GotoSSH is committed to helping you improve work efficiency.
There are some pics, they will show you to what this shell can do.
Normal auto login:
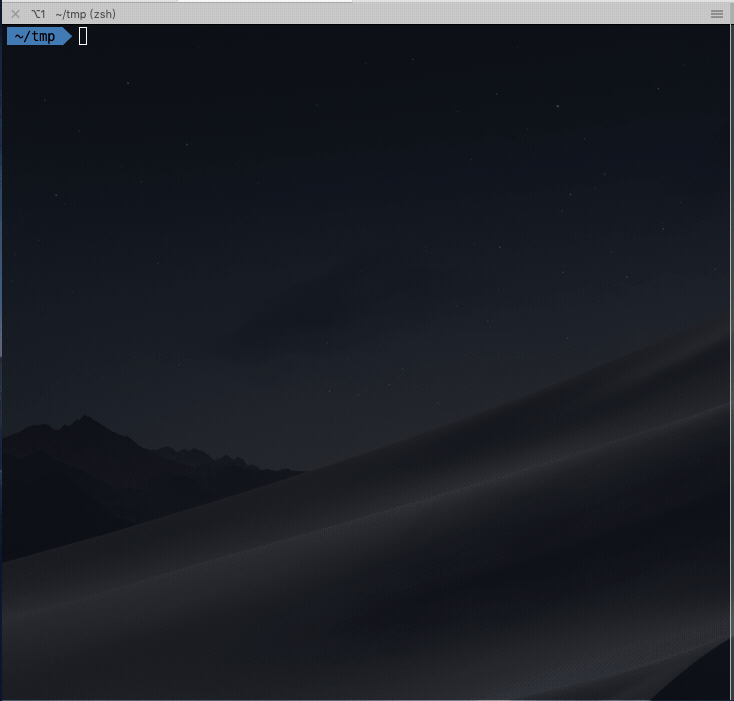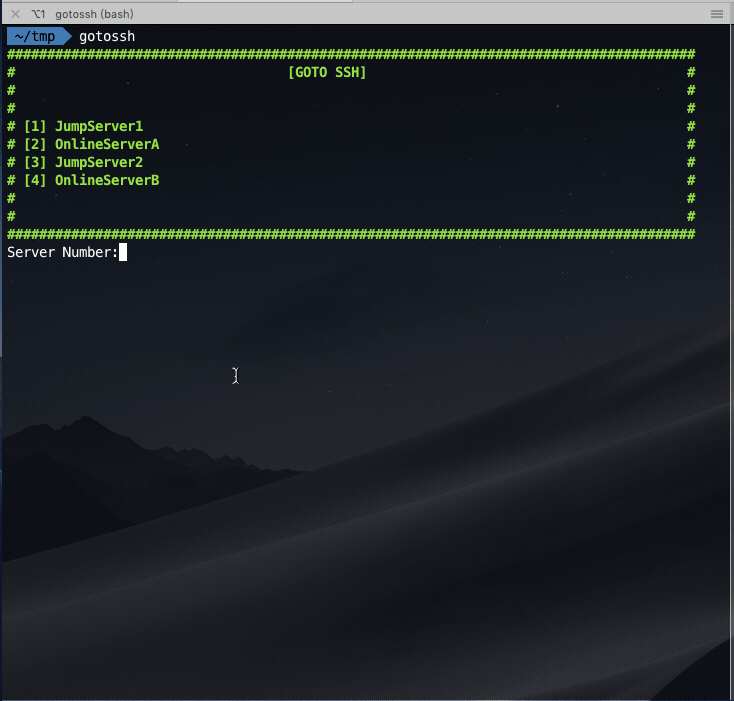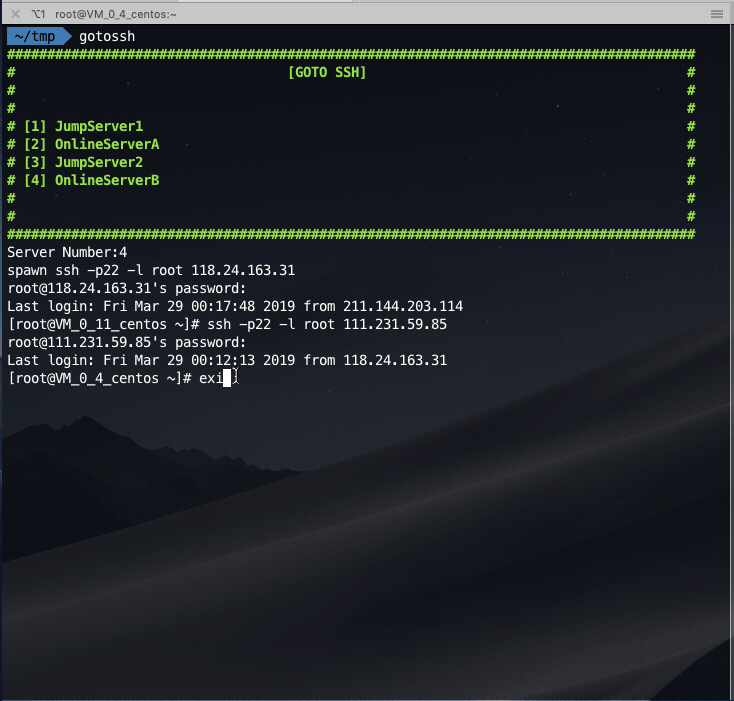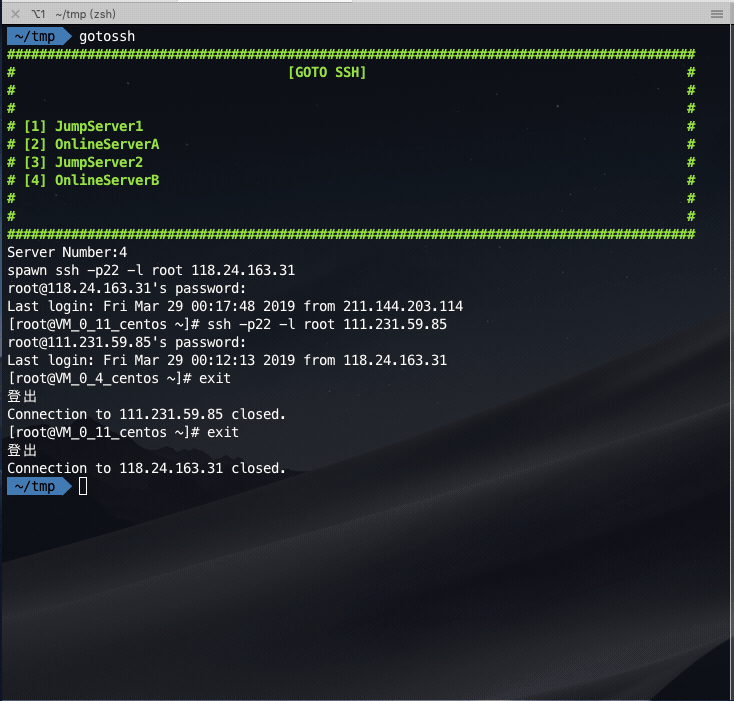
