Modern applications require developing code in different platforms and tools, leveraging the need of a mechanism to integrate and validate its changes. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) embody a culture, set of operating principles, and collection of practices that enable application development teams to deliver code changes more frequently and reliably.
The goal of CI is to establish a consistent and automated way to build, package, and test applications. With consistency in the integration process in place, teams are more likely to commit code changes more frequently, which leads to better collaboration and software quality. Most teams work with multiple environments other than the production, such as development and testing environments, and CD ensures there is an automated way to push code changes to them.
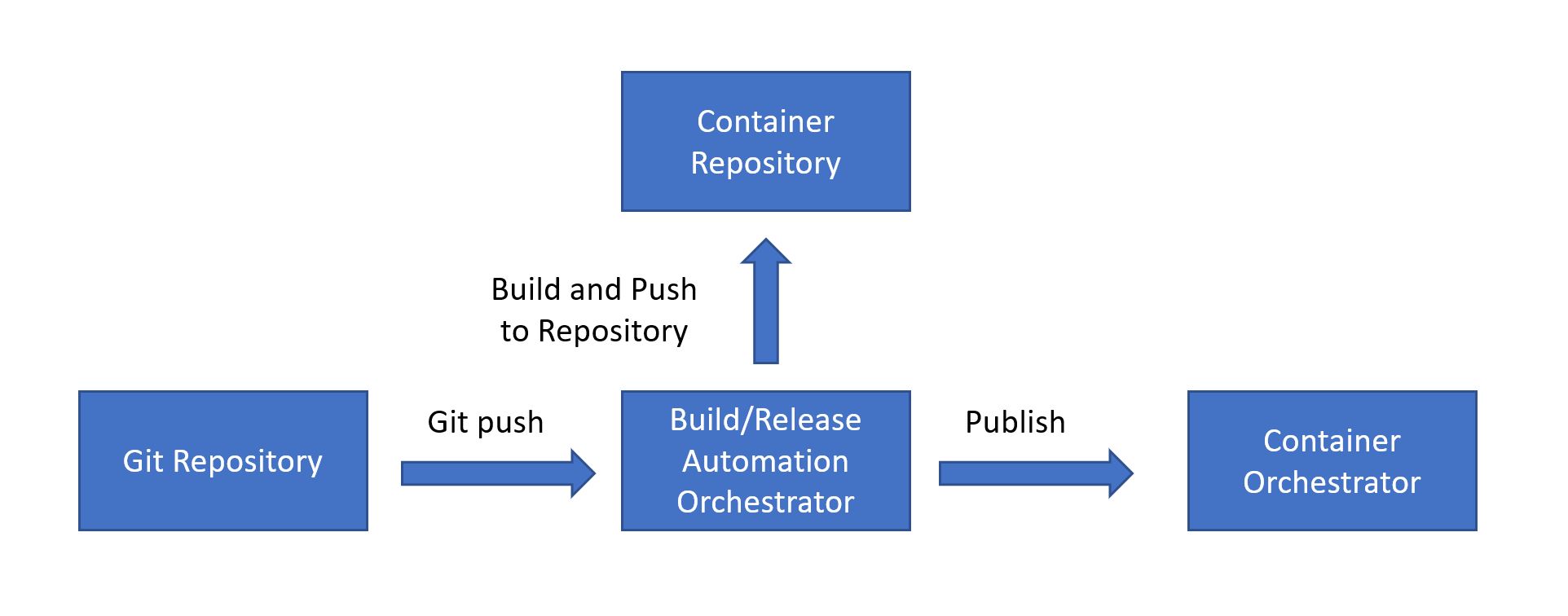
This pattern aims to define a general CI/CD pipeline for scalable solutions that require containers orchestration using Jenkins and AKS.
The image above is a generic architecture overview that can be implemented using different technologies and services. In this document we are describing the steps to set up a Jenkins server connected to a Kubernetes Cluster to receive the deployments. These are the services used for implementation:
- GitHub as the git repository;
- Jenkins as the build/release automation orchestrator server;
- Azure Container Registry as the container repository;
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) as container orchestrator.
We provided two different ways to create the necessary resources on your Azure Subscription:
- Manualy: You have to create all the resources needed, using arm templates, powershell or the Azure portal
- Using Terraform that will create the resources needed, Jenkins Server and AKS
To get started, deploy a jenkins VM by following this guide. After the Jenkins server is deployed, login and execute az login and set your desired subscription. If the azure cli is not installed on the machine, you may need to run azure-cli-install.sh. Once you have completed the az login process, run setup.sh on the jenkins server to deploy a k8s cluster and install all required server dependencies.
You will need to have Terraform installed on a client machine (not the server). You will also need to install the Azure-Cli and configure with az login. Verify that you are connected to the right subscription using az account list -o table. See az account for more information.
