Everyone can create money as long as there is credit.
QIAN aims to build a global, stable, low-threshold and decentralized stablecoin ecosystem that everyone can participate in.
With the popularity of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency, a new form of currency has emerged. However, due to the fluctuation of the price of cryptocurrency, it cannot be used as a trading medium, cannot be deferred, and cannot be used as the unit of accounting.
Based on the demand for stability, there has been stablecoin represented by Tether, in which market volume has reached billions of dollars. Incomplete statistics show that there are more than 60 stablecoin projects in the market (June 2019).
Seeing the huge opportunities in the market, global financial and Internet giants have also entered this market. On February 14, 2019, JP Morgan announced the launch of JPM Coin; on June 18, 2019, Facebook released cryptocurrency project Libra's white paper, joining dozens of well-known financial institutions and internet multinationals, plans to launch a cryptocurrency-based payment system.
A currency revolution sweeping the globe is taking place.
However, the mainstream stablecoin projects are still operated in a centralized or multi-centered manner, we still have to trust those institutions, while worrying about opaque and over-issued issues. The casting of stablecoin is still the privilege of big capital, and monopoly is still the way to chase maximum interests.
We believe that there must be another way, whether it is an international business giant or a mortal being, as long as it can prove its credit, it can participate in the generation of money equally, freely and conveniently, enjoy undifferentiated and non-discriminatory financial services in an open, inclusive and transparent ecosystem. It reflects the essence and spirit of the blockchain.
In order to achieve such a vision, relying on the open-source framework of The Force Protocol, we officially launched the stablecoin project - "QIAN".
除了卖出,加密资产还能通过质押获取流动性。
QIAN旨在搭建一个全球性的,门槛极低的,人人皆可参与创造,人人皆可参与流通的去中心化稳定币生态系统。
随着区块链技术和加密数字货币的流行,一种全新的货币形式已经出现。但是,由于加密数字货币的巨大波动性,使得其不能作为交易媒介,不能进行延期支付,也不能作为记帐单位。
基于对稳定性的需求,出现了以Tether为代表的稳定币,市场规模已达数十亿美元。据不完全统计,市场上稳定币项目已超过60家(2019年6月)。
看到稳定币市场的巨大机会,全球金融和互联网巨头也纷纷布局。2019年2月14日,JP Morgan 宣布推出稳定币——JPM Coin;2019年6月18日,Facebook发布加密货币项目Libra白皮书,联合数十家知名金融机构和在线商户,计划推出基于加密货币的支付系统。
一场席卷全球的货币革命正在发生。
然而,主流的稳定币项目仍然以中心化或多中心化的方式运营着,我们仍然不得不信任这些机构,同时担忧着不透明,超发等问题。货币的铸造仍然是大资本的特权,垄断仍然是追逐最大利益的手段。
我们相信,一定存在另外的一种形式,不管是国际商业巨头,还是芸芸众生,只要能够证明自己的信用,就可以平等、自由、便捷地参与到货币的创造中来,在一个开放、包容和透明的生态系统中享受无差别和无歧视的金融服务。而这,正体现了区块链的本质和精髓。
为了这样的愿景,依托The Force Protocol开源框架,The Force Protocol正式启动稳定币项目——“QIAN”。
Let's start with a brief introduction to the QIAN, and the next chapters will cover specific implementation details.
Since ancient times, there have been shells, beads, sticks, metal money, banknotes, etc. as currency. Everyone uses a certain currency because it has a consensus on certain groups of people or all human beings. The essence of money is value credit, so we believe that everyone can create money as long as there is a proper value credit tool.
In the blockchain world, token is a direct manifestation of credit. Therefore, the cryptocurrency or crypto-assets with better liquidity can be used as guarantee for the issuance of decentralized stablecoin. Through a certain price stabilization mechanism, the exchange rate stability to fiat currency can be achieved.
- QIAN uses crypto-assets as the underlying support assets;
- QIAN will initially maintain a 1:1 exchange rate with the US dollar, and will issue a 1:1 exchange rate with the international mainstream currencies such as the Euro, Japanese Yen, RMB and Libra in the future;
- The QIAN system is prioritized developing on Bitcoin RSK sidechain and Ethereum, and will be upgraded based on the mainstream cross-chain architecture;
- The QIAN system is committed to the ultimate decentralized operation, but this will be a gradual process;
- The QIAN system is based on the open-source framework of The Force Protocol and is part of The Force Protocol ecosystem.
- At least 100% cryptoasset support;
- Stablecoin holders can redeem collateral with market price at any time;
- Carefully select the underlying cryptoassets portfolio to reduce systemic risk;
- Dynamic interest adjustment mechanism to maintain and adjust QIAN's development and stability.
- Emergency Risk Fund.
