I develop this tool based on the java package Apache Commons DbUtils.
This tool provides an easy-to-use interface for operating mysql database.
Also, this tool supports XML database configuration and Java Bean.
Function:
query, update and insert data.
The configuration parameters for mysql:
connectURI:127.0.0.1:3306
database name:crawler
user name:root
password:112233
The operational table is 'carsales'. The data in this table is as follows:
The code for querying one column data is as follows:
package com.test;
import java.util.List;
import com.db.MYSQLControl;
public class QueryOneColumn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MYSQLControl control = new MYSQLControl("127.0.0.1:3306", "crawler", "root", "112233");
List<Object> list = control.getListOneBySQL("select month from carsales", "month");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i).toString());
}
}
}Running this code, we can obtain the following results:
2007-01-01
2007-02-01
2007-03-01
2007-04-01
2007-05-01
2007-06-01
2007-07-01
2007-08-01
2007-09-01
2007-10-01
2007-11-01
...
The code for updating table is as follows:
package com.test;
import com.db.MYSQLControl;
public class UpdateData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MYSQLControl control = new MYSQLControl("127.0.0.1:3306", "crawler", "root", "112233");
control.executeUpdate("update carsales set sales = '4000' "
+ "where month = '2007-10-01'");
System.out.println("finish updating!");
}
}Running this code, we can find that:
The code for creating a table is as follows:
package com.test;
import com.db.MYSQLControl;
public class CreateTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MYSQLControl control = new MYSQLControl("127.0.0.1:3306", "crawler", "root", "112233");
String sql = "CREATE TABLE newcarsales " +
"(month varchar(50), " +
"sales varchar(255), " +
" PRIMARY KEY ( month ))";
control.executeUpdate(sql);
}
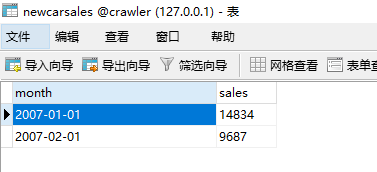
}Running this code, we can find that:
If we want to query multiple columns, we must use java bean.
First, we create a model as follows:
package com.model;
public class CarSaleModel {
private String month;
private String sales;
public String getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(String month) {
this.month = month;
}
public String getSales() {
return sales;
}
public void setSales(String sales) {
this.sales = sales;
}
}Next, we query multiple columns' data as follows:
import java.util.List;
import com.db.MYSQLControl;
import com.model.CarSaleModel;
public class QueryMultColumn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MYSQLControl control = new MYSQLControl("127.0.0.1:3306", "crawler", "root", "112233");
List<CarSaleModel> listData = control.getListInfoBySQL("select month, sales from carsales", CarSaleModel.class);
for (CarSaleModel model : listData) {
System.out.println(model.getMonth() + "\t" + model.getSales());
}
}
}Running this code, we can obtain that:
2007-01-01 14834
2007-02-01 9687
2007-03-01 18173
2007-04-01 18508
2007-05-01 19710
2007-06-01 20311
2007-07-01 17516
2007-08-01 17535
2007-09-01 17743
2007-10-01 4000
2007-11-01 17250
...The code for inserting list is as follows:
package com.test;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.db.MYSQLControl;
import com.model.CarSaleModel;
public class InsertListData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MYSQLControl control = new MYSQLControl("127.0.0.1:3306", "crawler", "root", "112233");
List<CarSaleModel> saleList = new ArrayList<CarSaleModel>();
CarSaleModel model1 = new CarSaleModel();
model1.setMonth("2007-01-01");
model1.setSales("14834");
CarSaleModel model2 = new CarSaleModel();
model2.setMonth("2007-02-01");
model2.setSales("9687");
//add data
saleList.add(model1);
saleList.add(model2);
try {
control.insertListData(saleList, "newcarsales");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Running this code, we can find that:
This code is often used in crawler project.
We can use XML file to configure the database:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config>
<connectionInfo>
<node1>
<nodeName>node1</nodeName>
<url>jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/crawler</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>112233</password>
</node1>
<node2>
<nodeName>node2</nodeName>
<url>jdbc:mysql://114.213.252.26:3306/crawler</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>112233</password>
</node2>
</connectionInfo>
</config>Next, we can use the following code to operate the database based on the xml file:
package com.test;
import java.util.List;
import com.db.MYSQLControl;
import com.model.CarSaleModel;
public class XMLMySQLDo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MYSQLControl control = new MYSQLControl("node1");
List<CarSaleModel> listData = control.getListInfoBySQL("select month, sales from carsales", CarSaleModel.class);
for (CarSaleModel model : listData) {
System.out.println(model.getMonth() + "\t" + model.getSales());
}
}
}Running this code, we can obtain that:
2007-01-01 14834
2007-02-01 9687
2007-03-01 18173
2007-04-01 18508
2007-05-01 19710
2007-06-01 20311
2007-07-01 17516
2007-08-01 17535
2007-09-01 17743
2007-10-01 4000
2007-11-01 17250
...