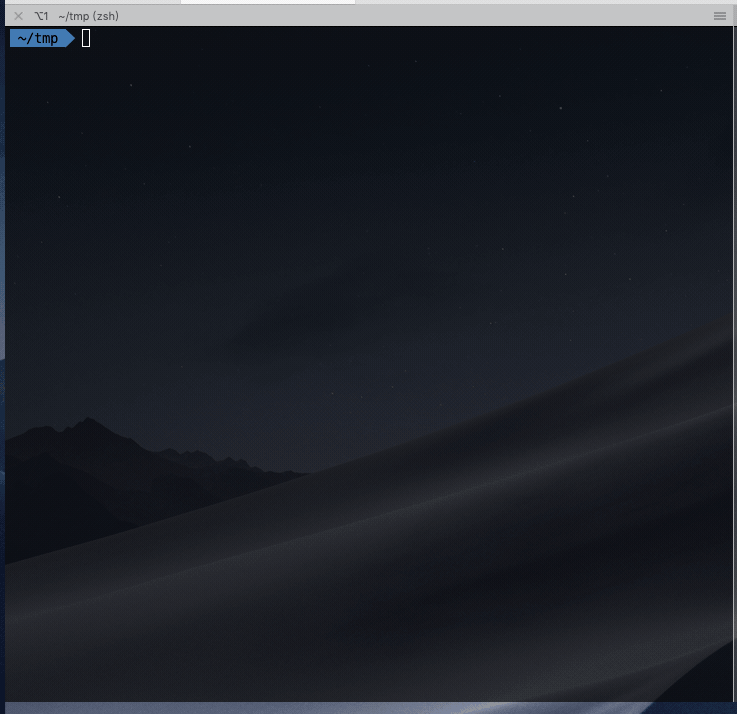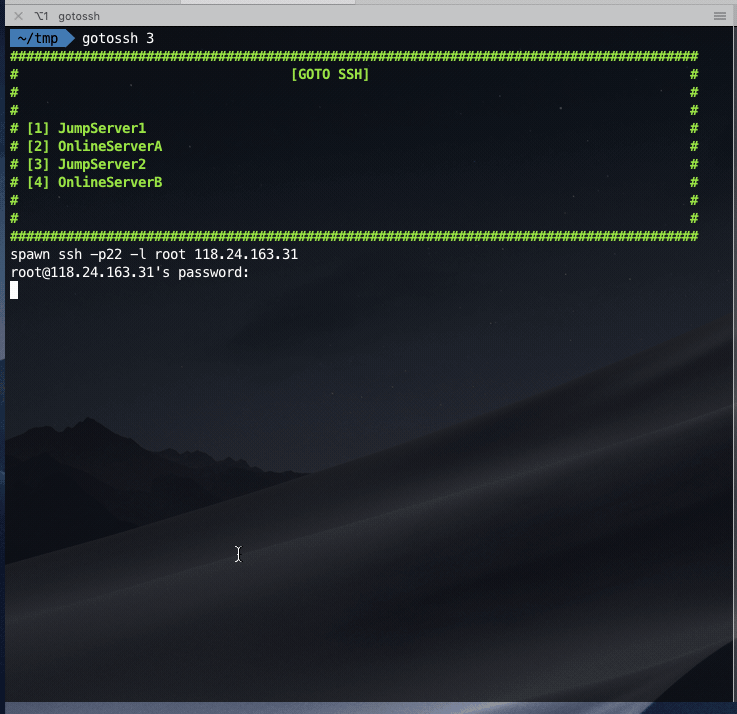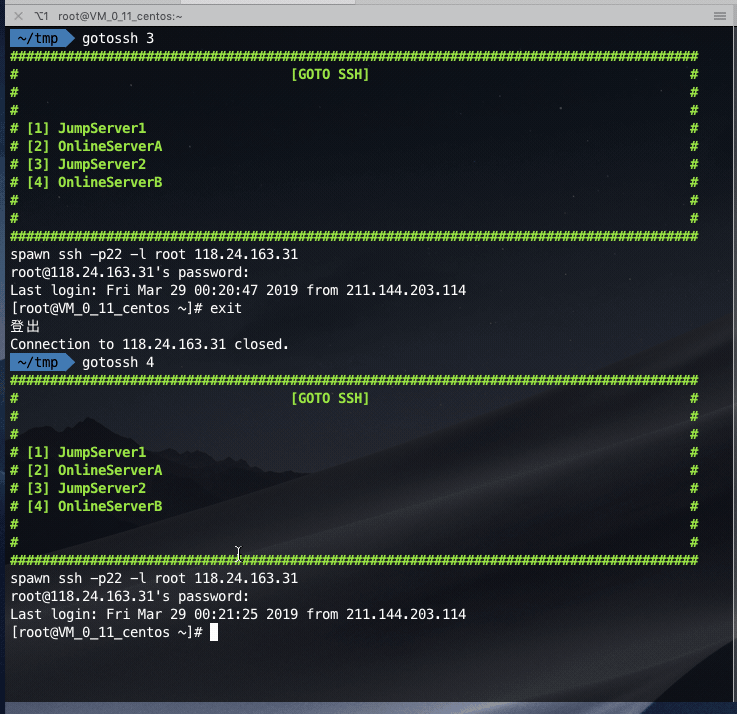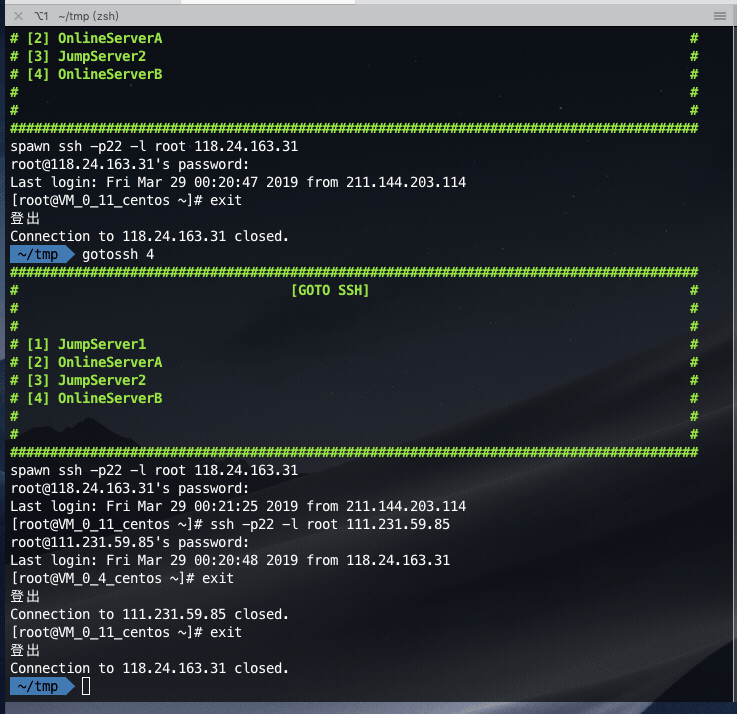
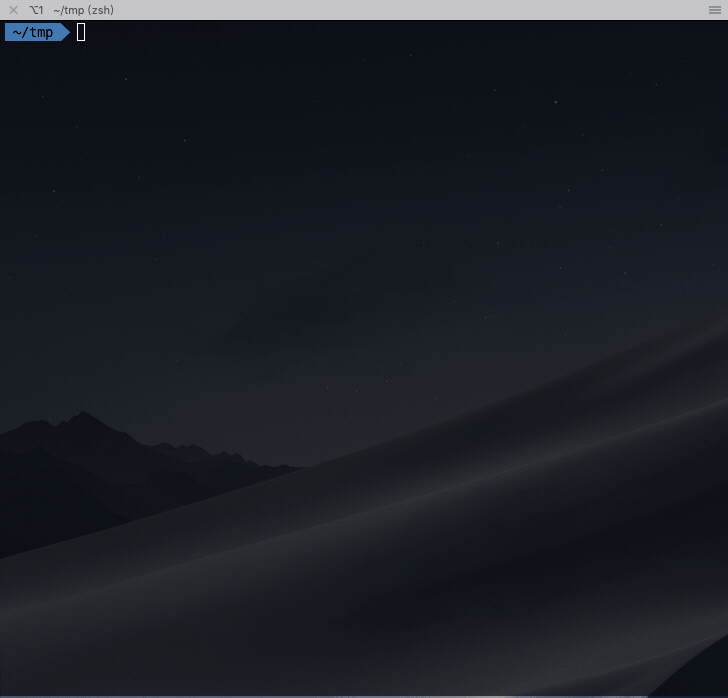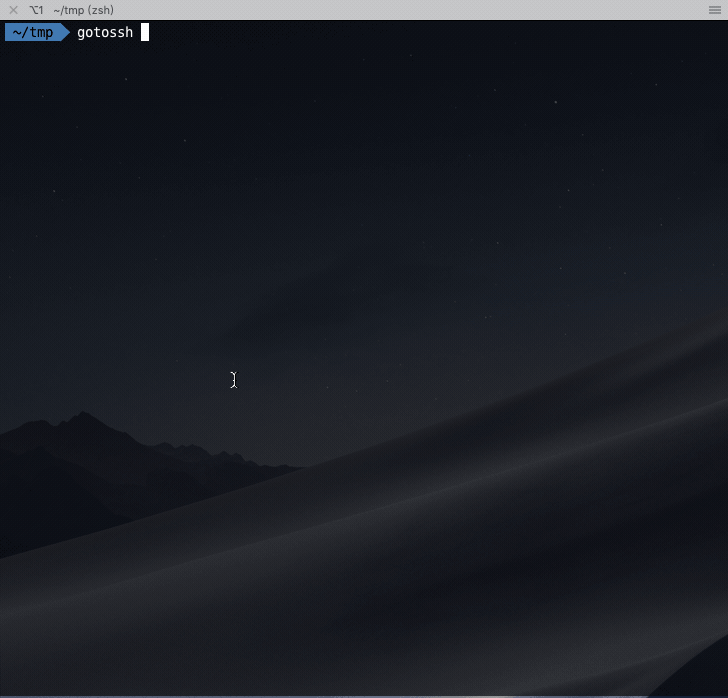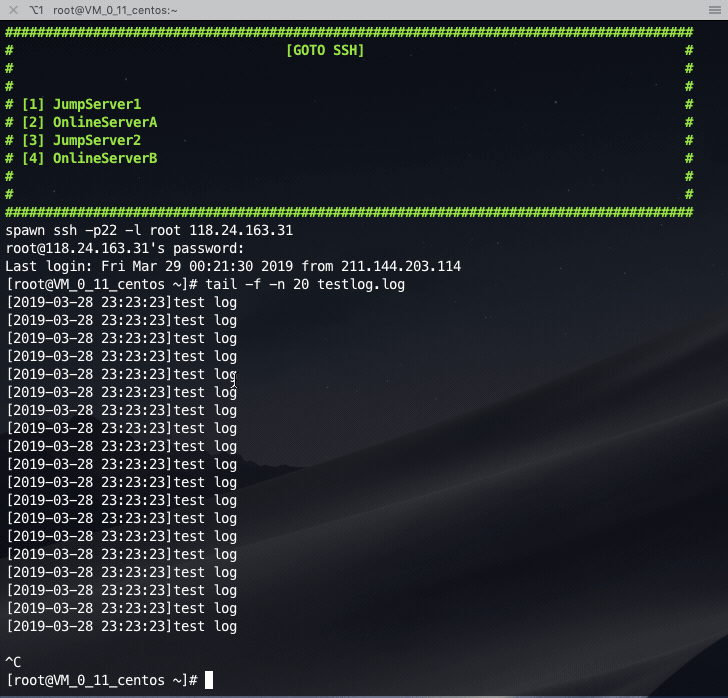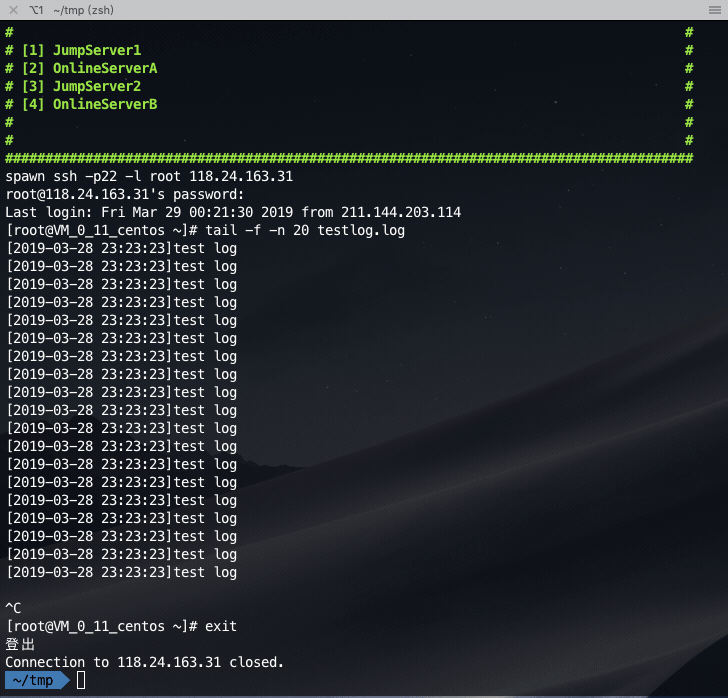
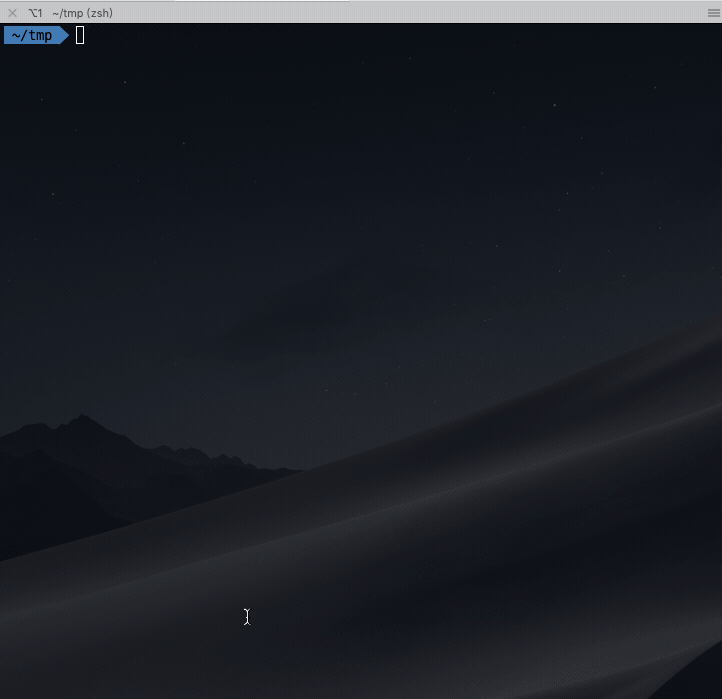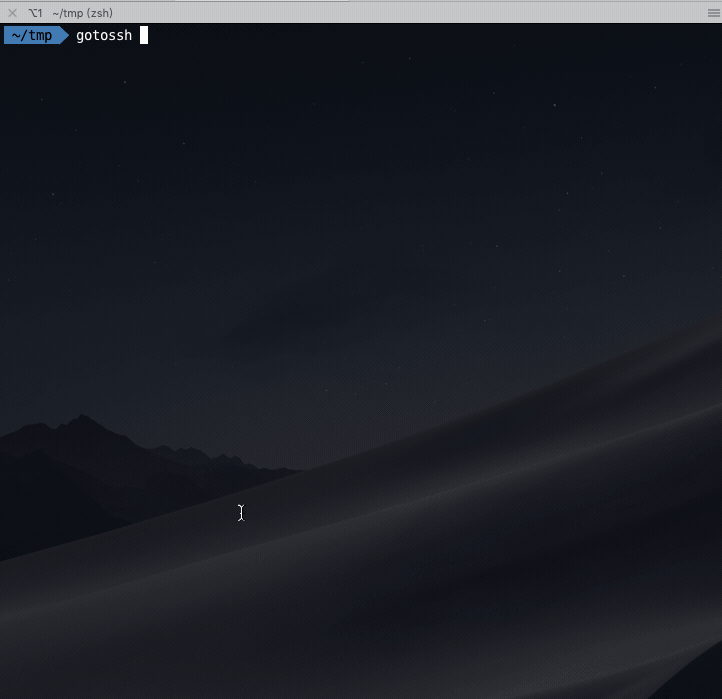