QIAN: Same meaning as “money” in mandarin Chinese, also in I Ching (the Book of Changes), “the QIAN Diagram” stands for the sky and represents the law of the operation of all things in the universe. It is the highest positive spirit and energy. Following the two important meaning, we named the first stablecoin in Bitcoin ecosystem as QIAN. QIAN is a stablecoin created by The Force Protocol project development team, cycling on Bitcoin RSK sidechain and Ethereum, which can be generated (mint) or destroyed (burn), can be used for lending, investment, payment, value storing and other application scenarios.
FOR: The Force Protocol Eco-Token, also governance token of the QIAN system for voting on QIAN ecology governance and maintaining QIAN price stability.
我们首先对钱(QIAN)进行简单介绍,接下来的其他章节将介绍具体实现细节。
从古至今,作为货币的有贝壳、珠子、棍子、金属货币、纸币等。大家使用某种货币,是因为在其上附加了某类人群或全体人类的共识。货币的本质是价值信用,因此我们认为,只要有适当的价值信用工具,人人皆可创造货币。
在区块链世界里,token(暂译为通证)是信用的直接体现。所以,只要拥有较好流动性的加密数字货币或通证化资产(以下统称为“加密资产”),就可以用来为货币的发行做担保,通过一定的价格稳定机制,可以实现对法币的汇率稳定。
- QIAN 以加密资产为底层支持资产;
- QIAN 在初始将与美元保持 1:1 的汇率,未来将可能发行与其他国际主流货币 1:1 汇率的版本;
- QIAN 系统优先在比特币 RSK 侧链和以太坊上实现,后续将基于主流跨链架构进行升级;
- QIAN 系统致力最终于实行完全去中心化运作,但这将是一个渐进的过程;
- QIAN 系统基于The Force Protocol开源框架开发,是The Force Protocol生态系统的一部分。
- 至少 100% 加密资产支持;
- 稳定币持有者随时可以按市场价格赎回质押品;
- 精选底层加密资产组合,降低系统性风险;
- 动态利息调整机制,维持和调整 QIAN 的发展和稳定。
- 风险缓释金机制。
QIAN:同“乾”,在《易经》当中,乾卦代表天,代表宇宙万物运转的规律,是最崇高的正向能量和精神,遵循这个重要的涵义,我们将比特币生态当中首个去中心化稳定币命名为 QIAN。 QIAN 由The Force Protocol团队所开发,是原力金融生态的重要成员,在比特币 RSK 侧链和以太坊网络内流通,可以被创造(mint)也可以被销毁(burn),用于借贷、投资、支付、储值等应用场景。
FOR:The Force Protocol生态代币,也是 QIAN 系统治理代币,用于对 QIAN 生态治理投票和维持 QIAN 价格稳定。
QIAN is generated by the user pledging cryptoasset to the smart contract, at the initial stage, the system will require pledge rate (the pledge value / generated QIAN value) to be no less than 120%. The initial underlying assets will be dominated by cryptocurrencies such as BTC and ETH. After a certain period of stable operation, the system will consider incorporating cryptoassets such as offline asset tokens with strong consensus as collateral. Considering the high volatility and high correlation of these token assets, excess assets will be required to be pledged.
For each type of cryptoasset, the core parameters of the system configuration include:
- Minimum pledge rate: Below this pledge rate will trigger the system mandatory clearing process;
- Maximum coinage: refers to the maximum amount of QIAN that can be generated in the system for specific cryptoassets;
- Liquidation fines: The proportion of pledges that are punishable by the system when the specific pledge rate is lower than the minimum pledge rate. Generally speaking, the higher the volatility of the cryptoassets, the higher the liquidation penalty.
In order to avoid QIAN price fluctuations, diversify risks and improve stability, the QIAN system will select pledges from mainstream cryptocurrency and tokenized assets, including but not limited to: asset type, market value, liquidity, volatility, issuer, issue area, etc. Since QIAN is a decentralized system, everyone is free to participate in casting QIAN. Therefore, the QIAN system's cryptoassets portfolio management has a flexible portfolio management strategy, the system does not deliberately maintain the ratio of each cryptoasset in the system. However, as mentioned earlier, the system will set the maximum coinage for different cryptoassets, the low volatility cryptoassets will have higher maximum coinage.
QIAN 由用户向智能合约质押加密资产生成,初始阶段系统将要求质押率(质押物价值/QIAN 价值比率)不得低于120%。初期的底层资产将以 BTC、ETH 等加密数字货币为主,待系统稳定运作一定时期后,将考虑纳入具备共识的线下资产 token 等加密资产作为发行抵押物。考虑到 token 类资产的高波动性和高相关性,将要求超额质押该类资产。
对于每一种加密资产,系统配置的核心参数包括:
- 最低质押率:低于该质押率将触发系统强制清算流程;
- 最高铸币量:指该类加密资产在系统中所能铸造QIAN的最大量;
- 清算罚金:当质押率低于最低质押率后由系统罚没的质押物比例,通常而言,加密资产的波动率越高,清算罚金越高。
为了避免 QIAN 的价格波动,分散风险,提升稳定性,QIAN 系统将从主流加密数字货币和 token 化资产中选择质押物,选择的指标包括但不限于:资产类型、市值、流动性、波动率、发行主体、发行地区等。由于 QIAN 是一个去中心化的系统,人人皆可自由参与铸造 QIAN。因此,QIAN 系统的加密资产组合管理是一个弹性较大的组合管理策略,系统并不刻意维持各加密资产在系统中所占的比率。但是,如前文所述,系统将为不同加密资产设置最大铸币量,低波动性的加密资产将拥有更高的最大铸币量。
In order to maintain the development and stability of the QIAN ecosystem, the pledge of cryptoassets to cast QIAN will likely generate interest. Interest is a mechanism for adjusting the supply of stablecoins. Interest could be paid in two ways. This decision will be determined by an automatic algorithm.
