Spring Cloud Release Train is a curated set of dependencies across a range of Spring Cloud projects. You consume it by using the spring-cloud-dependencies POM to manage dependencies in Maven or Gradle. The release trains have names, not versions, to avoid confusion with the sub-projects. The names are an alphabetic sequence (so you can sort them chronologically) with names of London Tube stations ("Angel" is the first release, "Brixton" is the second).
In order to generate the release train documentation, please update the project with versions for a given release train and then execute the following command:
$ ./mvnw clean install -Pdocs,train-docs -pl train-docsIn order to upload the documentation to the documentation server just execute the following command:
$ ./mvnw clean deploy -Pdocs,train-docs -pl train-docs|
Important
|
If you’re releasing milestones don’t forget to add -Pmilestone and if GA -Pcentral.
|
Spring Cloud is released under the non-restrictive Apache 2.0 license, and follows a very standard Github development process, using Github tracker for issues and merging pull requests into main. If you want to contribute even something trivial please do not hesitate, but follow the guidelines below.
All commits must include a Signed-off-by trailer at the end of each commit message to indicate that the contributor agrees to the Developer Certificate of Origin. For additional details, please refer to the blog post Hello DCO, Goodbye CLA: Simplifying Contributions to Spring.
This project adheres to the Contributor Covenant code of conduct. By participating, you are expected to uphold this code. Please report unacceptable behavior to [email protected].
None of these is essential for a pull request, but they will all help. They can also be added after the original pull request but before a merge.
-
Use the Spring Framework code format conventions. If you use Eclipse you can import formatter settings using the
eclipse-code-formatter.xmlfile from the Spring Cloud Build project. If using IntelliJ, you can use the Eclipse Code Formatter Plugin to import the same file. -
Make sure all new
.javafiles to have a simple Javadoc class comment with at least an@authortag identifying you, and preferably at least a paragraph on what the class is for. -
Add the ASF license header comment to all new
.javafiles (copy from existing files in the project) -
Add yourself as an
@authorto the .java files that you modify substantially (more than cosmetic changes). -
Add some Javadocs and, if you change the namespace, some XSD doc elements.
-
A few unit tests would help a lot as well — someone has to do it.
-
If no-one else is using your branch, please rebase it against the current main (or other target branch in the main project).
-
When writing a commit message please follow these conventions, if you are fixing an existing issue please add
Fixes gh-XXXXat the end of the commit message (where XXXX is the issue number).
Spring Cloud Build comes with a set of checkstyle rules. You can find them in the spring-cloud-build-tools module. The most notable files under the module are:
└── src ├── checkstyle │ └── checkstyle-suppressions.xml (3) └── main └── resources ├── checkstyle-header.txt (2) └── checkstyle.xml (1)
-
Default Checkstyle rules
-
File header setup
-
Default suppression rules
Checkstyle rules are disabled by default. To add checkstyle to your project just define the following properties and plugins.
<properties>
<maven-checkstyle-plugin.failsOnError>true</maven-checkstyle-plugin.failsOnError> (1)
<maven-checkstyle-plugin.failsOnViolation>true
</maven-checkstyle-plugin.failsOnViolation> (2)
<maven-checkstyle-plugin.includeTestSourceDirectory>true
</maven-checkstyle-plugin.includeTestSourceDirectory> (3)
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin> (4)
<groupId>io.spring.javaformat</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-javaformat-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin> (5)
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-checkstyle-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin> (5)
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-checkstyle-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
</build>
-
Fails the build upon Checkstyle errors
-
Fails the build upon Checkstyle violations
-
Checkstyle analyzes also the test sources
-
Add the Spring Java Format plugin that will reformat your code to pass most of the Checkstyle formatting rules
-
Add checkstyle plugin to your build and reporting phases
If you need to suppress some rules (e.g. line length needs to be longer), then it’s enough for you to define a file under ${project.root}/src/checkstyle/checkstyle-suppressions.xml with your suppressions. Example:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE suppressions PUBLIC "-//Puppy Crawl//DTD Suppressions 1.1//EN" "https://www.puppycrawl.com/dtds/suppressions_1_1.dtd"> <suppressions> <suppress files=".*ConfigServerApplication\.java" checks="HideUtilityClassConstructor"/> <suppress files=".*ConfigClientWatch\.java" checks="LineLengthCheck"/> </suppressions>
It’s advisable to copy the ${spring-cloud-build.rootFolder}/.editorconfig and ${spring-cloud-build.rootFolder}/.springformat to your project. That way, some default formatting rules will be applied. You can do so by running this script:
$ curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-build/main/.editorconfig -o .editorconfig
$ touch .springformatIn order to setup Intellij you should import our coding conventions, inspection profiles and set up the checkstyle plugin. The following files can be found in the Spring Cloud Build project.
