这个repo记录Java语言下使用测试驱动开发(Test-Driven Development, TDD) 来实现4种斐波那契函数。从零到一,自己独立构思设计。这是 Dr. Venkat Subramaniam (或者查看 Personal Homepage of UH)2022年Software Design 课程的一部分(课程大纲),老师亲自进行Code Review,体验完整的Agile开发。
任务
Fibonacci函数的4种实现方式:
- 命令式
- 函数式
- 普通递归
- 记忆化递归
其中,记忆化递归需要复用普通递归的代码,并且测试记忆化递归比普通递归执行速度快。
设计要求
-
好的代码质量
-
轻量化设计
-
最少的代码
-
自动测试
-
代码覆盖
-
持续集成
-
尽可能地复用代码
可学习到的技术
测试驱动开发 (TDD), 自动化测试 (CT),持续集成 (CI),敏捷开发 (Agile),使用Jacoco查看代码coverage,使用pmd进行静态代码检查等。
这里实现四种斐波那契数列函数比较简单,但是逐个实现,并且逐渐写单元测试,持续集成的过程还是学习到很多。比如从第一种实现到第二种实现,它的测试就不能仅仅是copy paste,需要重构测试的代码,需要用到类,用到类的继承,用到封装,方便代码的复用。
可学习到的设计原则
单一职责原则(SRP), 别重复原则(DRY), 开闭原则(OCP), 依赖倒置原则(DIP)等。
The Fibonacci series of numbers start with 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, ... where values at position 0 and 1 are 1, and values at each position after that are a sum of values at the previous two positions.
Write four implementations of a function to compute the Fibonacci number at a given position.
Please start with one implementation at a time rather than rushing through all of them at the same time.
The four implementations are described below:
- An imperative iteration. Given a position n, loop through totaling values until you reach the value for the given position.
- A functional iteration. Given a position n, loop through totaling values until you reach the value for the given position. Avoid explicit mutability.
- A simple recursion. Given a position, compute the value at a position using the expression fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2).
- A memoized recursion. Given a position, look up to see if the value has been precomputed and if so return that value. Otherwise, use recursion to compute the value.
Confirm that the memoized version is faster than the recursive version.
Reuse as much code as possible.
Please bring forward the practices, techniques, and tools you have learned so far. This includes:
- Good code quality
- Lightweight design
- Minimum code
- Automated testing
- Code coverage
- Continuous integration
Once you complete coding, please answer the following:
- What design principles did you use in this assignment? Discuss.
YOUR RESPONSE GOES HERE
- Any surprises or things that you did not expect?
YOUR RESPONSE GOES HERE
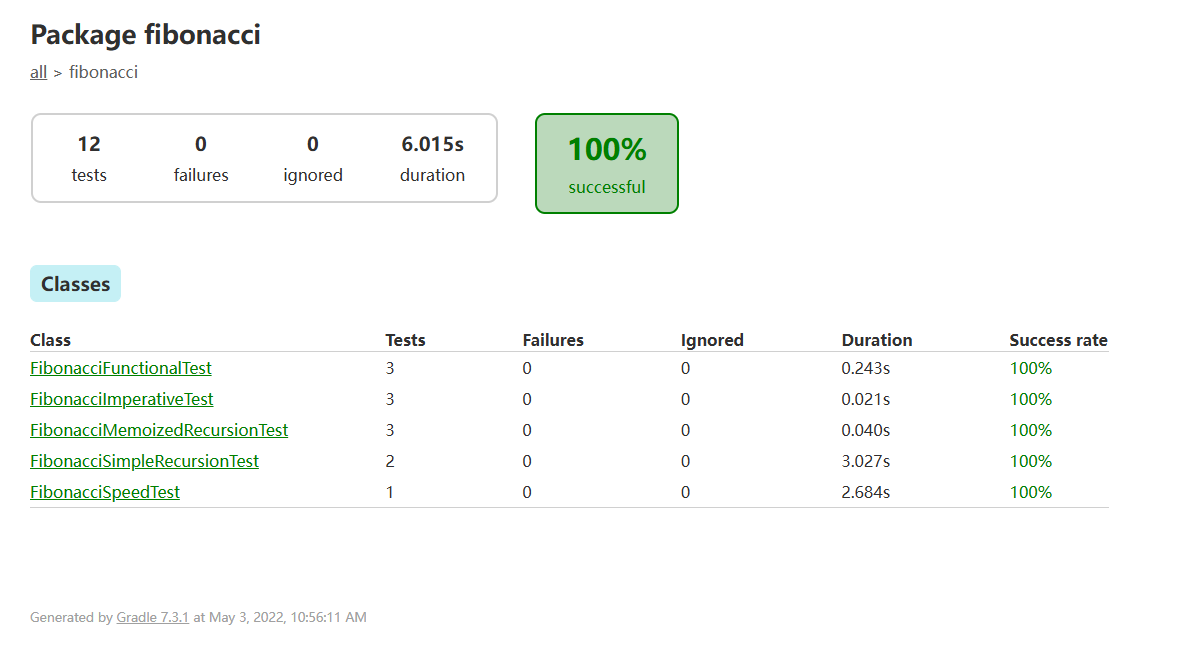
Result of tests
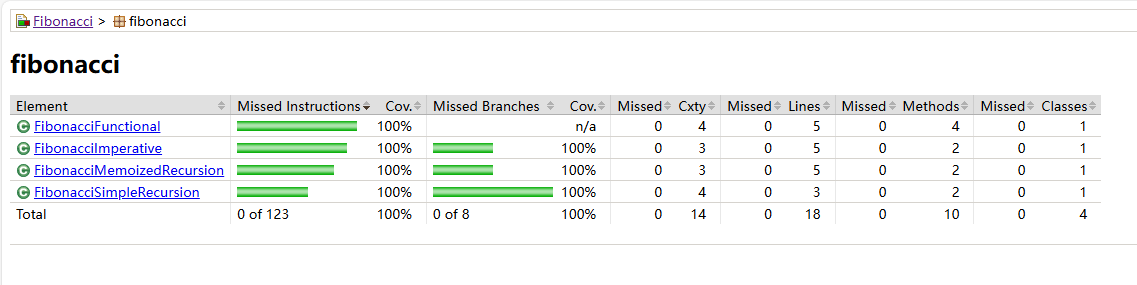
Result of Jacoco
在TDD_Fibonacci文件夹下,有如下的主要文件:
Fibonacci/
├── src
│ └── fibonacci
│ ├── Fibonacci.java
│ ├── FibonacciFunctional.java
│ ├── FibonacciImperative.java
│ ├── FibonacciMemoizedRecursion.java
│ └── FibonacciSimpleRecursion.java
└── test
└── fibonacci
├── FibonacciFunctionalTest.java
├── FibonacciImperativeTest.java
├── FibonacciMemoizedRecursionTest.java
├── FibonacciSimpleRecursionTest.java
├── FibonacciSpeedTest.java
└── FibonacciTest.java
conf/: pmd进行静态代码检查的规则
tests.txt: 各种要进行的测试
build.gradle.kts: gradle自动构建的脚本(kotlin)Java 8 及以上: 需要支持lambda表达式
Junit5: Unit test
gradle: 4.4.1 及以上
clone这个repo
https://github.com/shizhengLi/TDD_Fibonacci.git运行构建
cd TDD_Fibonacci/TDD_Fibonacci
./gradlew查看code coverage在:/TDD_Fibonacci/build/reports/jacoco/test/html/index.html (注:先构建之后才能出现build文件夹)