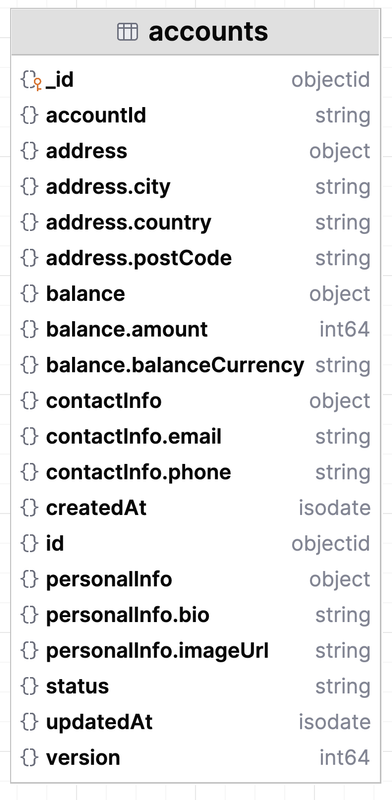
In this project, the microservice uses Clean Architecture and CQRS. A tech stack used Kotlin, Spring WebFlux with coroutines,PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Kafka, and Arrow-kt functional library which like the documentation says brings idiomatic functional programming to Kotlin.
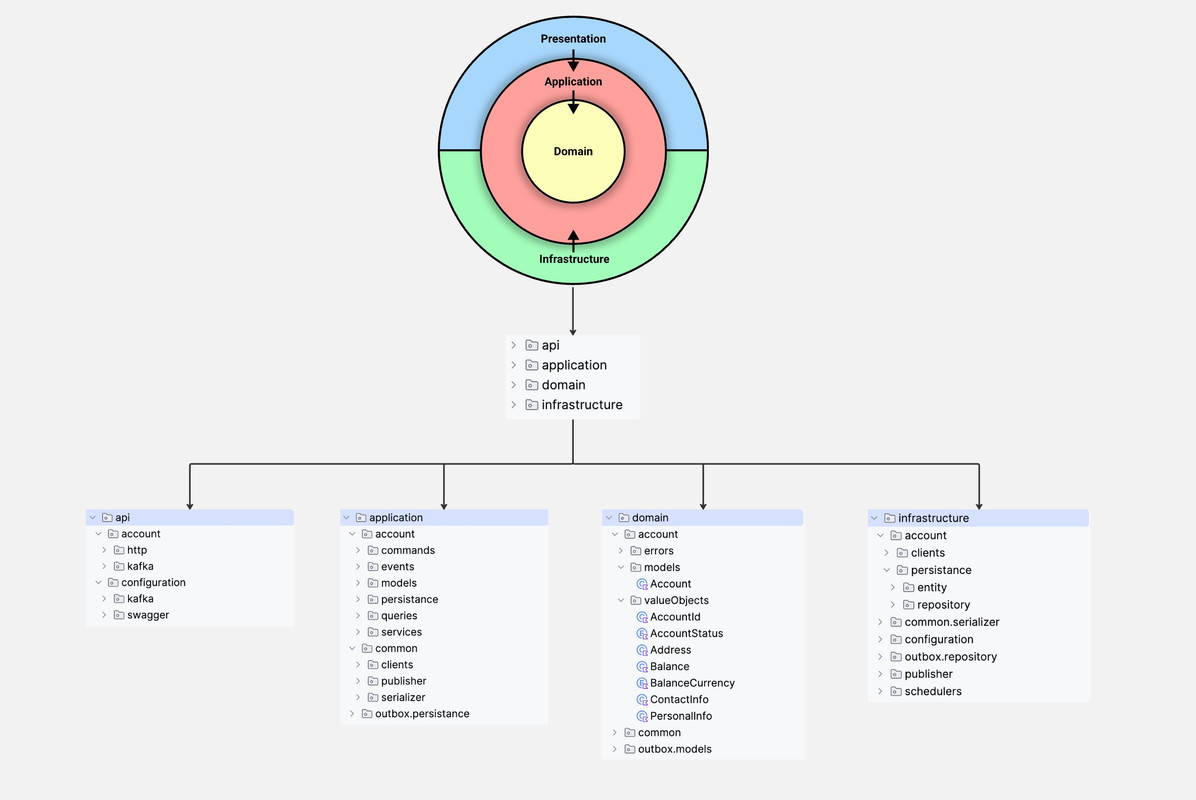
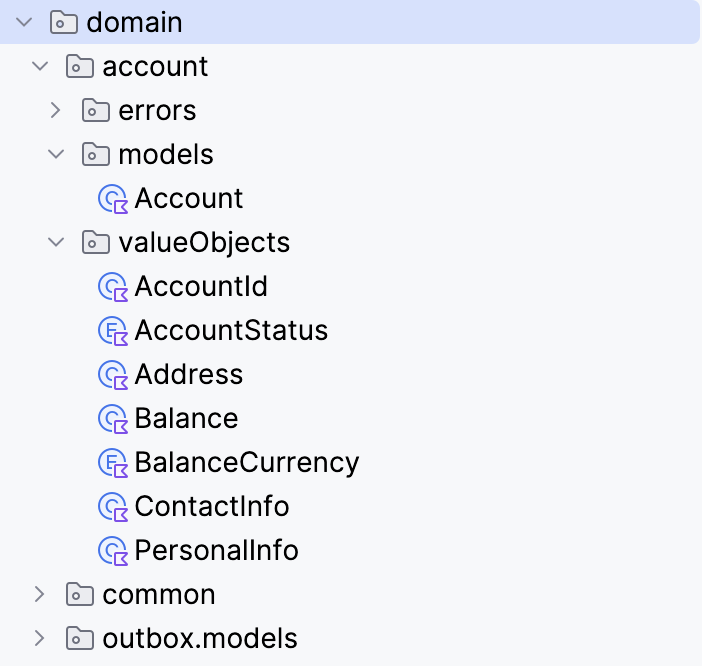
Clean Architecture is one of the more popular software design approaches, it follows the principles of Dependency Inversion, Single Responsibility, and Separation of Concerns. It consists of concentric circles representing different layers, with the innermost layer being the most abstract and the outermost layer representing the user interface and infrastructure. By separating the concerns of the various components and enforcing the dependency rule, it becomes much easier to understand and modify the code. Depending on abstractions allows you to design your business logic flexibly, without having to know the implementation details. The domain layer and the application layer are the core of the Clean Architecture. These two layers together form the application core, encapsulating the most important business rules of the system. Clean Architecture is a domain-centric architectural approach that separates business logic from technical implementation details.
