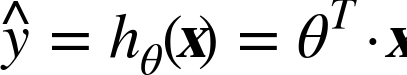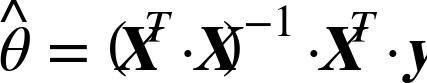Linear regression implementation with Numpy
A linear model makes a prediction by simply computing a weighted sum of the input features, plus a constant called the bias term.
Equation y = θ+ X1θ1 + X2θ2 + ...
vectorized form of above equation
Therefore, to train a Linear Regression model, you need to find the value of θ that minimizes the RMSE. In practice, it is simpler to minimize the Mean Square Error (MSE) than the RMSE, and it leads to the same result (because the value that minimizes a function also minimizes its square root)
The MSE of a Linear Regression hypothesis hθ on a training set X is calculated using below equation .
MSE cost function for a Linear Regression model
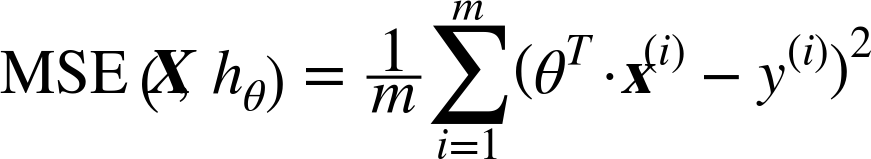
The reason for the operations is that the summation of the squared errors gives us a unique and simple global number, the difference between expected and real number gives us the proper distance, and the square power gives us a positive number, which penalizes distances in a more-than-linear fashion.
To find the value of θ that minimizes the cost function, there is a closed-form solution
For more info : https://github.com/spatil6/Machine-Learning-algorithm-from-scratch/Mathematics_of_machine_learning.docx