When the algorithm determines that it needs to improve the system's risk tolerance, the payment direction of interest is paid by the QIAN creators to the system, the interest can be paid in FOR or QIAN, the interest will be converted into FOR, and locked in smart contract; When the QIAN system needs to encourage the mints to increase QIAN liquidity, the interest payment direction will be paid to the QIAN creators by the system, and the interest is paid by the unlocked FOR from smart contract.
The system will support QIAN holders to redeem equivalent cryptoassets at their market prices with 1 QIAN = 1 USD, which is the primary mechanism for securing QIAN prices. Any deviation from the stable exchange rate will cause the price to return due to the existence of arbitrage participants.
The redemption mechanism becomes complicated when the QIAN system supports multiple cryptoassets. In theory, QIAN holders can redeem any pledge in the system. However, in order to maintain the relative stability of the system's cryptoassets portfolio, certain restrictions need to be added on the basis of satisfying users to redeem any pledged assets at any time. Our solution is that when users redeem cryptoasset, the system dynamically displays the redeemable amount supported by each cryptoasset in real time, users redeem the cryptoasset according to the restriction will not significantly change the distribution of the cryptoassets in the entire system.
The redeemable amount of each cryptoasset is always in dynamic change. In the QIAN system, the adjustment mechanism for the redeemable amount of each cryptoasset goes through two stages.
At the beginning of the multi-asset collateral system, we will introduce a systemic parameter - redemption adjustment factor α (determined by community vote, for instance, α can be 5%), we assume the original portion of pledge assets i 's value in the system (converted to QIAN) is Wi, and the real proportion after redemption is wi, then the redeemable amount needs to be met: for any asset i in the system,
Wi (1-α) ≤ wi ≤ Wi (1+α)
Wi will be updated every time a pledged asset is added, quit or cleared, but Wi will not be updated when redeemed.
By introducing the adjustment factor, it can be ensured that the proportion of various underlying assets is in a healthy change interval. However, when a certain underlying asset reaches the maximum redemption amount, the user who needs to be redeemed can only wait for other users to pledge the asset to the system. This type of asset will undoubtedly affect the liquidity of the system and will not solve the problem fundamentally. Therefore, this strategy can only be adopted at the beginning of the system and when the overall business scale is still small.
In the second phase, we will adopt a dynamic interest rate adjustment mechanism for the redemption and pledge operations of each underlying asset. First, the redemption limit for each type of asset will remain. In order for the underlying asset to maintain a healthy pledge rate, when the redeemable amount of any asset i in the system is close to Wi (1-α), the system will pay interest in FOR to the operation of casting QIAN with asset i pledge to stimulate more behavior on casting QIAN and maintain asset i's pledge amount.
The crypto asset redemption mechanism may bring problem, due to the randomness of assets type redeemed by the QIAN holder, in the extreme case, the remaining assets of the system may not enough to repay the mint of the original pledge cryptoasset. Under such circumstances, the system unlocks (unlock) FOR token and replenishes the difference by auction. In addition, the system will charge a certain fee for redemption.