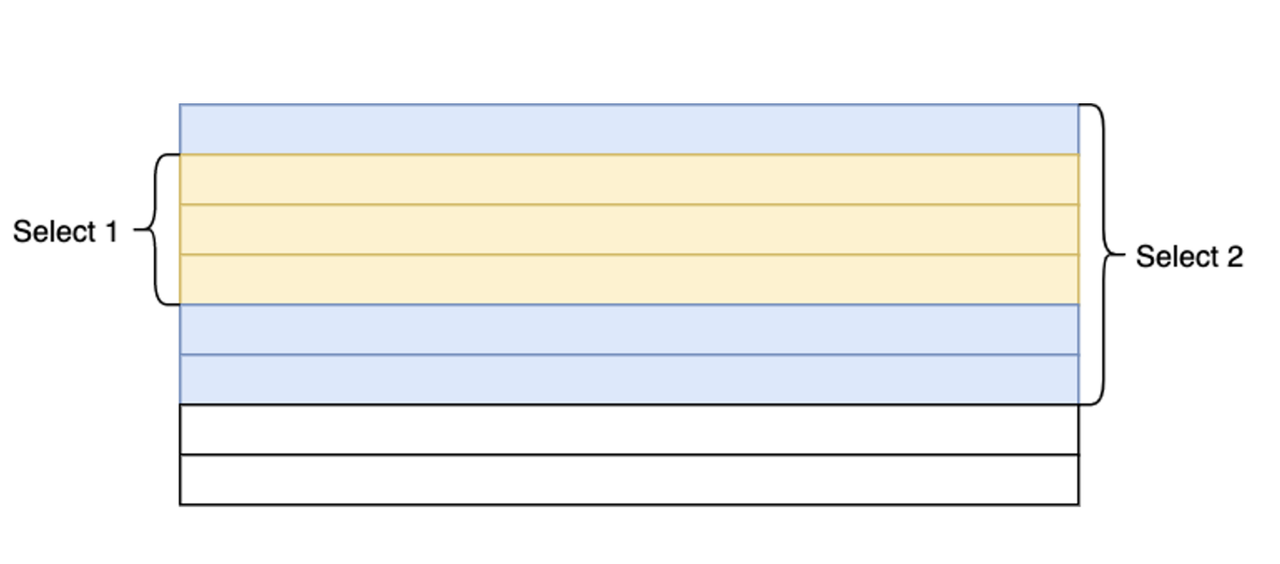
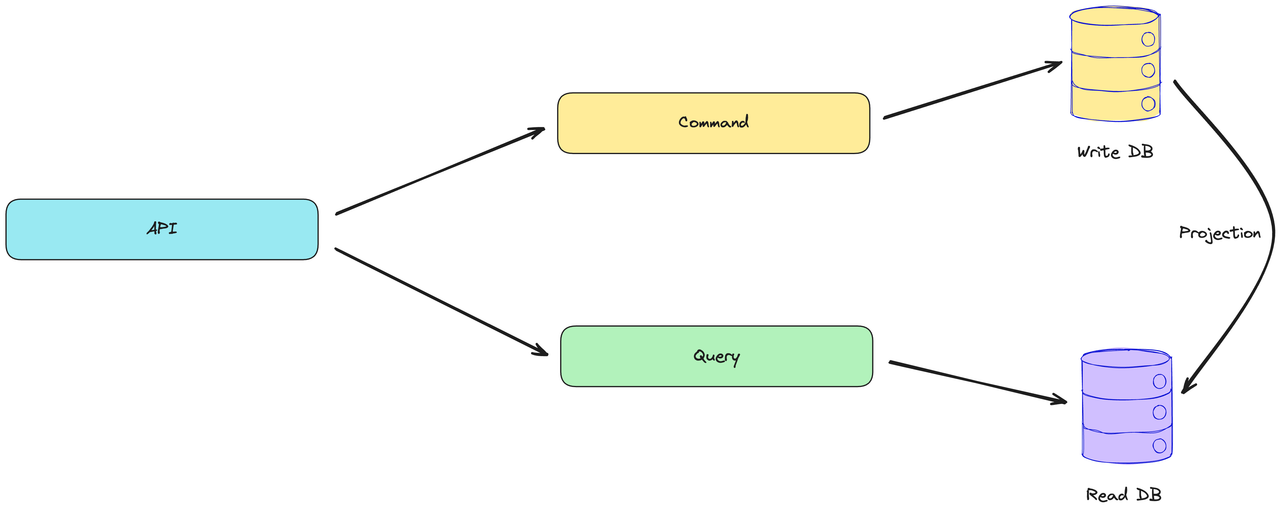
CQRS stands for Command and QueryResponsibility Segregation, a pattern that separates reads and writes into different models, using commands to update data, and queries to read data. Using CQRS, you should have a strict separation between the write model and the read model. Those two models should be processed by separate objects and not be conceptually linked together. Those objects are not physical storage structures but are, for example, command handlers and query handlers. They’re not related to where and how the data will be stored. They’re connected to the processing behavior. Command handlers are responsible for handling commands, mutating state, or doing other side effects. Query handlers are responsible for returning the result of the requested query. It gives us: Scalability - allows for independent scaling of read and write operations. Performance - By separating read and write operations, you can optimize each for performance. Reads can be optimized for fast retrieval by using denormalized data structures, caching, and specialized read models tailored to specific query needs.Flexibility - allows us to model your read and write sides of the application differently, which provides flexibility in designing the data structures and processing logic to best suit the requirements of each operation. This flexibility can lead to a more efficient and maintainable system, especially in complex domains where the read and write requirements differ significantly. One of the common misconceptions about CQRS is that the commands and queries should be run on separate databases. This isn’t necessarily true; only that the behaviors and responsibilities for both should be separated. This can be within the code, within the structure of the database, or (if the situation calls for it), different databases.
Nothing in an inner circle can know anything at all about something in an outer circle. In particular, the name of something declared in an outer circle must not be mentioned by the code in the inner circle. That includes functions and classes. variables, or any other named software entity. In the real world understanding clean architecture can vary from person to person. Since clean architecture emphasizes principles such as separation of concerns, dependency inversion, and abstraction layers, different developers may interpret and implement these principles differently based on their own experiences, knowledge, and project requirements. This article shows my personal view of one of the possible implementations ways. Ultimately, the goal of clean architecture is to create software systems that are maintainable, scalable, and easy to understand.