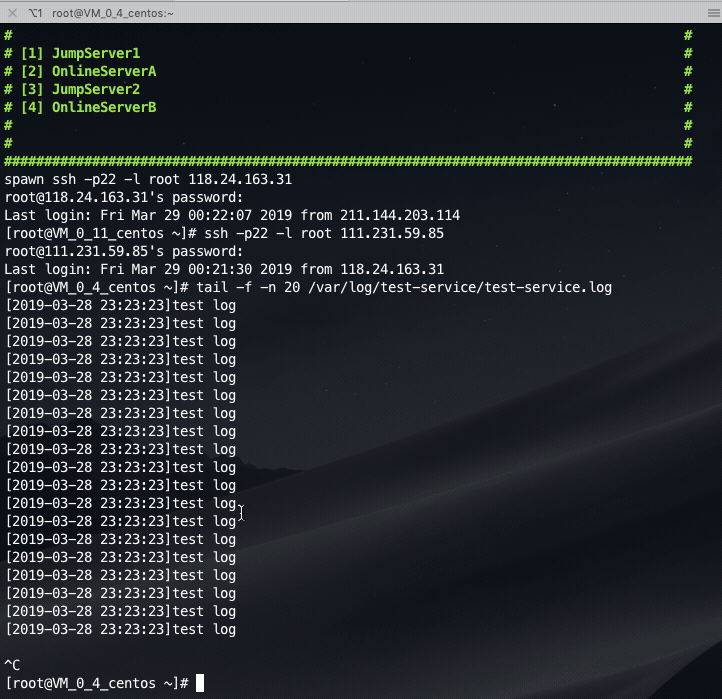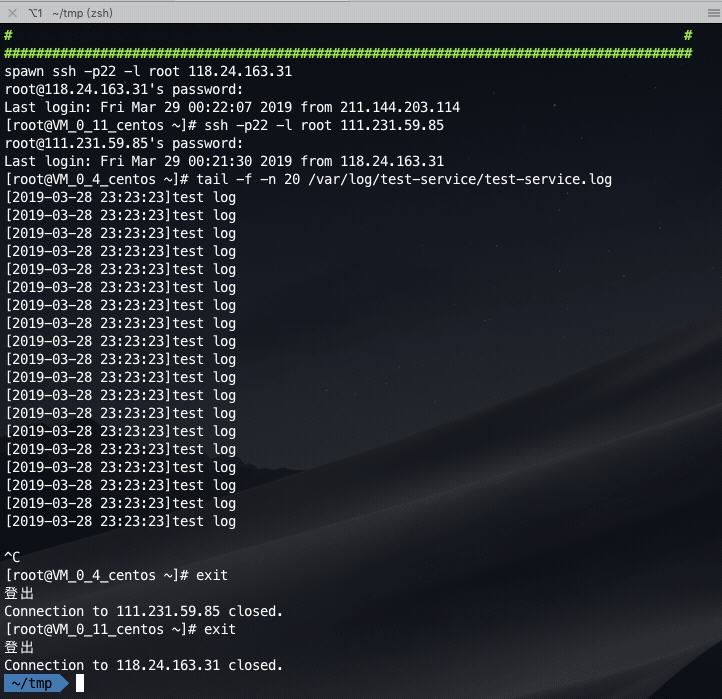
Login the jump server first, and then jump to the online server:
Login the server and view the log:
Login the jump server and then login the online sever to view the log:
Copy file from the remote server:
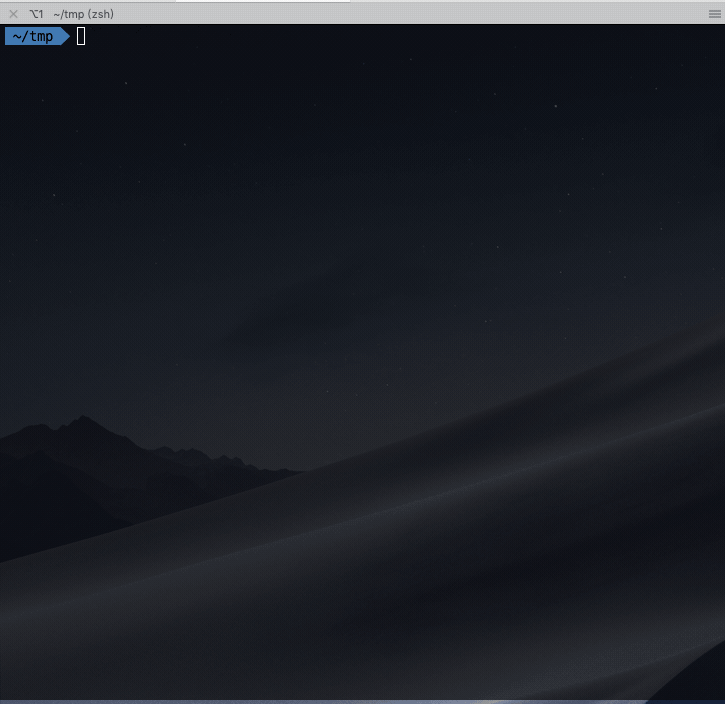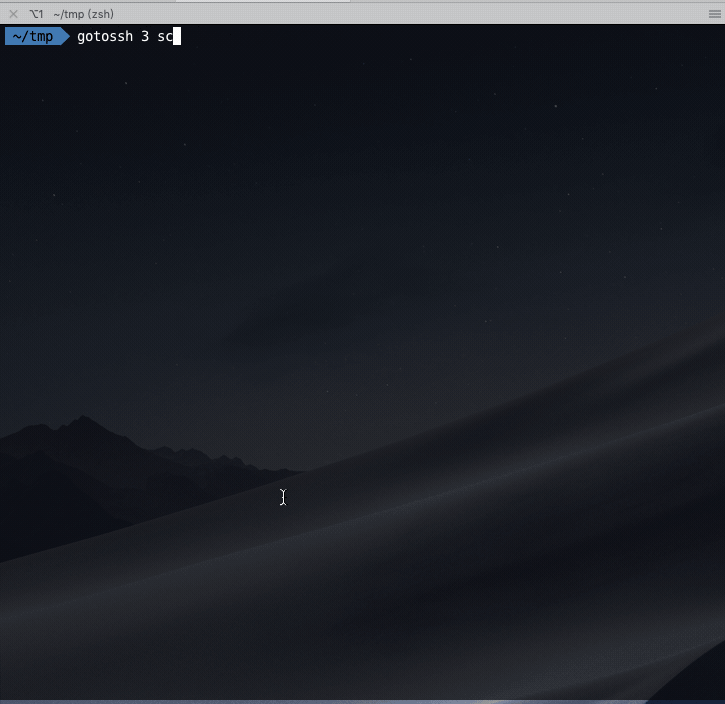