为了维持 QIAN 生态的发展和稳定,质押加密资产铸造 QIAN 将可能产生利息。利息是调整稳定币供应量的一种机制,利息是双向支付的,这个决策将由自动算法决定。
当算法认为 QIAN 系统应该提升系统整体风险承受能力时,利息的支付方向是 QIAN 铸造者支付给系统,支付的利息可以是 FOR 或者 QIAN,利息将全部转换成 FOR,并锁定(lock);当系统认为 QIAN 系统应该激励铸币者以提升 QIAN 流通量时,利息的支付方向是系统支付给 QIAN 铸造者,支付的利息为解锁出的 FOR 。
系统将支持QIAN持有者以 1 QIAN = 1 USD 按市场价格赎回等值的加密资产,这是保障 QIAN 价格稳定的主要机制。任何对稳定汇率的偏离,都将会因为套利参与者的存在而使得价格回归。
当 QIAN 系统支持多种加密资产时,赎回机制将变得复杂。理论上,QIAN 持有者可赎回系统中的任何质押物。但是,为了维持系统加密资产组合的相对稳定,在满足用户随时赎回任何质押资产的基础上,需要增加一定的限制。我们的方案是,当用户赎回加密资产时,系统实时动态呈现各加密资产支持的可赎回量,用户按该限制赎回加密资产将不会大幅改变整个系统加密资产的分布情况。
各种加密资产的可赎回量始终处在动态变化中,在 QIAN 系统,对于各部分加密资产可赎回量的调整机制会经过两个阶段。
在多资产抵押系统上线初期,我们将引入一个系统参数——赎回调整因子 α (由社区投票确定,比如 α 可为5%),我们假设质押资产 i 在系统中的原始资产价值占比(换算成 QIAN )为 Wi,赎回后真实占比为 wi,则可赎回量需要满足:对于系统中任意资产 i,
Wi (1-α) ≤ wi ≤ Wi (1+α)
其中,Wi 在每次质押资产新增、退出或清算时更新计算,但赎回不更新计算。
通过引入调整因子,可以保证各种底层资产的占比处在健康的变化区间内,然而,当某种底层资产达到最大赎回量之后,还需要赎回的用户只能等待有用户向系统质押该类资产,这无疑会影响系统的流动性,没有从根本上解决问题,因此这种策略只能在系统初期,整体业务规模还不大的时候采用。
在第二阶段,我们将对每种底层资产的赎回、质押操作采取动态利率调节机制。首先,各类资产的赎回量限制将会保留,为了让底层资产保持健康的质押率,当系统中任意资产 i 的可赎回量接近 Wi (1-α) 时,系统将会对质押 i 铸造 QIAN 的操作支付 FOR 利息,以刺激更多的铸 QIAN 行为,维持 i 的质押量。
加密资产可赎回机制可能会带来这样的问题,由于 QIAN 持有者赎回的资产类型存在随机性,在极端情况下,系统剩余资产不足够偿还原始质押加密资产的铸币者,此时,系统将解锁(unlock)治理代币 FOR 并通过拍卖的形式补齐差额。此外,系统将对赎回收取一定手续费。
The system needs to obtain external prices in real time to monitor changes in pledge rates for timely liquidation and risk control. Oracle provides timely external price information for the system, including the stablecoin QIAN, the governance token FOR and the pledged token. In the absence of a mature decentralized oracle solution, the system maintains a whitelist of price feeding addresses which are added or deleted by community governance voting. Each price feeding includes price information and expiration time, the system calculates the median of all valid price feedings as the final price. After the industry-recognized oracle plan is invented, the system will switch to the corresponding decentralized oracle to ensure a fair, open and transparent price feeding mechanism.
When the user's pledge rate is lower than the minimum requirement, the pledge assets will be liquidated. However, when the price of the pledged assets falls rapidly, the system may not be liquidated in time; in addition, the system will charge or pay interest, collect asset withdrawal fees, clearing fees, and so on. Therefore, the system may have a surplus or loss. It is necessary to introduce an external trading platform to realize the bidding transaction between QIAN, FOR and the pledged assets.
系统需要实时获取外部价格以监控质押率的变化,以便及时清算,控制风险。预言机为系统提供及时的外部价格信息,包括稳定币 QIAN 、治理代币 FOR 及质押代币。在没有成熟的去中心化预言机解决方案时,系统将维护一个喂价地址白名单,该白名单由社区治理投票新增或去除。每个喂价都包含价格信息和价格有效期,系统从所有有效喂价中计算出中位值作为最终价格。在有了行业普遍认可的预言机方案之后,系统将会切换到对应的去中心化预言机,以保证喂价机制的公平、公正、公开、透明。
当用户的质押率低于最低要求时,其质押资产将被清算处理。然而,当质押资产价格下跌迅速时,系统可能清算不及时;此外,系统会收取或支付利息,收取提现手续费,清算费等。因此,系统可能出现盈余或者亏损。这时,就需要引入外部交易平台,实现 QIAN、FOR 和质押资产之间的竞价交易。
The platform will eventually be completely handed over to community governance. The main players in the platform include the QIAN creator, the QIAN holder and the holder of the governance token FOR. The purpose of platform governance is to balance the interests of all participants and maintain a stable and sustainable development of the system on the basis of certain trade-offs.
The main risk that the QIAN creator takes in the system is the liquidation risk caused by the price falling of the pledged assets. The benefits which QIAN creator enjoys include obtaining liquidity or gaining leverage. Based on research on similar projects in the industry, we believe that QIAN's casting should be encouraged within a reasonable risk range, which is beneficial to the development of the QIAN system, so we have designed an adjustable interest mechanism.
The core claim of QIAN holders is their exchange rate stability, so we designed the function to redeem equivalent pledge asset at any time.