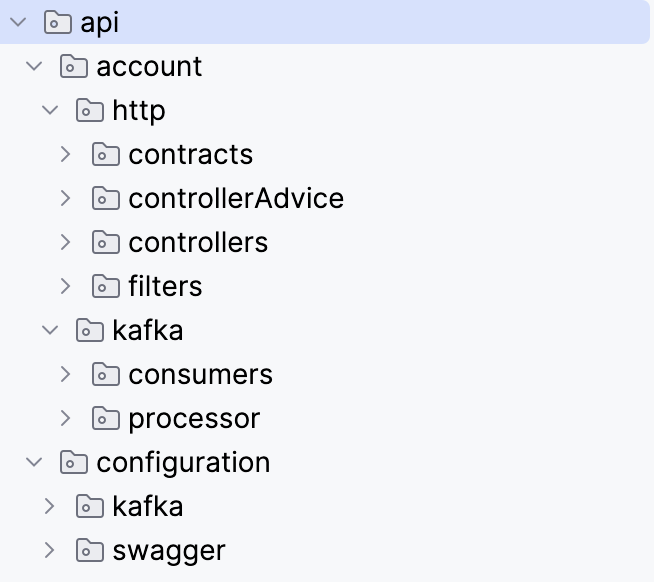
The Presentation layer (named api here) is most outside layer and the entry point to our system. The most important part of the Presentation layer is the Controllers, which define the API endpoints in our system presented to the outside world and responsible for:
- Handling interaction with the outside world
- Presenting, displaying, or returning responses with the data
- Translating the outside requests data (map requests to application layer commands)
- Works with framework-specific configuration setup
- Works on top of the application layer
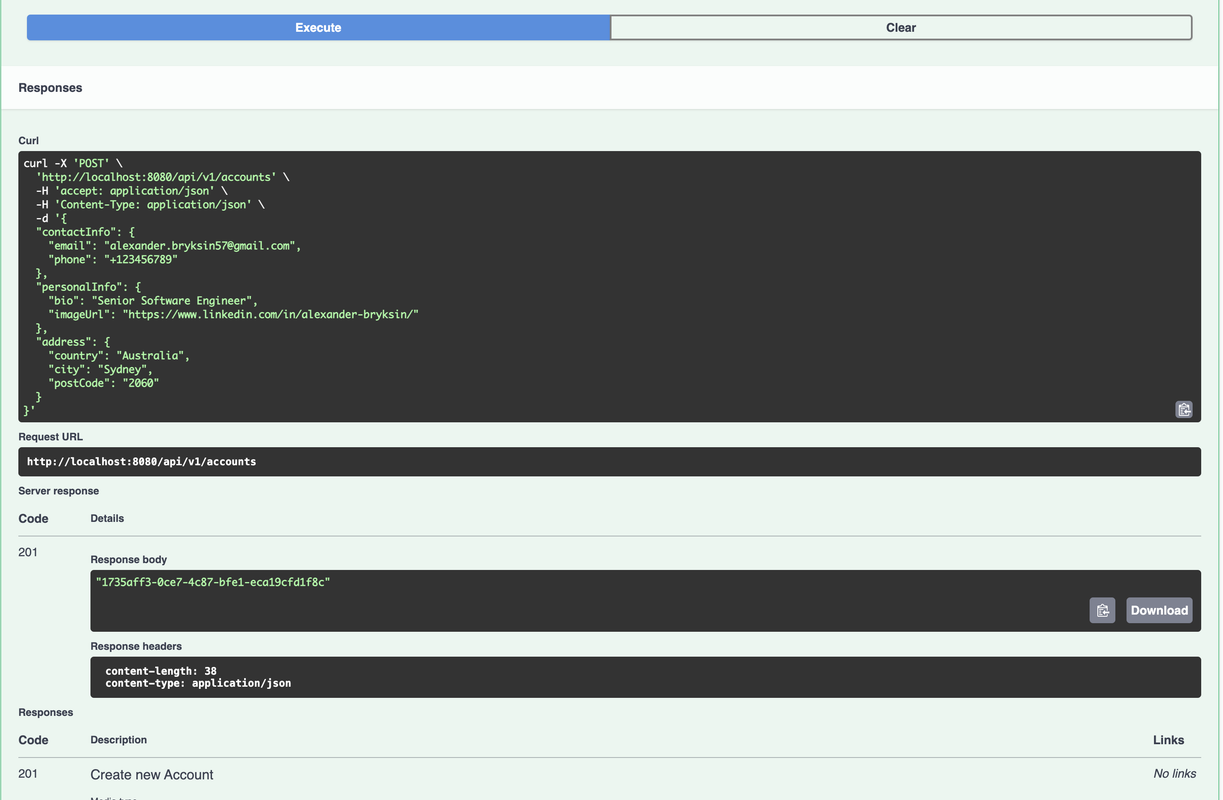
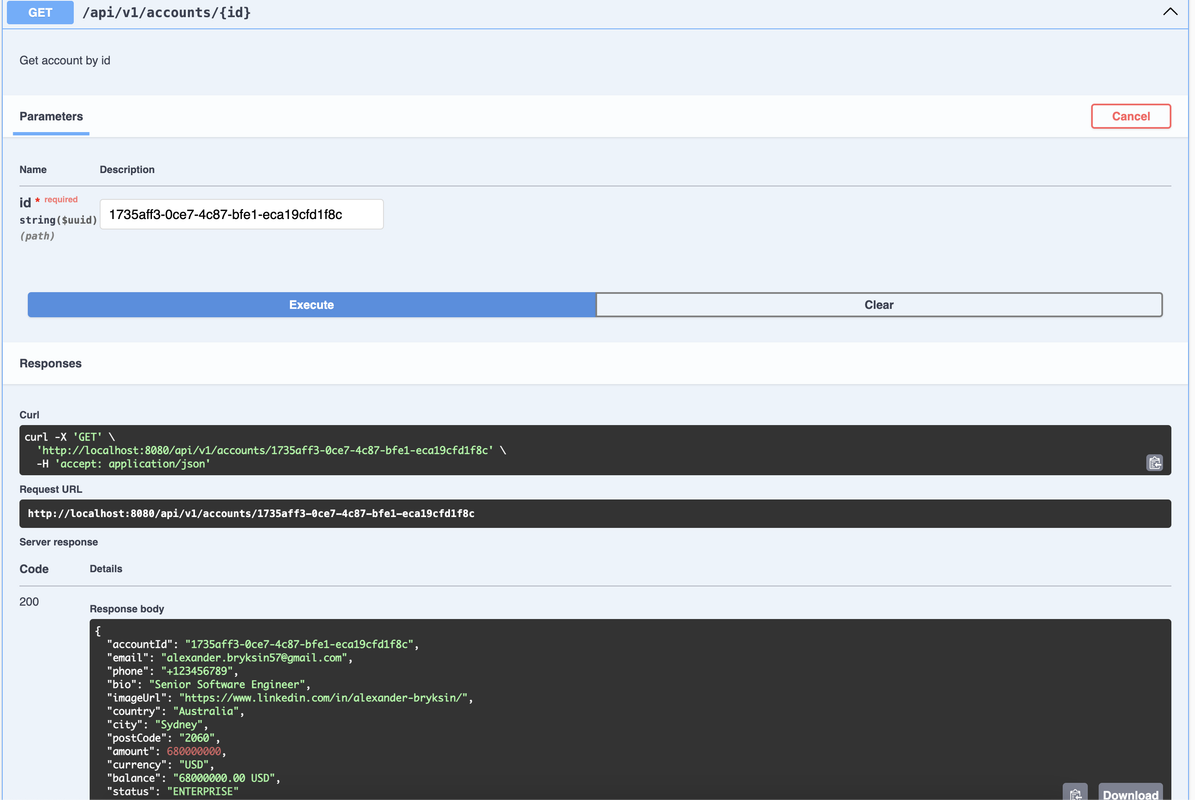
Let's look at the full way of command requests in the microservice. First things first, it accepts REST HTTP requests, validates input, if it's secured checks credentials, etc., then maps the request to the DTO the command and calls AccountCommandService handle method. For example, let's look at creating new account and deposit balance commands methods call flow:
@Tag(name = "Accounts", description = "Account domain REST endpoints")
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = ["/api/v1/accounts"])
class AccountController(
private val accountCommandService: AccountCommandService,
private val accountQueryService: AccountQueryService
) {
@Operation(
method = "createAccount", operationId = "createAccount", description = "Create new Account",
responses = [
ApiResponse(
description = "Create new Account",
responseCode = "201",
content = [Content(
mediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE,
schema = Schema(implementation = AccountId::class)
)]
),
ApiResponse(
description = "bad request response",
responseCode = "400",
content = [Content(schema = Schema(implementation = ErrorHttpResponse::class))]
)],
)
@PostMapping
suspend fun createAccount(
@Valid @RequestBody request: CreateAccountRequest
): ResponseEntity<out Any> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountCommandService.handle(request.toCommand()).bind()
}.fold(
ifLeft = { mapErrorToResponse(it) },
ifRight = { ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(it) }
)
@Operation(
method = "depositBalance", operationId = "depositBalance", description = "Deposit balance",
responses = [
ApiResponse(
description = "Deposit balance",
responseCode = "200",
content = [Content(
mediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE,
schema = Schema(implementation = BaseResponse::class)
)]
),
ApiResponse(
description = "bad request response",
responseCode = "400",
content = [Content(schema = Schema(implementation = ErrorHttpResponse::class))]
)],
)
@PutMapping(path = ["/{id}/deposit"])
suspend fun depositBalance(
@PathVariable id: UUID,
@Valid @RequestBody request: DepositBalanceRequest
): ResponseEntity<out Any> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountCommandService.handle(request.toCommand(AccountId(id))).bind()
}.fold(
ifLeft = { mapErrorToResponse(it) },
ifRight = { okResponse(it) }
)
}The Application layer contains the use cases of the application. A use case represents a specific interaction or action that the system can perform. Each use case is implemented as a command or a query. It is part of the whole application core like a Domain layer and is responsible for:
- Executing the application use cases (all the actions and commands allowed to be done with the system)
- Fetch domain objects
- Manipulating domain objects
The application layer AccountCommandService has the business logic, which runs required business rules validations, then applies changes to the domain aggregate, persists domain objects in the database, produces the domain events, and persists in the outbox table within one single transaction. The current application used some not-required small optimization for outbox publishing, after the command service commits the transaction, we publish the event, but we don't care if this publishes fails, because of polling publisher realized as Spring scheduler anyway will process it.