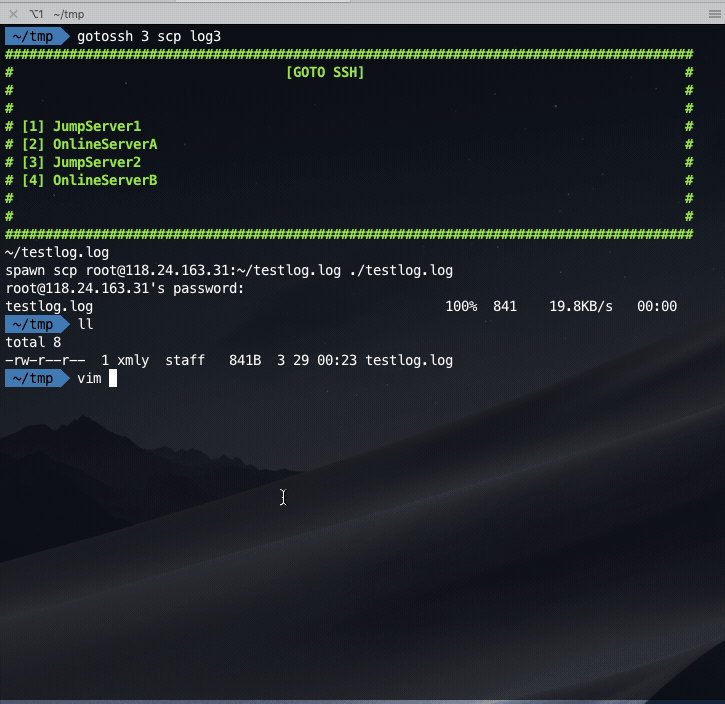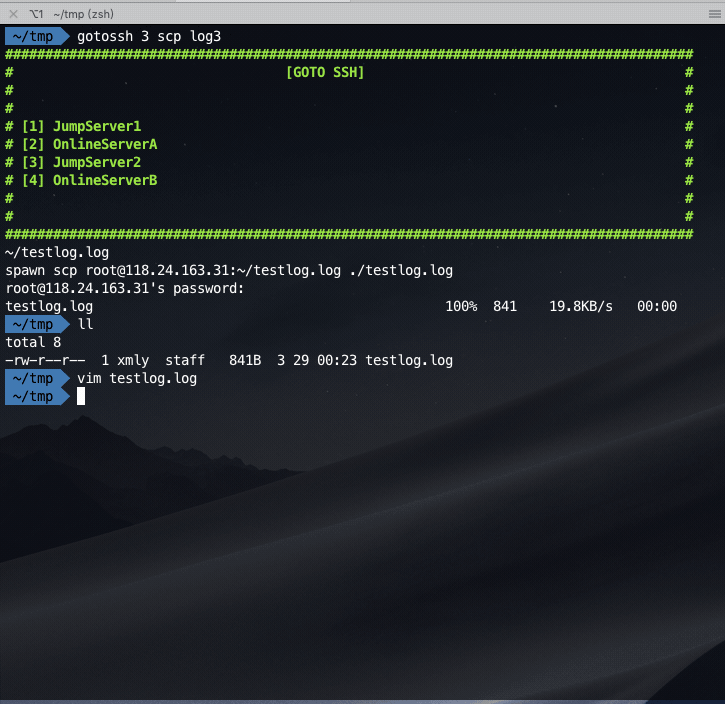
Copy file from the online server:
CentOS :
$ sudo yum install -y expectUbuntu :
$ sudo apt-get install tcl tk expectMac :
$ brew install expect$ git clone https://github.com/MFrank2016/GotoSSH.git
$ cd GotoSSH
$ chmod a+x gotossh
$ sudo cp gotossh /usr/local/bin/$ vim ~/.gotossh_config
server_name|ip|username|password|port|rely_server_no
[Server1]
commend=tail -f -n 10 testlog.log
[scp]
log1=~/testlog.logThe config file consists of three parts.
The first part is the server base info:
server_name|ip|username|password|port|rely_server_no
For example:
JumpServer1|118.24.163.31|root|testpassword|22|0
OnlineServerB|111.231.59.85|root|testpassword2|22|1
The last column of the config means this server relies another server, so this shell will login that server first.(the no starts form 1, so 0 means this server doesn’t rely others)
The second part is custom commend, you could set any commend here for each server.
[Server1]
commend=tail -f -n 10 testlog.log
Server1 means it's set for the first server.
commend is the name of your commend, that could be any name you like, and the actual commend is behind the equals sign.
So you could use it by this way:
gotossh 1 commend
And it will login the first server and excute your commend.
Notice that, if your commend needs a password, like 'scp root@xxxx:xxx xxx', you should add the pwd after the commend.