The FOR holder will be responsible of the final benefit or risk of the entire system. The management of QIAN system is determined by the vote of FOR holder. The voted proposal can modify the internal management variables of the QIAN platform, which including but not limited to:
- Add new pledged asset
- Choose a trusted oracle
- Adjust interest
- Adjust the withdrawal fee
- Risk parameters: debt ceiling, liquidation ratio, stabilization fee, penalty ratio
平台最终将会完全移交给社区管理。平台的主要参与者包括 QIAN 铸造者,QIAN 持有者及治理代币 FOR 的持有者。平台治理的目的在于平衡所有参与者的利益关系,在一定权衡和取舍的基础上,维持系统的稳定和持续健康发展。
QIAN 铸造者在系统中主要承担的风险是质押资产价格下跌导致的清算风险,享受的利益包括获得流动性或获得杠杆。基于对行业中类似方案的研究,我们认为,在合理的风险范围内,QIAN 的铸造应该是被鼓励的,这有利于 QIAN 系统的发展,所以我们设计了可调整的利息机制。
QIAN 持有者的核心诉求在于其汇率稳定性,因此我们设计了随时可赎回等值质押资产的功能。
FOR 持有者将是整个系统最后收益或风险的承担者。平台的管理是通过 FOR 持有者进行投票确定的,被投票选中的提案可以修改 QIAN 平台的内部管理变量,这些变量包括但不限于:
- 增加新的质押资产
- 选择可信任的预言机
- 调整利息
- 调整提现手续费
- 风险参数:债务上限、清算比率、稳定费用、罚金比例
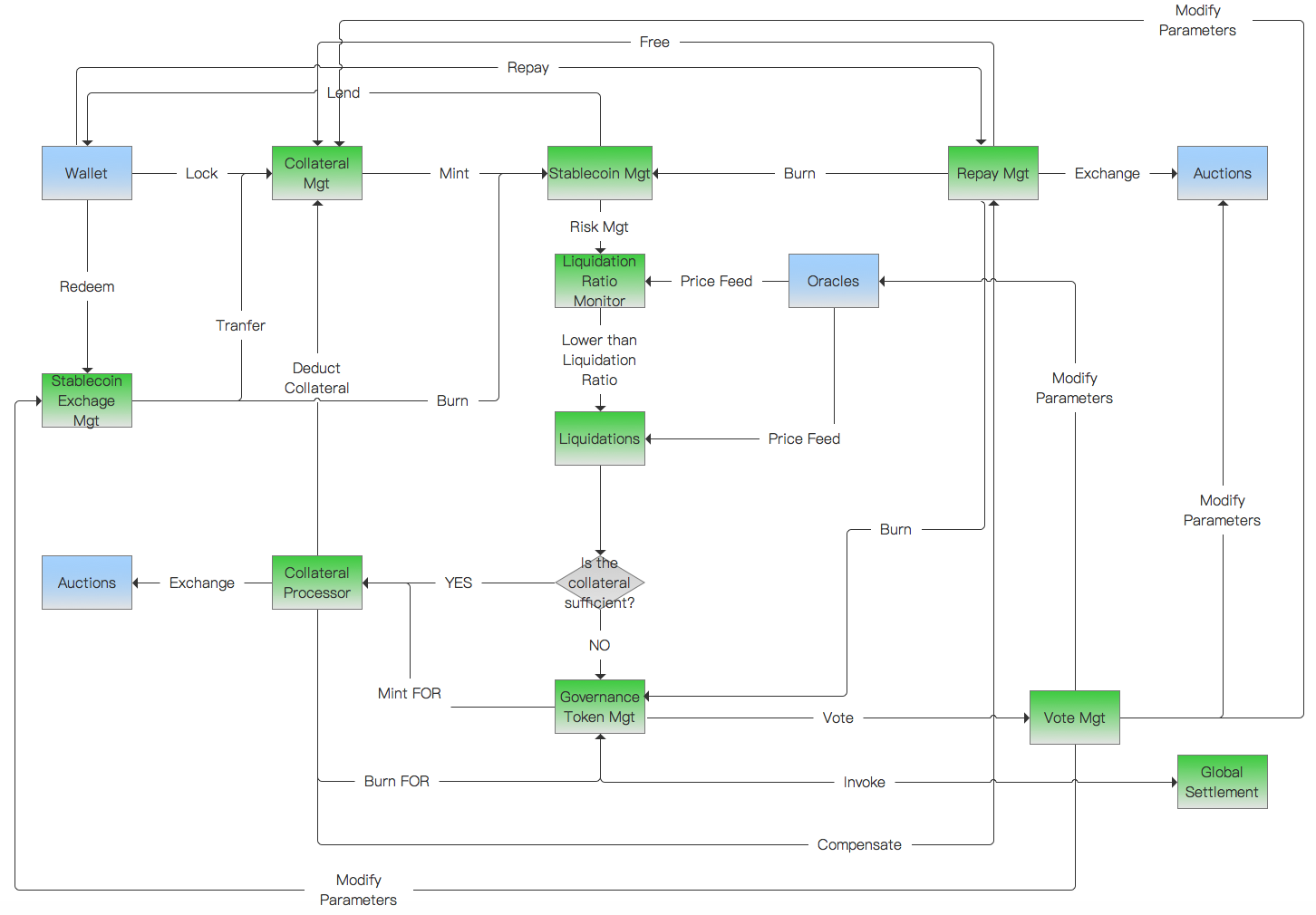
External system
User Wallet: User's Blockchain Wallet.
