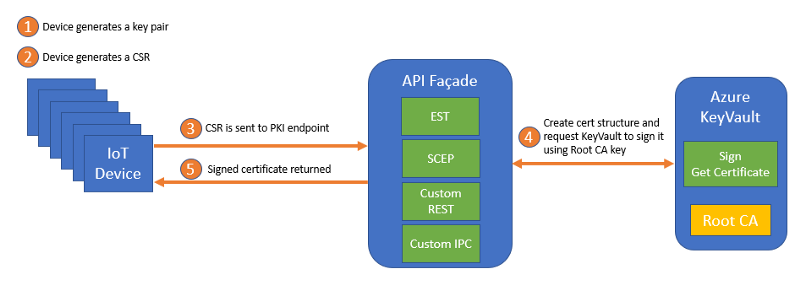
Please refer to this blog post for details.
az keyvault create --name <KEYVAULT_NAME> \
--resource-group keyvault-ca \
--enable-soft-delete=true \
--enable-purge-protection=true
Both the Console App and the Web API use the DefaultAzureCredential for accessing the Key Vault. When running locally, they will use the developer authentication and, in the cloud, managed identity.
You need to first aquire the object ID of your Azure user:
az ad user show --id <YOUR_EMAIL_ADDRESS>
and then give it accesss to the Key Vault keys and certificates:
az keyvault set-policy --name <KEYVAULT_NAME> \
--object-id <OBJECT_ID> \
--key-permissions sign \
--certificate-permissions get list update create
Note: The quickest way to setup dev environment is by opening this solution in VSCode which will allow leveraging the dev container provided in this repo.
Clone this repository. There are two projects (KeyVaultCA and KeyVaultCA.Web) containing appsettings.json files. The settings specified there can also be overridden with environment variables or command line arguments.
The following common block must be filled in, for all usages of the projects.
"KeyVault": {
"KeyVaultUrl": "<Key Vault URL>",
"IssuingCA": "<Name of the issuing certificate in KeyVault.>",
"CertValidityInDays": "<Validity period for issued certificates (maximum is 365 days)>",
"CertPathLength": "<Path length of the certificate chain which gives the maximum number of non-self-issued intermediate certificates that may follow this certificate in a valid certification path. For the Root CA certificate stored in KV, the value should be at least 1, for the others, obtained through the EST server, is sufficient to have 0.>"
}
For overriding settings from command line arguments on Linux, use a syntax similar to KeyVault__KeyVaultUrl and for Windows, KeyVault:KeyVaultUrl.
Run the API Facade like this (feel free to use your own values for the subject):
cd KeyVaultCA
dotnet run --Csr:IsRootCA "true" --Csr:Subject "C=US, ST=WA, L=Redmond, O=Contoso, OU=Contoso HR, CN=Contoso Inc"
-
First generate the private key:
openssl genrsa -out mydevice.key 2048 -
Create the CSR:
openssl req -new -key mydevice.key -out mydevice.csr
openssl req -in mydevice.csr -out mydevice.csr.der -outform DER -
Run the API Facade and pass all required arguments:
cd KeyVaultCA
dotnet run --Csr:IsRootCA "false" --Csr:PathToCsr <PATH_TO_CSR_IN_DER_FORMAT> --Csr:OutputFileName <OUTPUT_CERTIFICATE_FILENAME>
If desired, values can also be set in the Csr block of the appsettings.json.
"Csr": {
"IsRootCA": "<Boolean value. To register a Root CA, value should be true, otherwise false.>",
"Subject": "<Subject in the format 'C=US, ST=WA, L=Redmond, O=Contoso, OU=Contoso HR, CN=Contoso Inc'.>",
"PathToCsr": "<Path to the CSR file in .der format.>",
"OutputFileName": "<Output file name for the certificate.>"
}
Use the EST Façade Web API to request a certificate
DISCLAIMER: NOT all of the EST methods are implemented. It is only:
The endpoints above are used by and work with Azure IoT Edge 1.2 which supports certificate enrollment via EST.
When calling the EST endpoints for:
- generating the device identity certificate (needed for authenticating to the IoT Hub), use the URL like in the example -
https://example-est.azurewebsites.net/.well-known/est - generating the Edge CA certificate (needed for authenticating the IoT edge modules), use
caas part of the URL - e.g.https://example-est.azurewebsites.net/ca/.well-known/est.
Provide the following variables in the appsettings.json of the KeyVaultCA.Web project, which will also be used when publishing the Web API to Azure:
KeyVaultUrl- url of your KeyVault the format depending on whether it is accessible via public or private endpoint:- for a public endpoint, the format is
https://<KEYVAULT_NAME>.vault.azure.net/ - for a private endpoint with Azure built-in DNS integration, the format can be either the public url or
https://<KEYVAULT_NAME>.privatelink.vaultcore.azure.net/ - for a private endpoint with custom DNS integration, the format is
https://<KEYVAULT_NAME>.vaultcore.azure.net/
- for a public endpoint, the format is
IssuingCA- name of the certificate in the KeyVault to issue your leaf certificate.CertValidityInDays- specifies validity period for issued certificates (maximum is 365 days).Auth- Authentication mode for the EST API. Possible values are:
- Basic - add the following environment variables:
EstUsername- username for the EST endpointEstPassword- password for the EST endpoint
- x509 - via certificates
- put your trusted CA certificates into the
KeyVaultCA.Web\TrustedCAsdirectory. Make sure to specify CopyToOutput. Note that certificates downloaded from Azure Key Vault are by default encoded as a base64 string. - if you choose to publish the
KeyVaultCA.Webapp to an Azure App Service, make sure to go to Configuration -> General Setttings -> Incoming client certificates -> set Client certificate mode toRequire.
- put your trusted CA certificates into the
To ensure that the published Web API can access the Key Vault, go to the App Service that will host the KeyVaultCA.Web, click on Identity and turn on the System-Assigned one.
Then go to the Key Vault and create a new access policy for the same identity with:
- Key Permissions: Sign
- Certificate Permissions: Get, List, Update, Create.
The implementation returns the IssuingCA via the /cacerts endpoint.
Refer to this repo for details on IoT Edge configuration, including PKCS#11 and EST.
The KeyVaultCA console app uses a Console logger, for which the severity can be changed in the appsettings.json.
The KeyVaultCA.Web writes logs to an Azure Application Insights instance, for which the connection string must be added in the appsettings.json. Additionally, the logging must be turned on from the Azure portal by going to the Web App and into the Application Insights settings.
Detailed instructions for using the Terraform scripts can be found here.
When the user selects the certificate authentication mode for EST server, the code uses Header Forwarding to forward the used protocol to the App Service and ensure that the client certificate is negotiated as part of a TLS handshake. More details on the usage of header forwarding can be found here.