└── src ├── checkstyle │ └── checkstyle-suppressions.xml (3) └── main └── resources ├── checkstyle-header.txt (2) ├── checkstyle.xml (1) └── intellij ├── Intellij_Project_Defaults.xml (4) └── Intellij_Spring_Boot_Java_Conventions.xml (5)
-
Default Checkstyle rules
-
File header setup
-
Default suppression rules
-
Project defaults for Intellij that apply most of Checkstyle rules
-
Project style conventions for Intellij that apply most of Checkstyle rules
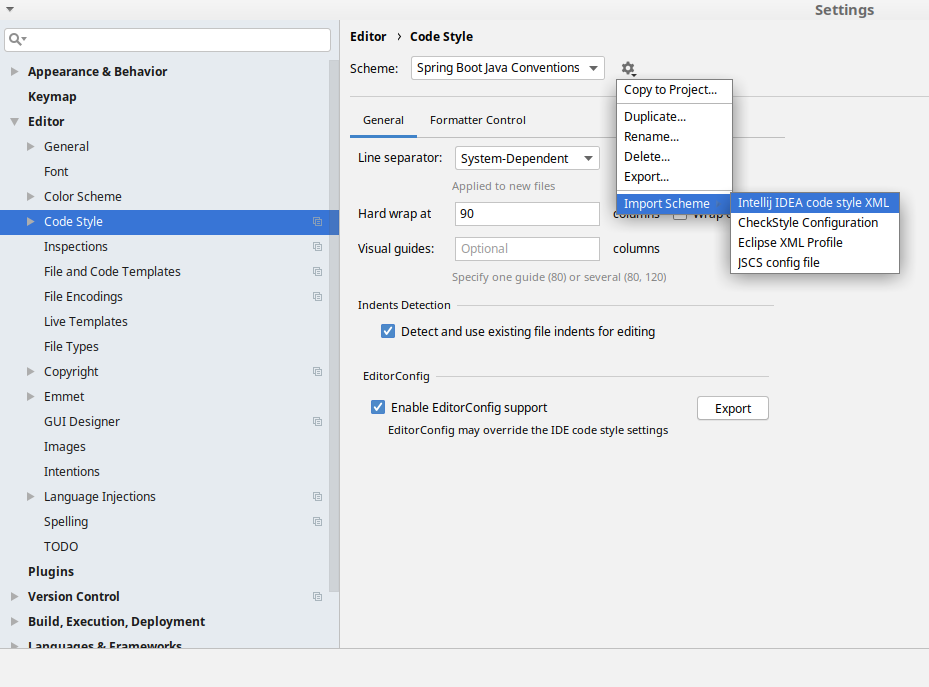
Go to File → Settings → Editor → Code style. There click on the icon next to the Scheme section. There, click on the Import Scheme value and pick the Intellij IDEA code style XML option. Import the spring-cloud-build-tools/src/main/resources/intellij/Intellij_Spring_Boot_Java_Conventions.xml file.