Oracle: Provides market price of pledge, stablecoin and governance token.
Trading platform: Provides exchanges or auctions of pledges, stablecoin and governance token.
Internal system
Pledge Manager: Provides functions such as pledge locking, unlocking, and parameter configuration, etc.
Stabilized Coin Manager: Provides stablecoin generation, destruction and other functions.
Repayment processor: Provides function of repayment, settlement of debt, etc.
Pledge rate monitor: Calculate the pledge rate at regular intervals, trigger the replenishment reminder, force liquidation, etc.
Liquidator: Calculate the debt situation, the amount of pledges required, etc.
Pledge processor: Responsible for raising pledges and performing redemption, calling reimbursement, etc.
Governance Token Manager: Provides functions such as lock and unlock of governance token.
Governance Voter: Initiate or participate in community governance voting and modify system parameters based on voting results.
Stablecoin Redemption Manager: Responsible for converting the stablecoins into the equivalent of pledges with 1 QIAN = 1 USD.
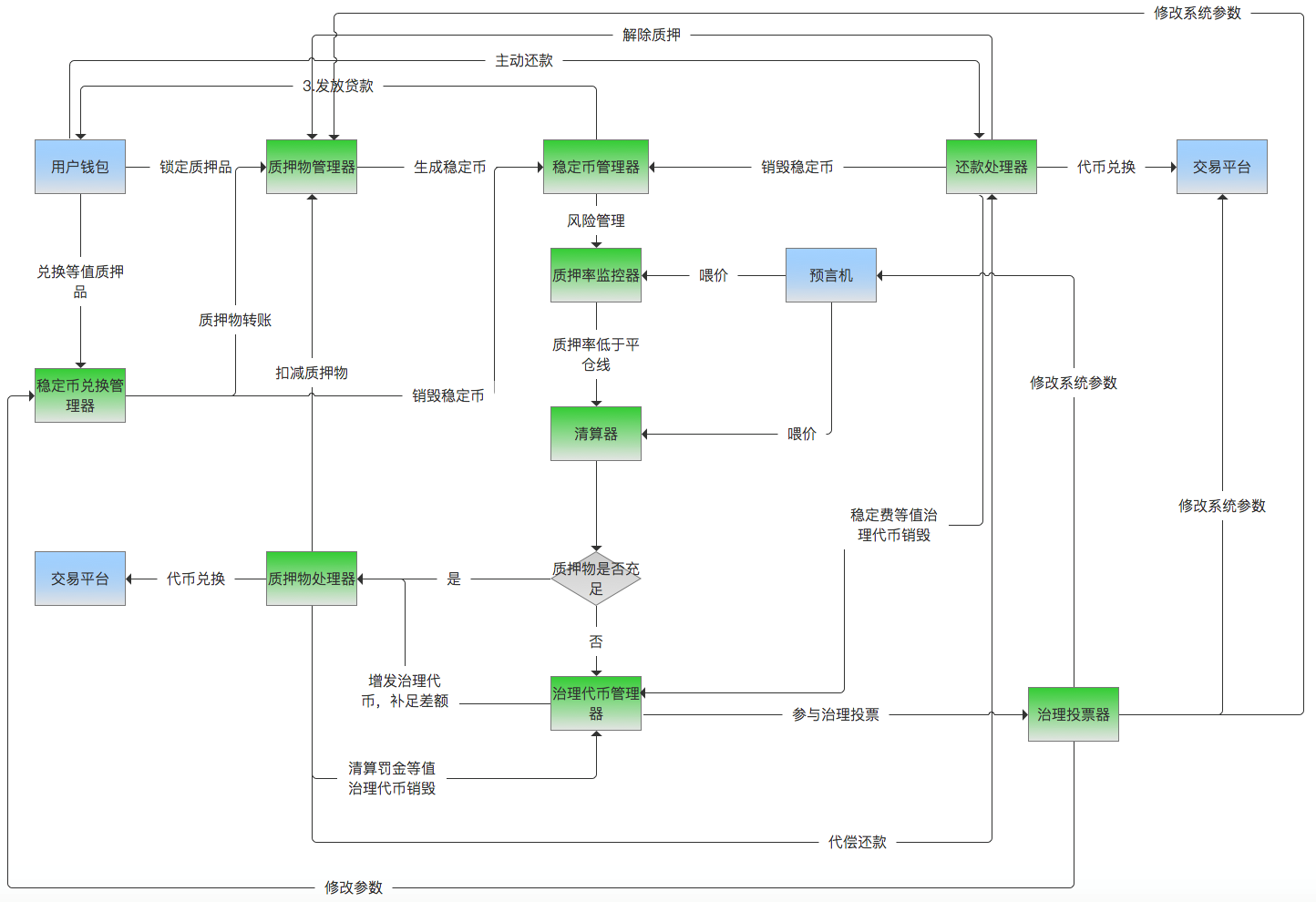
外部系统
用户钱包:用户区块链钱包。
预言机:提供质押物、稳定币、治理代币市场价格。
交易平台:提供质押物、稳定币、治理代币相互之间的兑换交易或者拍卖。
内部系统
质押物管理器:提供质押物锁定、解锁、质押物参数配置等功能。
稳定币管理器:提供稳定币生成、销毁等功能。
还款处理器:处理还款,结清债务。
质押率监控器:定时计算质押率,触发补仓提醒、强制平仓等。
清算器:计算债务情况,需要质押品数量等。
质押物处理器:负责筹集质押物并执行兑换,调用代偿还款等。
治理代币管理器:提供治理代币锁定、解锁等功能。
治理投票器:发起或参与社区治理投票,并根据投票结果修改系统参数。
稳定币兑换管理器:负责将稳定币按 1 QIAN = 1 USD 兑换出等值的质押物。
In the early days, QIAN will firstly develop on RSK and Ethereum. In the follow-up, we will migrate the QIAN system to the Force Protocol financial application public blockchain to build a stable currency system that truly supports the pledge of multiple cryptoassets. The Force Protocol financial application public blockchain may partly develop based on Tendermint Core and COSMOS SDK, and has a distributed financial application consensus mechanism originally developed by The Force Protocol team to support asset cross-chain circulation and large-scale distributed financial applications.