Arrow greatly improves developer experience because Kotlin doesn’t ship the Either type with the standard SDK. Either is an entity whose value can be of two different types, called left and right. By convention, the Right is for the success case, and the Left for the error one. It allows us to express the fact that a call might return a correct value or an error, and differentiate between the two of them. The Left/Right naming pattern is just a convention. Either is a great way to make the error handling in your code more explicit. Making the code more explicit reduces the amount of context that you need to keep in your head, which in turn makes the code easier to understand.
interface AccountCommandService {
suspend fun handle(command: CreateAccountCommand): Either<AppError, AccountId>
suspend fun handle(command: ChangeAccountStatusCommand): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun handle(command: ChangeContactInfoCommand): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun handle(command: DepositBalanceCommand): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun handle(command: WithdrawBalanceCommand): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun handle(command: UpdatePersonalInfoCommand): Either<AppError, Unit>
}
@Service
class AccountCommandServiceImpl(
private val accountRepository: AccountRepository,
private val outboxRepository: OutboxRepository,
private val tx: TransactionalOperator,
private val eventPublisher: EventPublisher,
private val serializer: Serializer,
private val emailVerifierClient: EmailVerifierClient,
private val paymentClient: PaymentClient
) : AccountCommandService {
override suspend fun handle(command: CreateAccountCommand): Either<AppError, AccountId> = eitherScope(ctx) {
emailVerifierClient.verifyEmail(command.contactInfo.email).bind()
val (account, event) = tx.executeAndAwait {
val account = accountRepository.save(command.toAccount()).bind()
val event = outboxRepository.insert(account.toAccountCreatedOutboxEvent(serializer)).bind()
account to event
}
publisherScope.launch { publishOutboxEvent(event) }
account.accountId
}
override suspend fun handle(command: DepositBalanceCommand): Either<AppError, Unit> = eitherScope(ctx) {
paymentClient.verifyPaymentTransaction(command.accountId.string(), command.transactionId).bind()
val event = tx.executeAndAwait {
val foundAccount = accountRepository.getById(command.accountId).bind()
foundAccount.depositBalance(command.balance).bind()
val account = accountRepository.update(foundAccount).bind()
val event = account.toBalanceDepositedOutboxEvent(command.balance, serializer)
outboxRepository.insert(event).bind()
}
publisherScope.launch { publishOutboxEvent(event) }
}
}Domain layer encapsulates the most important business rules of the system, it is the place where we have to start building core business rules, at the Domain-centric architecture, we start developing from the domain. The responsibilities of the domain layer:
- Defining domain models
- Defining rules, domain and business errors
- Executing the application business logic
- Enforcing the business rules
Domain models have data and behavior and represent the domain. We have two approaches for designing - rich and anemic domain models. Anemic models allow external manipulation of our data, and it's usually antipattern because the domain object itself doesn't control its own data. Rich domain models contain both data and behavior, then richer behavior then richer domain model. It exposes only a specific set of public methods, which allows manipulation of data only in the way the domain approves, encapsulates logic, and does validations. Rich domain model properties are read-only by default.