Terraform needs to be installed on either Windows and Linux. Here we are covering the usage of Linux as you can use WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux). The script we have provided checks if Terraform is available on your system, and will install it if not.
Run the script create_azure_resources.sh, this script will do the following:
- Create an Azure Resource Group
- Create a Virtual Network
- Create a Subnet
- Create a Public IP Address
- Create a Network Interface attached to the subnet and using the Public IP Address
- Create a Network Security Group, with two rules Allow SSH (over port 22)and Allow Http (over port 8080)
- Create an Ubuntu Server
- Create an Azure Kuberntes Service
The items above will be create by Terraform, using the following commands.
#terraform will create the Jenkins VM, AKS Cluster and set the jenkins vm to use the AKS Cluster.
#Initialize terraform project
terraform init
#Apply the changes, we are using a secrets.tfvars to provide sensitive information
terraform apply -var-file=secrets.tfvarsThe other part of the script will setup the Linux Server, installing:
- Java VM
- Jenkins
- Kubectl
- Helm
for that we are using
ssh `eval terraform output admin_username`@`eval terraform output jenkins_pip` 'bash -s' < ../../scripts/setup_jenkins.shAfter completing the steps above, if you wish to use the sample Jenkinsfile in a Jenkins pipeline, start by creating an Azure container registry by following this guide. Once created, replace the values in the Jenkinsfile KUBE_CONTEXT (set to value of: k8sClusterName from setup.sh). Next, create a Global Credential in Jenkins for ACR_ID, ACR_LOGINSERVER, and ACR_PASSWORD and supply the appropriate values respectively. Finally, create a new pipeline project and copy over the contents of the modified Jenkinsfile. You should be able to successfully deploy the azure-voting-app-redis helm chart to your K8s cluster by kicking off a build of your new pipeline project.
Next, run the following on the jenkins server to add a secret for pulling your image from ACR to your k8s deployment:
kubectl create secret -n azure-voting-app-redis docker-registry regcred --docker-server=$ACR_LOGINSERVER --docker-username=$ACR_ID --docker-password=$ACR_PASSWORD [email protected]
To verify your deployment is accessbile over the internet, run:
kubectl get --all-namespaces svc
You should see an output similar to:
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
azure-voting-app-redis azure-vote-back ClusterIP 10.0.107.198 <none> 6379/TCP 24m
azure-voting-app-redis azure-voting-app-redis LoadBalancer 10.0.33.36 40.121.149.238 8080:31797/TCP 24m
default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 1h
kube-system heapster ClusterIP 10.0.123.33 <none> 80/TCP 1h
kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.0.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 1h
kube-system kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.0.248.20 <none> 80/TCP 1h
kube-system tiller-deploy ClusterIP 10.0.94.105 <none> 44134/TCP 57m
In this case, our service would be accessbile at http://40.121.149.238:8080
Azure resources:
- Jenkins VM
- Service Principal
- Azure Container Registry
- AKS (Kubernetes Cluster)
Server Dependencies:
- Docker
- Kubectl
- helm
- JQ
- Azure Cli
Creating Azure Container Registry
Install azure-cli
AZ_REPO=$(lsb_release -cs)
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/azure-cli/ $AZ_REPO main" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/azure-cli.list
curl -L https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y azure-cli
Install Docker
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com | sudo -E sh
Add jenkins user to Docker Group
sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins
Restart jenkins service
sudo service jenkins restart
(Optional) - test that the jenkins user has sufficient permissions for docker
sudo su jenkins
docker info
#if previous command is successful
exit
Install kubectl
az login
sudo az aks install-cli
(Optional) - test that kubectl is available in PATH
kubectl version
Get Azure Kubernetes Service configuration for admin and jenkins user
az login
az aks get-credentials --resource-group={RESOURCEGROUP} --name={CLUSTERNAME}
sudo su jenkins
az aks get-credentials --resource-group={RESOURCEGROUP} --name={CLUSTERNAME}
exit
(Optional) verify.kube/config exists in /var/lib/jenkins
cat /var/lib/jenkins/.kube/config
Install Helm
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-helm/helm-v2.9.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xzvf helm-v2.9.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
Initializing Helm
#When installing Tiller, 'helm init' will attempt to install the latest released version. You can specify an alternative image with '--tiller-image' or -i
#To install a specific version of Tiller use `helm init -i gcr.io/kubernetes-helm/tiller:vX.X`.
