| Examples provided in this repository and in the documentation are [separately licensed](./LICENSE-examples), as are some of the [custom components](./LICENSE-CustomComponents). |