This git repository is only updated with new releases of fullrmc. A private repository is used for development.
FUndamental Library Language for Reverse Monte Carlo or fullrmc is a molecular/atomic stochastic fitting platform to reverse modeling experimental data. fullrmc is not a standard RMC software but exceeds in its capabilities and functionalities traditional RMC and Metropolis-Hastings algoritm. Therefore RMC appellation in fullrmc, is not accurate but it’s retained to respecting the community terminology. RMC is probably best known for its applications in condensed matter physics and solid state chemistry. RMC is used to solve an inverse problem whereby an atomic model is adjusted until its atoms position have the greatest consistency with a set of experimental data. fullrmc is a python package with its core and calculation modules optimized and compiled in Cython/c. fullrmc’s Engine sub-module is the main module that contains the definition of ‘Engine’ which is the main and only class used to launch the stochastic calculation. fullrmc is a fully object-oriented package where everything can be overloaded allowing easy development, implementation and maintenance of the code. It's core sub-package and modules are fully optimized written in cython/C. fullrmc is unique in its approach, among other functionalities:
- Atomic and molecular systems are supported.
- All types (not limited to cubic) of periodic boundary conditions systems are supported.
- Atoms can be grouped into groups so the system can evolve atomically, clusterly, molecularly or any combination of those.
- Every group can be assigned a different move generator (translation, rotation, a combination of moves generators, etc).
- Selection of groups to perform moves can be done manually OR automatically, randomly OR NOT !!
- Supports Artificial Intelligence and Reinforcement Machine Learning algorithms.
- Reserve your virtual machine(s) with the needed requirements (cpus, memory, storage) and run fullrmc using its advanced user interface.
- Features such as multiframe computing including all of the statistical, mesoscopic and nanoscopic computations are only available in the cloud version of fullrmc.
- A fullrmc virtual machines are multi-users and multi-sessions ready. The owner of the machine can allow users to sign up and run their dersired calculations.
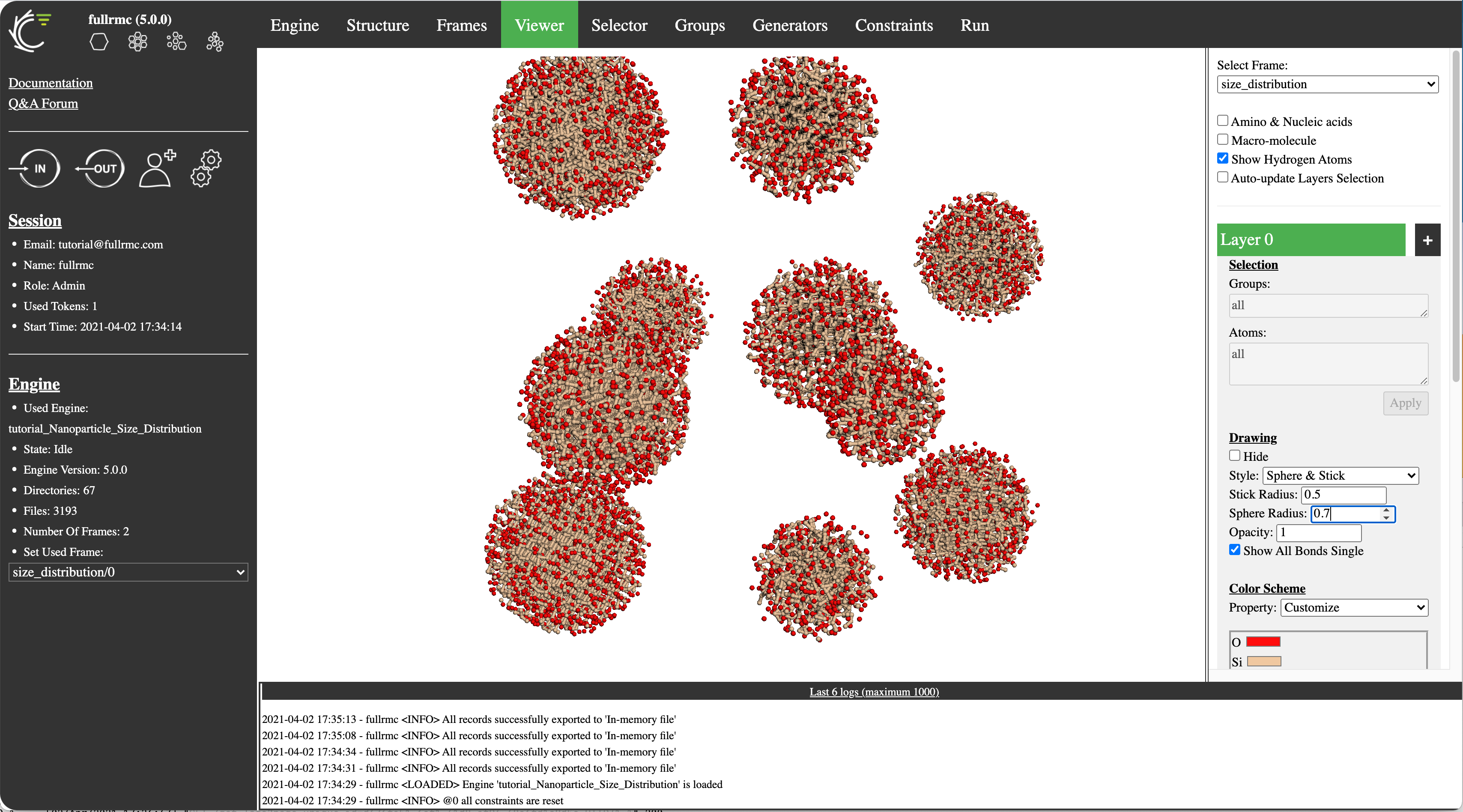
- fullrmc is now available on the cloud with an advanced user interface
- fullrmc cloud version provides additional features that are not open sourced
- Mixture models: Using multiframe meta-structure, fullrmc cloud allows to model complex systems such as multi-phase systems, distribution of nanoparticles in solution, etc.