The QIAN system code will also maintain a fully open-source strategy and will gradually integrate into the financial open platform of The Force Protocol, becoming part of The Force Protocol financial application development architecture, providing technical service to teams around the world which wish to create a decentralized stablecoin system, eventually create a global open cryptocurrency market.
初期, QIAN 将优先在 RSK 和以太坊上搭建。后续,我们会将 QIAN 系统迁移至The Force Protocol金融应用公链,以搭建真正支持多加密资产质押的稳定币系统。The Force Protocol金融应用公链计划部分基于 Tendermint Core 和 COSMOS SDK 开发,同时具备The Force Protocol团队原创的分布式金融应用共识机制,可以支持资产跨链流通和大规模的分布式金融应用开展。
QIAN 系统的代码也将保持全部开源的策略,并会逐步融入The Force Protocol的金融开放平台,成为The Force Protocol金融应用开发架构的一部分,为更多希望创造去中心化稳定币系统的团队提供技术服务,最终创造出一个全球化的开放加密数字货币市场。
-
Contains all the script files involved in The Force Protocol stablecoin system, in which
- The deployment-related file name is "deploy*"
- Compiler "solcc",
- Tool for merging multiple source files then outputting, "solcm",
- Scripts for modifing system parameters: debtor_tdc, testoken_approve, feeder_set, ctoken_*, ...
- Export script "export", responsible for exporting the contract address generated after the deployment is completed.
- Makefile, the working principle of the Makefile script is naturally suitable for the scenario where there is a dependency between the files. In this project, the Makefile is used to build the dependencies between the modules (contracts) and the dependencies between the bin/abi files and the source code. For example,
debtordepends onstablecoin,debtor.sol, so whenstablecoinis redeployed ordebtor.solis modified,debtoralso needs to be redeployed. - rt, the original meaning of rt is "runtime", which is a tool library that provides underlying support for all other scripts. For example: provides web3 objects, provides yargs parameter parsing objects, provides configuration file object parsing, etc.
-
The default deployment output file directory.
Every time a module (contract) is successfully deployed, a file with the same name will be generated in this directory. The file content is the address of the contract being deployed.
-
The default abi/bin build directory.
Each sol source code will be compiled to generate a corresponding .bin and corresponding .abi files, which are stored in this directory.
-
Contains all contract source code for The Force Protocol stablecoin.
- approval.sol: the voting contract, which is also an authority, voting target can be a proposal or an account. Address which wins the vote will have the authority to modify the system state.
- arith.sol: special math function library.
- authority.sol: system permissions management contract.
- collateral.sol: contract provides function for listing and redeeming of collaterals.
- debtor.sol: debt manager contract.
- ceth.sol: the contract with ETH as collateral, is a derived class of collateral.sol.
- feeder.sol: price feeder contract.
- govtoken.sol: FOR governing token packaging.
- stderc20.sol: ERC20 standard implementation.
- stablecoin.sol: stablecoin token contract, is a derivative contract of stderc20.sol.
- ctoken.sol: the contract with ERC20 as collateral, is a derivative contract of collateral.sol.
- virtualwallet.sol: virtual wallet contract, temporarily considered to be used to modify the bidder's asset holding status at auction, the bidder needs to first recharge to the virtual wallet.
-
- src/ Contains contract method wrappers that all front ends need to call.
- res/ Contains resources such as all module deployment address files (deployed.json) and configuration files that are exported.
- abi/ Contains abi files for all modules.
- test/ Test script.
-
Configuration file for "kovan" test network. Other supported network configuration files are also available, such as "rinkeby.json" for configuring the rinkeby test network.