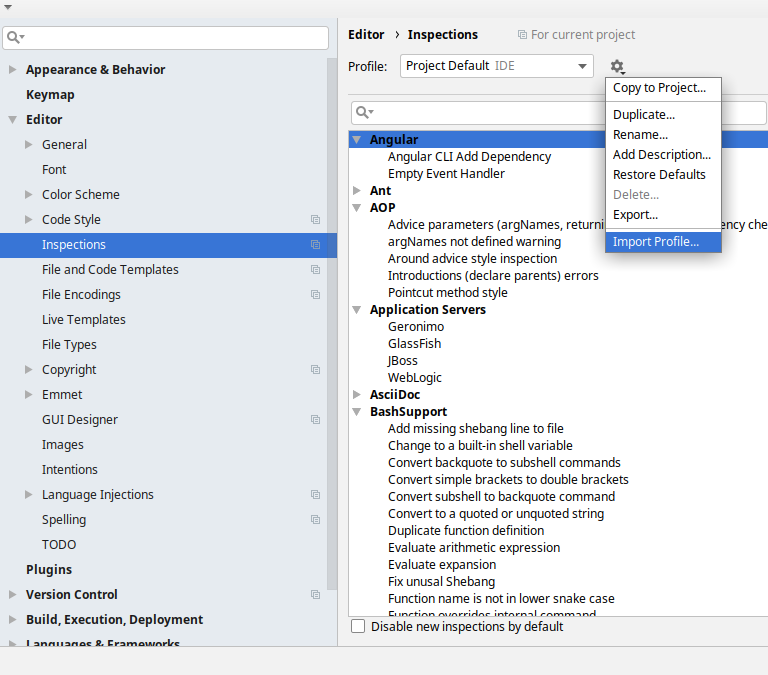
Go to File → Settings → Editor → Inspections. There click on the icon next to the Profile section. There, click on the Import Profile and import the spring-cloud-build-tools/src/main/resources/intellij/Intellij_Project_Defaults.xml file.
To have Intellij work with Checkstyle, you have to install the Checkstyle plugin. It’s advisable to also install the Assertions2Assertj to automatically convert the JUnit assertions
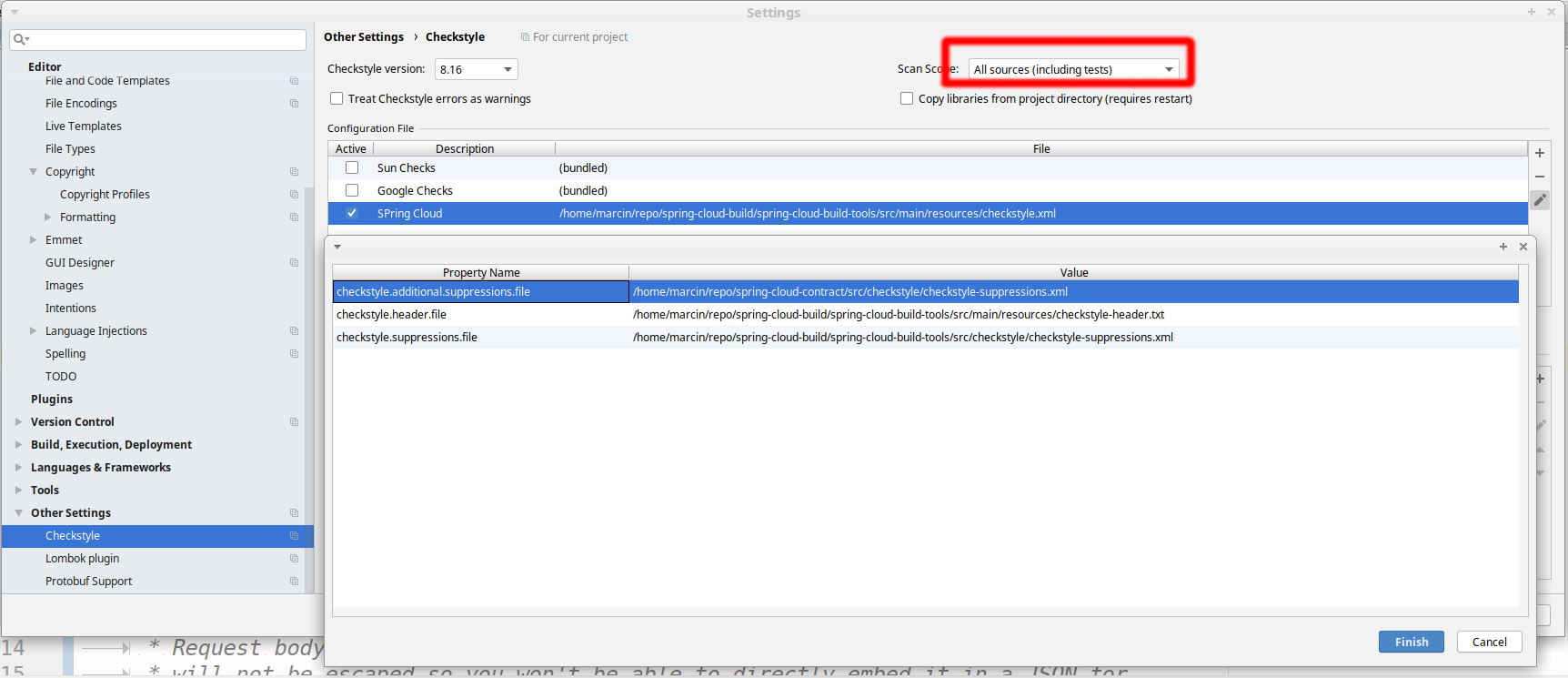
Go to File → Settings → Other settings → Checkstyle. There click on the + icon in the Configuration file section. There, you’ll have to define where the checkstyle rules should be picked from. In the image above, we’ve picked the rules from the cloned Spring Cloud Build repository. However, you can point to the Spring Cloud Build’s GitHub repository (e.g. for the checkstyle.xml : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-build/main/spring-cloud-build-tools/src/main/resources/checkstyle.xml). We need to provide the following variables:
-
checkstyle.header.file- please point it to the Spring Cloud Build’s,spring-cloud-build-tools/src/main/resources/checkstyle-header.txtfile either in your cloned repo or via thehttps://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-build/main/spring-cloud-build-tools/src/main/resources/checkstyle-header.txtURL. -
checkstyle.suppressions.file- default suppressions. Please point it to the Spring Cloud Build’s,spring-cloud-build-tools/src/checkstyle/checkstyle-suppressions.xmlfile either in your cloned repo or via thehttps://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-build/main/spring-cloud-build-tools/src/checkstyle/checkstyle-suppressions.xmlURL. -
checkstyle.additional.suppressions.file- this variable corresponds to suppressions in your local project. E.g. you’re working onspring-cloud-contract. Then point to theproject-root/src/checkstyle/checkstyle-suppressions.xmlfolder. Example forspring-cloud-contractwould be:/home/username/spring-cloud-contract/src/checkstyle/checkstyle-suppressions.xml.
|
Important
|
Remember to set the Scan Scope to All sources since we apply checkstyle rules for production and test sources.
|
Spring Cloud Build brings along the basepom:duplicate-finder-maven-plugin, that enables flagging duplicate and conflicting classes and resources on the java classpath.