#To install latest version of Tiller use the syntax below:
sudo helm init
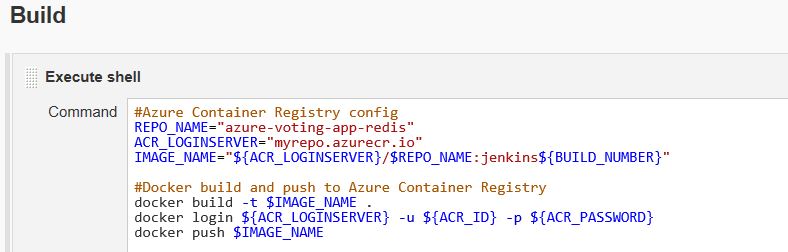
#Azure Container Registry config
REPO_NAME="azure-voting-app-redis"
ACR_LOGINSERVER="myrepo.azurecr.io"
IMAGE_NAME="${ACR_LOGINSERVER}/$REPO_NAME:jenkins${BUILD_NUMBER}"
#Docker build and push to Azure Container Registry
docker build -t $IMAGE_NAME .
docker login ${ACR_LOGINSERVER} -u ${ACR_ID} -p ${ACR_PASSWORD}
docker push $IMAGE_NAME
#HELM config
NAME="azure-voting-app-redis"
HELM_CHART="./helm/azure-voting-app-redis"
#Kubenetes config (for safety, in order to make sure it runs in the selected K8s context)
KUBE_CONTEXT="jenkinsupskillingcluster"
kubectl config --kubeconfig=/var/lib/jenkins/.kube/config view
kubectl config set-context $KUBE_CONTEXT
#Helm Deployment
helm --kube-context $KUBE_CONTEXT upgrade --install --force $NAME $HELM_CHART --set image.repository=${ACR_LOGINSERVER}/$REPO_NAME --set image.tag=jenkins${BUILD_NUMBER}
#If credentials are required for pulling docker image, supply the credentials to AKS by running the following:
#kubectl create secret -n $NAME docker-registry regcred --docker-server=${ACR_LOGINSERVER} --docker-username=${ACR_ID} --docker-password=${ACR_PASSWORD} [email protected]
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
ACR_LOGINSERVER = credentials('ACR_LOGINSERVER')
ACR_ID = credentials('ACR_ID')
ACR_PASSWORD = credentials('ACR_PASSWORD')
}
stages {
stage ('azure-voting-app-redis - Checkout') {
steps {
checkout([$class: 'GitSCM', branches: [[name: '*/master']], doGenerateSubmoduleConfigurations: false, extensions: [], submoduleCfg: [], userRemoteConfigs: [[url: 'https://github.com/ViniciusSouza/azure-voting-app-redis']]])
}
}
stage ('Build, Lint, & Unit Test') {
steps{
//exectute build, linter, and test runner here
sh '''
echo "exectute build, linter, and test runner here"
'''
}
}
stage ('Docker Build and Push to ACR'){
steps{
sh '''
#Azure Container Registry config
REPO_NAME="azure-voting-app-redis"
ACR_LOGINSERVER="myrepo.azurecr.io"
ACR_ID="myACRid"
ACR_PASSWORD="myACRpassword"
IMAGE_NAME="$ACR_LOGINSERVER/$REPO_NAME:jenkins${BUILD_NUMBER}"
#Docker build and push to Azure Container Registry
cd ./azure-vote
docker build -t $IMAGE_NAME .
cd ..
docker login $ACR_LOGINSERVER -u $ACR_ID -p $ACR_PASSWORD
docker push $IMAGE_NAME
'''
}
}
stage ('Helm Deploy to K8s'){
steps{
sh '''
#Docker Repo Config
REPO_NAME="azure-voting-app-redis"
ACR_LOGINSERVER="myrepo.azurecr.io"
#HELM config
NAME="azure-voting-app-redis"
HELM_CHART="./helm/azure-voting-app-redis"
#Kubenetes config (for safety, in order to make sure it runs in the selected K8s context)
KUBE_CONTEXT="jenkins-k8s-azure"
kubectl config --kubeconfig=/var/lib/jenkins/.kube/config view
kubectl config set-context $KUBE_CONTEXT
#Helm Deployment
helm --kube-context $KUBE_CONTEXT upgrade --install --force $NAME $HELM_CHART --set image.repository=$ACR_LOGINSERVER/$REPO_NAME --set image.tag=jenkins${BUILD_NUMBER}
#If credentials are required for pulling docker image, supply the credentials to AKS by running the following:
#kubectl create secret -n $NAME docker-registry regcred --docker-server=$ACR_LOGINSERVER --docker-username=$ACR_ID --docker-password=$ACR_PASSWORD [email protected]
'''
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'Build Steps Completed'
}
}
}
IP_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get svc $NAME -n $NAME -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[*].ip}")
while [ $IP_ADDRESS -ne "<pending>" ]
do
IP_ADDRESS=$(kubectl get svc $NAME -n $NAME -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[*].ip}")
sleep 60s
done
PORT=$(kubectl get svc node --namespace=node -o json | jq '.spec.ports[0].port')