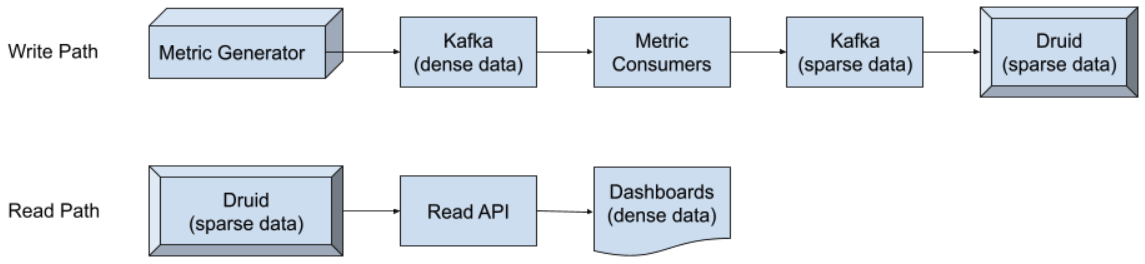
The core idea behind nbdb2 is sparseness.
On the write path, we convert dense data to sparse data to help reduce number of data points stored in the backend. This means that we drop “uninteresting data” on the write path. Eg. If a counter has an unchanging value, then instead of storing 1 datapoint every observation interval with the same value, we only store it once and drop the remaining datapoints.
On the read path, we convert sparse data back to dense before returning results to the user. Thus nbdb2 provides the illusion of “dense data” to the end user while using significantly less storage.
Over a large sample of metrics, we were able to realize >70% cost savings.
Three main components of nbdb2:
- Metric Consumers - Converts dense data into sparse data
- Druid is used as our datastore for storing sparse datapoints
- Quick Design Overview: Link
- Overview of various components:
- Overlord (manages assignment of ingest tasks): Link
- Coordinator (manages assignment of data segments): Link
- Middlemanagers / MMs (runs ingest tasks): Link
- Historicals (store data segments in SSDs & answer queries): Link
- Brokers (converts user queries into multiple historical + MM queries & combines results): Link
- Read API - This is a Flask app which serves as an intermediary between
Druid and metric query clients. It's responsibility is to provide the “illusion” of
dense data to the end user. It has 2 main functions:
- Fetch sparse data from Druid and convert it to dense
- Support Graphite / InfluxQL queries on top of the actual data: Druid supports "Druid SQL" - this service supports native time series query languages like Graphite and InfluxQL
To make it easier for building and running the system test for this project,
we have created a virtualized development environment using docker. All the
packages and libraries required to build, test and deploy the project is
pre-installed in the dev-vm.
To start the dev-vm, run the script nbdb_dev_box.sh from inside the
nbdb2 directory
$ ./nbdb_dev_box.sh
Our system-test suite builds the project, downloads the required binaries, deploys the services in their own docker containers and runs the system tests.
To run the system test suite, move to the python directory and run the
run_systest.sh script.
$ cd python
$ ./run_systest.sh