- Statistical calculation: using the concept of multiframe, fullrmc enrichs the single box approach with the statistical approach where multiple frames can be fit simulatenously using the same or different stochastic approach
- Mesoscopic: a mesoscopic system is a fullrmc multiframe atomic system where atoms from different subframes are considered far enough from each other to have any cross correlation showing in the experimental data.
- Nanoscopic: a nanoscopic system is like a mesoscopic one but correlation between atoms from different subframes is not negligeable.
- Coarse grains: multiframe coarse grain computation is enabled in the nanoscopic meta-structure conditions.
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/fullrmc
- Python (>= 2.7 and < 3) Starting from fullrmc 4.x.y python 3 is supported
- NumPy (lowest version tested is 1.7.1)
- cython (lowest version tested is 0.21.1)
- matplotlib (lowest version tested is 1.4)
- pdbparser (lowest version tested is 0.1.2 - 0.1.3 is used starting from fullrmc 0.3.0 - 0.1.4 is used starting from fullrmc 1.0.0 - 0.1.5 is used starting from fullrmc 1.0.1 - 0.1.7 is used starting from fullrmc 4.0.0 - 0.1.8 is used starting from fullrmc 4.0.2)
- pysimplelog (lowest version tested is 0.1.7 - 0.1.4 is used starting from fullrmc 1.2.0 - 2.0.0 is used starting from fullrmc 4.0.0)
- pyrep (lowest version tested is 1.0.2 is used starting from fullrmc 2.0.0 - 1.0.3 is used starting from fullrmc 3.0.0 - 1.0.4 is used starting from fullrmc 3.1.0 - 3.1.0 is used starting from fullrmc 4.0.1 - 3.2.0 is used starting from fullrmc 4.0.2)
- pylocker (3.0.0 is used starting from fullrmc 4.0.2)
numpy and cython must be installed and updated manually.
pip install -U "numpy>=1.17.4"
pip install -U "cython>=0.29.14"
pip install fullrmcEnsure all fullrmc required packages are installed and up to data by executing the following python script:
# check whether all packages are already installed
from __future__ import print_function
from pkg_resources import parse_version as PV
for name, ver in [('numpy' ,'1.17.4') ,
('cython' ,'0.29.14'),
('pyrep' ,'3.2.0') ,
('pdbparser' ,'0.1.8') ,
('pysimplelog','2.0.0') ,
('pylocker' ,'3.0.0') ,
('matplotlib' ,'3.1.2' )]:
try:
lib = __import__(name)
except:
print('%s must be installed for fullrmc to run properly.'%(name))
else:
if PV(lib.__version__) < PV(ver):
print('%s installed version %s is below minimum suggested version %s. Updating %s is highly) recommended.'%(name, lib.__version__, ver, name)
else:
print('%s is installed properly and minimum version requirement is met.'%(name))Locate python's site-packages by executing the following python script:
import os
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.__file__), 'site_packages')Navigate to site_packages folder and clone git repository from command line:
cd .../site_packages
git clone https://github.com/bachiraoun/fullrmc.git Change directory to .../site_packages/fullrmc/Extensions. Then compile fullrmc extensions from command line as the following:
cd .../site_packages/fullrmc/Extensions
python setup.py build_ext --inplacehttp://bachiraoun.github.io/fullrmc/
If you use fullrmc in a scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
Text entry:
Bachir Aoun; Fullrmc, a Rigid Body Reverse Monte Carlo Modeling Package Enabled with Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence; J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 1102–1111. DOI: 10.1002/jcc.24304
Bibtex entry:
@article {JCC:JCC24304,
author = {Aoun, Bachir},
title = {Fullrmc, a rigid body reverse monte carlo modeling package enabled with machine learning and artificial intelligence},
journal = {Journal of Computational Chemistry},
volume = {37},
number = {12},
issn = {1096-987X},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.24304},
doi = {10.1002/jcc.24304},
pages = {1102--1111},
keywords = {reverse monte carlo, rigid body, machine learning, pair distribution function, modeling},
year = {2016},
}
EndNote entry:
Provider: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
Content:text/plain; charset="UTF-8"
TY - JOUR
AU - Aoun, Bachir
TI - Fullrmc, a rigid body reverse monte carlo modeling package enabled with machine learning and artificial intelligence
JO - Journal of Computational Chemistry
JA - J. Comput. Chem.
VL - 37
IS - 12
SN - 1096-987X
UR - http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.24304
DO - 10.1002/jcc.24304
SP - 1102
EP - 1111
KW - reverse Monte Carlo
KW - rigid body
KW - machine learning
KW - pair distribution function
KW - modeling
PY - 2016
ER -
- Bachir Aoun (Author, Developer)