Domain models can be always valid or not, better to prefer always valid domain models, at any point in time when we're working with domain state, we know it's valid and don't need to write additional validations to check it, always valid domain models means always in the valid state. And one more important detail is Persistence ignorance - modeling the domain without taking into account how domain objects will be persisted.
class Account(
val accountId: AccountId = AccountId(),
) {
var contactInfo: ContactInfo = ContactInfo()
private set
var personalInfo: PersonalInfo = PersonalInfo()
private set
var address: Address = Address()
private set
var balance: Balance = Balance()
private set
var status: AccountStatus = AccountStatus.FREE
private set
var version: Long = 0
private set
var updatedAt: Instant? = null
private set
var createdAt: Instant? = null
private set
fun depositBalance(newBalance: Balance): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
if (balance.balanceCurrency != newBalance.balanceCurrency) raise(InvalidBalanceCurrency("invalid currency: $newBalance"))
if (newBalance.amount < 0) raise(InvalidBalanceAmount("invalid balance amount: $newBalance"))
balance = balance.copy(amount = (balance.amount + newBalance.amount))
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun withdrawBalance(newBalance: Balance): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
if (balance.balanceCurrency != newBalance.balanceCurrency) raise(InvalidBalanceCurrency("invalid currency: $newBalance"))
if (newBalance.amount < 0) raise(InvalidBalanceAmount("invalid balance amount: $newBalance"))
val newAmount = (balance.amount - newBalance.amount)
if ((newAmount) < 0) raise(InvalidBalanceError("invalid balance: $newBalance"))
balance = balance.copy(amount = newAmount)
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun updateStatus(newStatus: AccountStatus): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
status = newStatus
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun changeContactInfo(newContactInfo: ContactInfo): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
contactInfo = newContactInfo
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun changeAddress(newAddress: Address): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
address = newAddress
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun changePersonalInfo(newPersonalInfo: PersonalInfo): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
personalInfo = newPersonalInfo
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun incVersion(amount: Long = 1): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
if (amount < 1) raise(InvalidVersion("invalid version: $amount"))
version += amount
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun withVersion(amount: Long = 1): Account {
version = amount
updatedAt = Instant.now()
return this
}
fun decVersion(amount: Long = 1): Either<AppError, Account> = either {
if (amount < 1) raise(InvalidVersion("invalid version: $amount"))
version -= amount
updatedAt = Instant.now()
this@Account
}
fun withUpdatedAt(newValue: Instant): Account {
updatedAt = newValue
return this
}
}The next is the Infrastructure layer which contains implementations for external-facing services and is responsible for:
- Interacting with persistence solution
- Interacting with other services (http clients, message brokers, etc.)
- Has actual implementations of the interfaces from the application layer
- Identity concerns
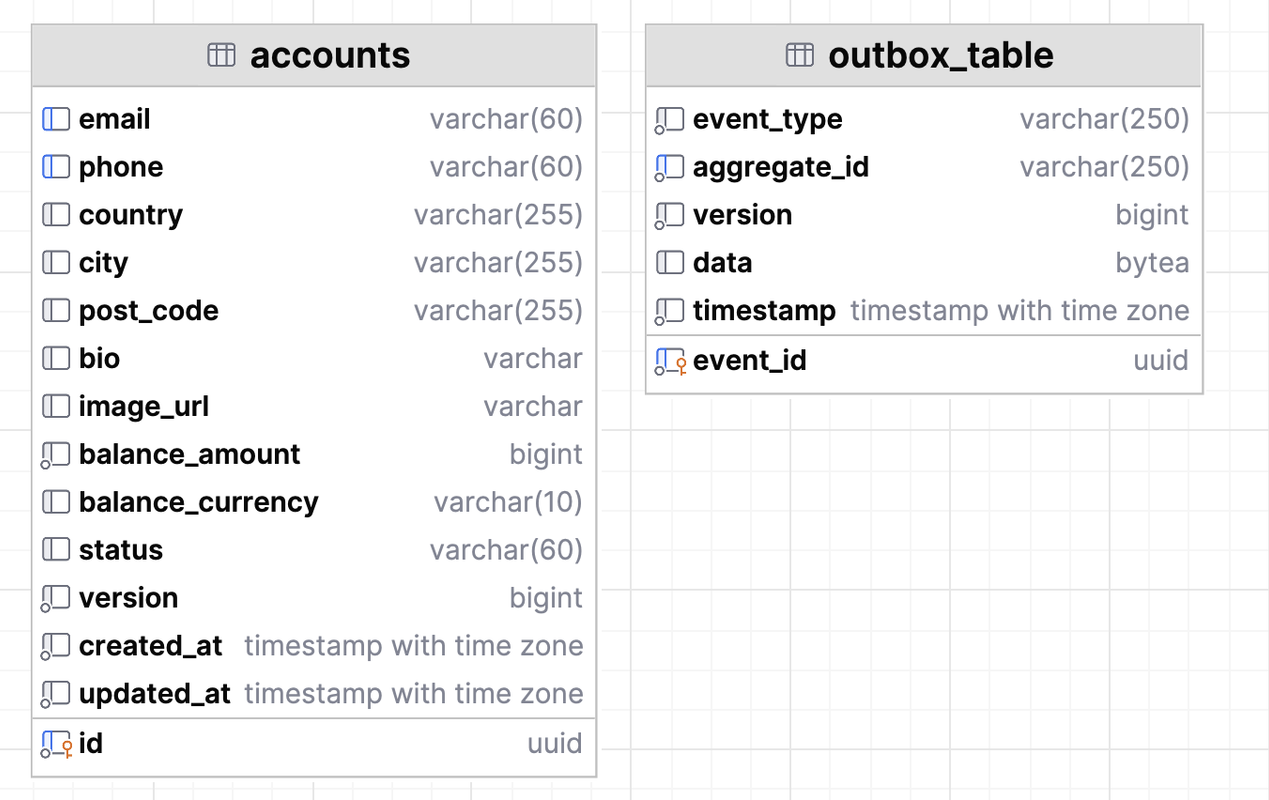
At the Infrastructure layer we have implementations of the application layer interfaces. As the main write database used PostgreSQL with r2dbc reactive driver, and **DatabaseClient ** with raw SQL queries, but if we want to use ORM entity, anyway we still pass domain objects through the other layers interfaces, and then inside the repository implementation code map to the ORM entities. For this project keep spring annotations as it is, but if we want cleaner implementation it's possible to move them to another layer. In this example, project sql schema is simplified and not normalized.