-
Main deployment tool
dtool <deploy|clean> [--argument | --argument value]
- With no parameters, deployed according to the results of the Makefile decision, may not be redeployed, or may be completely redeployed.
- --all, [optional] forced redeployment
- --feeder|stablecoin|govtoken|debtor|ethcoll|tokencoll, [optional] forced redeployment of a module and modules that depend on it.
- --network kovan|rinkeby|rsk|main|..., [required] the network name must be specified.
- With no parameters, clear all abi/bin files and deploy output files.
- --feeder|stablecoin|govtoken|debtor|ethcoll|tokencoll [required] merge and output the source code of the module (for upload to etherscan.io)
- --feeder|stablecoin|govtoken|debtor|ethcoll|tokencoll [required] the deployment address of the output module.
- --network kovan|rinkeby|rsk|main, [required] the network name must be specified.
- --script-name [arguments...], [required] a proxy to execute the script, for example:
dtool exec --network kovan feeder_set -t TES
Equals to execute
export RT_PRIK="0X..." && feeder_set -t TES -c kovan.js
Or
export RT_PRIK="0x..." && export RT_CONF="kovan.js" && feeder_set -t TES
-
包含稳定币系统中涉及的所有脚本文件, 其中
- 部署相关的文件名为 "deploy*"
- 编译器 "solcc",
- 用于合并多个源代码文件并输出的工具, "solcm",
- 修改系统参数的脚本: debtor_tdc, testoken_approve, feeder_set, ctoken_*, ...
- 部署导出脚本 "export", 用于导出部署完成后产生的合约地址.
- Makefile, 由于Makefile脚本的工作原理, 天然的适合于构建文件间存在依赖关系的场景。这里用于构建模块(合约)间的依赖关系以及bin/abi文件与源码的依赖关系, 比如,
debtor依赖于stablecoin,debtor.sol, 所以当stablecoin被重部署后或者debtor.sol被修改后,debtor也需要被重新部署. - rt 最初的意义是 "runtime", 它是一个为其他所有脚本提供底层支持的工具库. 比如: 提供web3对象, 提供 yargs 参数解析对象, 提供配置文件对象解析, ...
-
默认部署输出文件目录.
每成功部署一个模块(合约), 就会有一个相同的名称的文件产生在这个目录中. 文件内容为被部署的合约的地址.
-
默认的abi/bin生成目录.
每个sol源代码都会对应编译生成一个相应的.bin和相应的.abi文件, 这些文件被存放在这个目录中.
-
包含稳定币的所有合约源代码.
- approval.sol:投票合约, 同时也是一个 authority, 被投票的可以是提案或者账户, 投票胜出的地址将有权限修改系统状态.
- arith.sol:专用数学函数库.
- authority.sol:系统权限管理合约.
- collateral.sol:提供抵押物加入和兑换功能的合约
- debtor.sol:系统债务管理器合约
- ceth.sol:以ETH作为抵押物的合约, 是 collateral 的派生类.
- feeder.sol:喂价器合约
- govtoken.sol:FOR治理代币封装.
- stderc20.sol:ERC20 标准实现.
- stablecoin.sol:稳定币token合约, 是 stderc20 的派生合约.
- ctoken.sol:以ERC20作为抵押物的合约, 是 collateral 的派生合约.
- virtualwallet.sol:虚拟钱包合约, 暂时考虑是用作拍卖时修改出价人的资产持有状态, 竞拍者需要先充值到虚拟钱包.
-
- src/ 包含所有前端需要调用的合约方法封装.
- res/ 包含被导出的所有模块部署地址文件(deployed.json)和配置文件等资源.
- abi/ 包含所有模块的abi文件.
- test/ 测试脚本
-
配置文件, 适用于"kovan"测试网. 也可以提供其他支持的网络配置文件, 比如 "rinkeby.json" 用于配置rinkeby 测试网.
-
主部署工具
dtool <deploy|clean> [--argument | --argument value]
- 无参数, 根据Makefile判断的结果来部署, 可能一个都不会重新部署, 可能全部重新部署.
- --all, [可选] 强制重新部署
- --feeder|stablecoin|govtoken|debtor|ethcoll|tokencoll, [可选] 强制重新部署某一个模块及依赖它的模块.
- --network kovan|rinkeby|rsk|main|..., [必要] 必须指定网络名
- 无参数, 清空所有的abi/bin文件和部署输出文件
- --feeder|stablecoin|govtoken|debtor|ethcoll|tokencoll [必要] 合并并输出模块的源码(用于上传 etherscan.io)
- --feeder|stablecoin|govtoken|debtor|ethcoll|tokencoll [必要] 输出模块的部署地址.
- --network kovan|rinkeby|rsk|main, [必要] 必须指定网络名
- --script-name [arguments...], [必要] 代为执行脚本, 例如
dtool exec --network kovan feeder_set -t TES
等同于执行
export RT_PRIK="0X..." && feeder_set -t TES -c kovan.js
或者
export RT_PRIK="0x..." && export RT_CONF="kovan.js" && feeder_set -t TES