Duplicate finder is enabled by default and will run in the verify phase of your Maven build, but it will only take effect in your project if you add the duplicate-finder-maven-plugin to the build section of the projecst’s pom.xml.
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.basepom.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>duplicate-finder-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>For other properties, we have set defaults as listed in the plugin documentation.
You can easily override them but setting the value of the selected property prefixed with duplicate-finder-maven-plugin. For example, set duplicate-finder-maven-plugin.skip to true in order to skip duplicates check in your build.
If you need to add ignoredClassPatterns or ignoredResourcePatterns to your setup, make sure to add them in the plugin configuration section of your project:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.basepom.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>duplicate-finder-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<ignoredClassPatterns>
<ignoredClassPattern>org.joda.time.base.BaseDateTime</ignoredClassPattern>
<ignoredClassPattern>.*module-info</ignoredClassPattern>
</ignoredClassPatterns>
<ignoredResourcePatterns>
<ignoredResourcePattern>changelog.txt</ignoredResourcePattern>
</ignoredResourcePatterns>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>Since there is no code to compile in the starters they should do not need to compile, but a compiler has to be available because they are built and deployed as JAR artifacts. To install locally:
$ mvn install -s .settings.xml
and to deploy snapshots to repo.spring.io:
$ mvn install -DaltSnapshotDeploymentRepository=repo.spring.io::default::https://repo.spring.io/libs-snapshot-local
for a RELEASE build use
$ mvn install -DaltReleaseDeploymentRepository=repo.spring.io::default::https://repo.spring.io/libs-release-local
and for Maven Central use
$ mvn install -P central -DaltReleaseDeploymentRepository=sonatype-nexus-staging::default::https://oss.sonatype.org/service/local/staging/deploy/maven2
(the "central" profile is available for all projects in Spring Cloud and it sets up the gpg jar signing, and the repository has to be specified separately for this project because it is a parent of the starter parent which users in turn have as their own parent).