interface AccountRepository {
suspend fun getById(id: AccountId): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun save(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun update(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account>
}
@Repository
class AccountRepositoryImpl(
private val dbClient: DatabaseClient
) : AccountRepository {
override suspend fun save(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope<AppError, Account>(ctx) {
dbClient.sql(INSERT_ACCOUNT_QUERY.trimMargin())
.bindValues(account.withVersion(FIRST_VERSION).toPostgresEntityMap())
.fetch()
.rowsUpdated()
.awaitSingle()
account
}
override suspend fun update(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
dbClient.sql(OPTIMISTIC_UPDATE_QUERY.trimMargin())
.bindValues(account.withUpdatedAt(Instant.now()).toPostgresEntityMap(withOptimisticLock = true))
.fetch()
.rowsUpdated()
.awaitSingle()
account.incVersion().bind()
}
override suspend fun getById(id: AccountId): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
dbClient.sql(GET_ACCOUNT_BY_ID_QUERY.trimMargin())
.bind(ID_FIELD, id.id)
.map { row, _ -> row.toAccount() }
.awaitSingleOrNull()
?: raise(AccountNotFoundError("account for id: $id not found"))
}
}Important detail about outbox repository realisation:
The outbox repository, important detail here is to be able to handle the case of multiple pod instances processing in parallel outbox table, of course, we have idempotent consumers, but as we can, we have to avoid processing the same table events more than one time, to prevent multiple instances select and publish the same events, we use here FOR UPDATE SKIP LOCKED - this combination does the next thing, when one instance tries to select a batch of outbox events if some other instances already selected these records, first, one will skip locked records and select the next available and not locked, and so on. But again it's only my personal preferred way of implementation, the use of only polling publisher is usually default one. as an alternative possible to use debezium for example, but it's up to you.
interface OutboxRepository {
suspend fun insert(event: OutboxEvent): Either<AppError, OutboxEvent>
suspend fun deleteWithLock(
event: OutboxEvent,
callback: suspend (event: OutboxEvent) -> Either<AppError, Unit>
): Either<AppError, OutboxEvent>
suspend fun deleteEventsWithLock(
batchSize: Int,
callback: suspend (event: OutboxEvent) -> Either<AppError, Unit>
): Either<AppError, Unit>
}
@Component
class OutboxRepositoryImpl(
private val dbClient: DatabaseClient,
private val tx: TransactionalOperator
) : OutboxRepository {
override suspend fun insert(event: OutboxEvent): Either<AppError, OutboxEvent> = eitherScope(ctx) {
dbClient.sql(INSERT_OUTBOX_EVENT_QUERY.trimMargin())
.bindValues(event.toPostgresValuesMap())
.map { row, _ -> row.get(ROW_EVENT_ID, String::class.java) }
.one()
.awaitSingle()
.let { event }
}
override suspend fun deleteWithLock(
event: OutboxEvent,
callback: suspend (event: OutboxEvent) -> Either<AppError, Unit>
): Either<AppError, OutboxEvent> = eitherScope {
tx.executeAndAwait {
dbClient.sql(GET_OUTBOX_EVENT_BY_ID_FOR_UPDATE_SKIP_LOCKED_QUERY.trimMargin())
.bindValues(mutableMapOf(EVENT_ID to event.eventId))
.map { row, _ -> row.get(ROW_EVENT_ID, String::class.java) }
.one()
.awaitSingleOrNull()
callback(event).bind()
deleteOutboxEvent(event).bind()
event
}
}
override suspend fun deleteEventsWithLock(
batchSize: Int,
callback: suspend (event: OutboxEvent) -> Either<AppError, Unit>
): Either<AppError, Unit> = eitherScope(ctx) {
tx.executeAndAwait {
dbClient.sql(GET_OUTBOX_EVENTS_FOR_UPDATE_SKIP_LOCKED_QUERY.trimMargin())
.bind(LIMIT, batchSize)
.map { row, _ -> row.toOutboxEvent() }
.all()
.asFlow()
.onStart { log.info { "start publishing outbox events batch: $batchSize" } }
.onEach { callback(it).bind() }
.onEach { event -> deleteOutboxEvent(event).bind() }
.onCompletion { log.info { "completed publishing outbox events batch: $batchSize" } }
.collect()
}
}
private suspend fun deleteOutboxEvent(event: OutboxEvent): Either<AppError, Long> = eitherScope(ctx) {
dbClient.sql(DELETE_OUTBOX_EVENT_BY_ID_QUERY)
.bindValues(mutableMapOf(EVENT_ID to event.eventId))
.fetch()
.rowsUpdated()
.awaitSingle()
}
}The polling publisher implementation is a scheduled process that does the same job for publishing and deleting events at the given interval, as typed earlier and uses the same service method:
@Component
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "schedulers", value = ["outbox.enable"], havingValue = "true")
class OutboxScheduler(
private val outboxRepository: OutboxRepository,
private val publisher: EventPublisher,
) {
@Value("\${schedulers.outbox.batchSize}")
private var batchSize: Int = 30
@Scheduled(
initialDelayString = "\${schedulers.outbox.initialDelayMillis}",
fixedRateString = "\${schedulers.outbox.fixedRate}"
)
fun publishOutboxEvents() = runBlocking {
eitherScope {
outboxRepository.deleteEventsWithLock(batchSize) { publisher.publish(it) }.bind()
}.fold(
ifLeft = { err -> log.error { "error while publishing scheduler outbox events: $err" } },
ifRight = { log.info { "outbox scheduler published events" } }
)
}
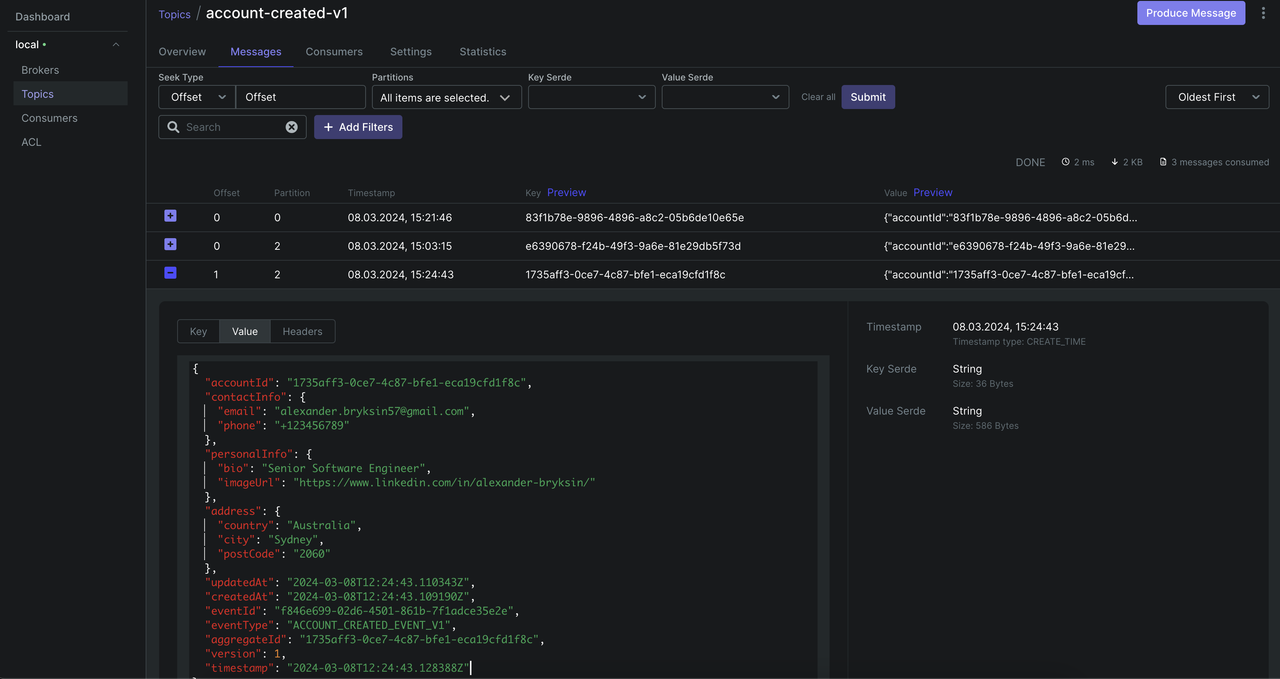