For example:
[Server1]
commend=scp [email protected]:/var/log/test-service/test-service.log ./test-server.log|testpassword2
The last part is the support of scp commend:
[scp]
log1=~/testlog.log
log2=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log
log1 and log2 are the name you set, and the actual path of the file in server is behind the equals sign.
You could use it like this:
gotossh 1 scp log1
It will copy the remote file on the first server to your local computer.
gotossh 2 scp log2
It will login the first server, and copy that file from the second server, and then copy that file to your local computer.
$ vim ~/.gotossh_config
JumpServer1|118.24.163.31|root|testpassword|22|0
OnlineServerB|111.231.59.85|root|testpassword2|22|1
[Server1]
log=tail -f -n 20 testlog.log
[Server2]
log=tail -f -n 20 /var/log/test-service/test-service.log
cd=cd /var/log/test-service/
[scp]
log3=~/testlog.log
log4=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log$ gotossh
######################################################################################
# [GOTO SSH] #
# #
# #
# [1] test_server - 192.168.0.1:root #
# [2] online_server - 192.168.2.2:root #
# #
# #
######################################################################################
Server Number:(Input Server Number Here)gotossh 1gotossh 2gotossh 1 log
gotossh 2 log
gotossh 2 cd
gotossh 1 scp log3
gotossh 2 scp log4
GotoSSH是一个一键登录SSH的脚本,可直接从跳板机登录到线上服务器,致力于帮助你提高工作效率。
这里有一些动态图,可以帮助你快速了解这个脚本能够做什么。
普通的一键登录:
一键登录跳板机,然后跳转登录线上服务器:
一键登录跳板机查看指定日志:
一键登录跳板机后跳转线上服务器查看指定日志:
然后是更加劲爆内容,一键从跳板机复制指定文件到本地:
一键从生产环境复制指定文件到本地:
CentOS :
$ sudo yum install -y expectUbuntu :
$ sudo apt-get install tcl tk expectMac :
$ sudo brew install expect$ git clone https://github.com/MFrank2016/GotoSSH.git
$ cd GotoSSH
$ chmod a+x gotossh
$ sudo cp gotossh /usr/local/bin/$ vim ~/.gotossh_config
server_name|ip|username|password|port|rely_server_no
[Server1]
commend=tail -f -n 10 testlog.log
[scp]
log1=~/testlog.log配置文件由三部分组成。
第一部分是服务器的基本信息。
server_name|ip|username|password|port|rely_server_no
举个栗子:
JumpServer1|118.24.163.31|root|testpassword|22|0
OnlineServerB|111.231.59.85|root|testpassword2|22|1
最后一列是代表该服务器依赖于哪个服务器,如果该列的值设置为0,代表不依赖于其他服务器,否则代表需要先登录其他服务器后才能登录该服务器,目前暂时只支持二连跳,不支持多跳转。
第二部分是自定义命令,你可以在这里为每台服务器单独设置一些自定义命令。
[Server1]
commend=tail -f -n 10 testlog.log
Server1 表示以下是为第一台服务器设置的命令,同理Server2则表示为第二台设置的命令。对于顺序没有要求,只要为需要设置自定义命令的服务器添加该选项即可。
commend 是命令的名字,可以随意取名,最好简单一点,方便输入,等号后面是实际执行的命令。
举个栗子:
gotossh 1 commend
只要你小手一点回车,脚本便会自动帮你登录到第一台服务器,然后执行上面的命令tail -f -n 10 testlog.log。
注意,如果你输入的命令需要密码的话,需要在命令后面把密码也带上,并且用|分隔。
举个栗子:
[Server1]
commend=scp [email protected]:/var/log/test-service/test-service.log ./test-server.log|testpassword2
配置文件的最后一部分是对于scp命令的支持。
[scp]
log1=~/testlog.log
log2=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log
log1 和 log2 都是随意起的名字,后面是服务器上你想要复制的文件路径,配置好之后,你就可以这样使用:
gotossh 1 scp log1
它就会自动把第一台服务器上的~/testlog.log文件复制到你的本地。
gotossh 2 scp log2
这个操作就更厉害了,因为第二台服务器设置了对第一台服务器的依赖,所以它会先登录第一台服务器,然后再复制第二台服务器上的文件到第一台服务器上,最后,退出到本地,将第一台服务器上的复制品再拷贝到本地。
$ vim ~/.gotossh_config
JumpServer1|118.24.163.31|root|testpassword|22|0
OnlineServerB|111.231.59.85|root|testpassword2|22|1
[Server1]
log=tail -f -n 20 testlog.log
[Server2]
log=tail -f -n 20 /var/log/test-service/test-service.log
cd=cd /var/log/test-service/
[scp]
log3=~/testlog.log
log4=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log$ gotossh
######################################################################################
# [GOTO SSH] #
# #
# #
# [1] test_server - 192.168.0.1:root #
# [2] online_server - 192.168.2.2:root #
# #
# #
######################################################################################
Server Number:(Input Server Number Here)gotossh 1gotossh 2gotossh 1 log
gotossh 2 log
gotossh 2 cd
gotossh 1 scp log3
gotossh 2 scp log4