}Domain event is something interesting from a business point of view, that happened within the system, something that already occurred. We're capturing the fact something happened with the system. After events have been published from the outbox table to the broker, in this application, it consumes them from the Kafka, and the consumers themselves call EventHandlerService methods, which builds a read model for out domain aggregates.
The read model of a CQRS-based system provides materialized views of the data, typically as highly denormalized views. These views are tailored to the interfaces and display requirements of the application, which helps to maximize both display and query performance. For error handling and retry, messages prefer to use separate retry topics and listeners. Using the stream of events as the write store, rather than the actual data at a point in time, avoids update conflicts on a single aggregate and maximizes performance and scalability. The events can be used to asynchronously generate materialized views of the data that are used to populate the read store. As with any system where the write and read stores are separate, systems based on this pattern are only eventually consistent. There will be some delay between the event being generated and the data store being updated. Here is Kafka consumer implementation:
@Component
class BalanceDepositedEventConsumer(
private val eventProcessor: EventProcessor,
private val kafkaTopics: KafkaTopics
) {
@KafkaListener(
groupId = "\${kafka.consumer-group-id:account_microservice_group_id}",
topics = ["\${topics.accountBalanceDeposited.name}"],
)
fun process(ack: Acknowledgment, record: ConsumerRecord<String, ByteArray>) = eventProcessor.process(
ack = ack,
consumerRecord = record,
deserializationClazz = BalanceDepositedEvent::class.java,
onError = eventProcessor.errorRetryHandler(kafkaTopics.accountBalanceDepositedRetry.name, DEFAULT_RETRY_COUNT)
) { event ->
eventProcessor.on(
ack = ack,
consumerRecord = record,
event = event,
retryTopic = kafkaTopics.accountBalanceDepositedRetry.name
)
}
@KafkaListener(
groupId = "\${kafka.consumer-group-id:account_microservice_group_id}",
topics = ["\${topics.accountBalanceDepositedRetry.name}"],
)
fun processRetry(ack: Acknowledgment, record: ConsumerRecord<String, ByteArray>) = eventProcessor.process(
ack = ack,
consumerRecord = record,
deserializationClazz = BalanceDepositedEvent::class.java,
onError = eventProcessor.errorRetryHandler(kafkaTopics.accountBalanceDepositedRetry.name, DEFAULT_RETRY_COUNT)
) { event ->
eventProcessor.on(
ack = ack,
consumerRecord = record,
event = event,
retryTopic = kafkaTopics.accountBalanceDepositedRetry.name
)
}
}At the application layer AccountEventsHandlerService is implemented in the following way:
interface AccountEventHandlerService {
suspend fun on(event: AccountCreatedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun on(event: BalanceDepositedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun on(event: BalanceWithdrawEvent): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun on(event: PersonalInfoUpdatedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun on(event: ContactInfoChangedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit>
suspend fun on(event: AccountStatusChangedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit>
}
@Component
class AccountEventHandlerServiceImpl(
private val accountProjectionRepository: AccountProjectionRepository
) : AccountEventHandlerService {
override suspend fun on(event: AccountCreatedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountProjectionRepository.save(event.toAccount()).bind()
}
override suspend fun on(event: BalanceDepositedEvent): Either<AppError, Unit> = eitherScope(ctx) {
findAndUpdateAccountById(event.accountId, event.version) { account ->
account.depositBalance(event.balance).bind()
}.bind()
}
private suspend fun findAndUpdateAccountById(
accountId: AccountId,
eventVersion: Long,
block: suspend (Account) -> Account
): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
val foundAccount = findAndValidateVersion(accountId, eventVersion).bind()
val accountForUpdate = block(foundAccount)
accountProjectionRepository.update(accountForUpdate).bind()
}
private suspend fun findAndValidateVersion(
accountId: AccountId,
eventVersion: Long
): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
val foundAccount = accountProjectionRepository.getById(accountId).bind()
validateVersion(foundAccount, eventVersion).bind()
foundAccount
}
}The infrastructure layer read model repository uses MongoDB Kotlin coroutines driver:
interface AccountProjectionRepository {
suspend fun save(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun update(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun getById(id: AccountId): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun getByEmail(email: String): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun getAll(page: Int, size: Int): Either<AppError, AccountsList>
suspend fun upsert(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account>
}@Component
class AccountProjectionRepositoryImpl(
mongoClient: MongoClient,
) : AccountProjectionRepository {
private val accountsDB = mongoClient.getDatabase(ACCOUNTS_DB)
private val accountsCollection = accountsDB.getCollection<AccountDocument>(ACCOUNTS_COLLECTION)
override suspend fun save(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope<AppError, Account>(ctx) {
val insertResult = accountsCollection.insertOne(account.toDocument())
log.info { "account insertOneResult: $insertResult, account: $account" }
account
}
override suspend fun update(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
val filter = and(eq(ACCOUNT_ID, account.accountId.string()), eq(VERSION, account.version))
val options = FindOneAndUpdateOptions().upsert(false).returnDocument(ReturnDocument.AFTER)
accountsCollection.findOneAndUpdate(
filter,
account.incVersion().bind().toBsonUpdate(),
options
)
?.toAccount()
?: raise(AccountNotFoundError("account with id: ${account.accountId} not found"))
}
override suspend fun upsert(account: Account): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
val filter = and(eq(ACCOUNT_ID, account.accountId.string()))
val options = FindOneAndUpdateOptions().upsert(true).returnDocument(ReturnDocument.AFTER)
accountsCollection.findOneAndUpdate(
filter,
account.toBsonUpdate(),
options
)
?.toAccount()
?: raise(AccountNotFoundError("account with id: ${account.accountId} not found"))
}
override suspend fun getById(id: AccountId): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountsCollection.find<AccountDocument>(eq(ACCOUNT_ID, id.string()))
.firstOrNull()
?.toAccount()
?: raise(AccountNotFoundError("account with id: $id not found"))
}
override suspend fun getByEmail(email: String): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
val filter = and(eq(CONTACT_INFO_EMAIL, email))
accountsCollection.find(filter).firstOrNull()?.toAccount()
?: raise(AccountNotFoundError("account with email: $email not found"))
}
override suspend fun getAll(
page: Int,
size: Int
): Either<AppError, AccountsList> = eitherScope<AppError, AccountsList>(ctx) {
parZip(coroutineContext, {
accountsCollection.find()
.skip(page * size)
.limit(size)
.map { it.toAccount() }
.toList()
}, {
accountsCollection.find().count()
}) { list, totalCount ->
AccountsList(
page = page,
size = size,
totalCount = totalCount,
accountsList = list
)
}
}
}And read queries way through the layers is very similar, we accept HTTP requests at the api layer:
@Tag(name = "Accounts", description = "Account domain REST endpoints")
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = ["/api/v1/accounts"])
class AccountController(
private val accountCommandService: AccountCommandService,
private val accountQueryService: AccountQueryService
) {
@Operation(
method = "getAccountByEmail", operationId = "getAccountByEmail", description = "Get account by email",
responses = [
ApiResponse(
description = "Get account by email",
responseCode = "200",
content = [Content(
mediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE,
schema = Schema(implementation = AccountResponse::class)
)]
),
ApiResponse(
description = "bad request response",
responseCode = "400",
content = [Content(schema = Schema(implementation = ErrorHttpResponse::class))]
)],
)
@GetMapping(path = ["/email/{email}"])
suspend fun getAccountByEmail(
@PathVariable @Email @Size(
min = 6,
max = 255
) email: String
): ResponseEntity<out Any> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountQueryService.handle(GetAccountByEmailQuery(email)).bind()
}.fold(
ifLeft = { mapErrorToResponse(it) },
ifRight = { ResponseEntity.ok(it.toResponse()) }
)
}the application layer AccountQueryService methods:
interface AccountQueryService {
suspend fun handle(query: GetAccountByIdQuery): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun handle(query: GetAccountByEmailQuery): Either<AppError, Account>
suspend fun handle(query: GetAllAccountsQuery): Either<AppError, AccountsList>
}@Service
class AccountQueryServiceImpl(
private val accountRepository: AccountRepository,
private val accountProjectionRepository: AccountProjectionRepository
) : AccountQueryService {
override suspend fun handle(query: GetAccountByIdQuery): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountRepository.getById(query.id).bind()
}
override suspend fun handle(query: GetAccountByEmailQuery): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountProjectionRepository.getByEmail(query.email).bind()
}
override suspend fun handle(query: GetAllAccountsQuery): Either<AppError, AccountsList> = eitherScope(ctx) {
accountProjectionRepository.getAll(page = query.page, size = query.size).bind()
}
}and uses PostgreSQL or MongoDB repositories to get the data depending on the query use case:
@Component
class AccountProjectionRepositoryImpl(
mongoClient: MongoClient,
) : AccountProjectionRepository {
private val accountsDB = mongoClient.getDatabase(ACCOUNTS_DB)
private val accountsCollection = accountsDB.getCollection<AccountDocument>(ACCOUNTS_COLLECTION)
override suspend fun getByEmail(email: String): Either<AppError, Account> = eitherScope(ctx) {
val filter = and(eq(CONTACT_INFO_EMAIL, email))
accountsCollection.find(filter)
.firstOrNull()
?.toAccount()
?: raise(AccountNotFoundError("account with email: $email not found"))
}
}In real-world applications, we have to implement many more necessary features, like k8s health checks, circuit breakers, rate limiters, etc., this project is simplified for demonstration example, purposes. I hope this article is useful, please start it if it is helpful for you. For feedback or questions, feel free to contact me by email or any messengers :)