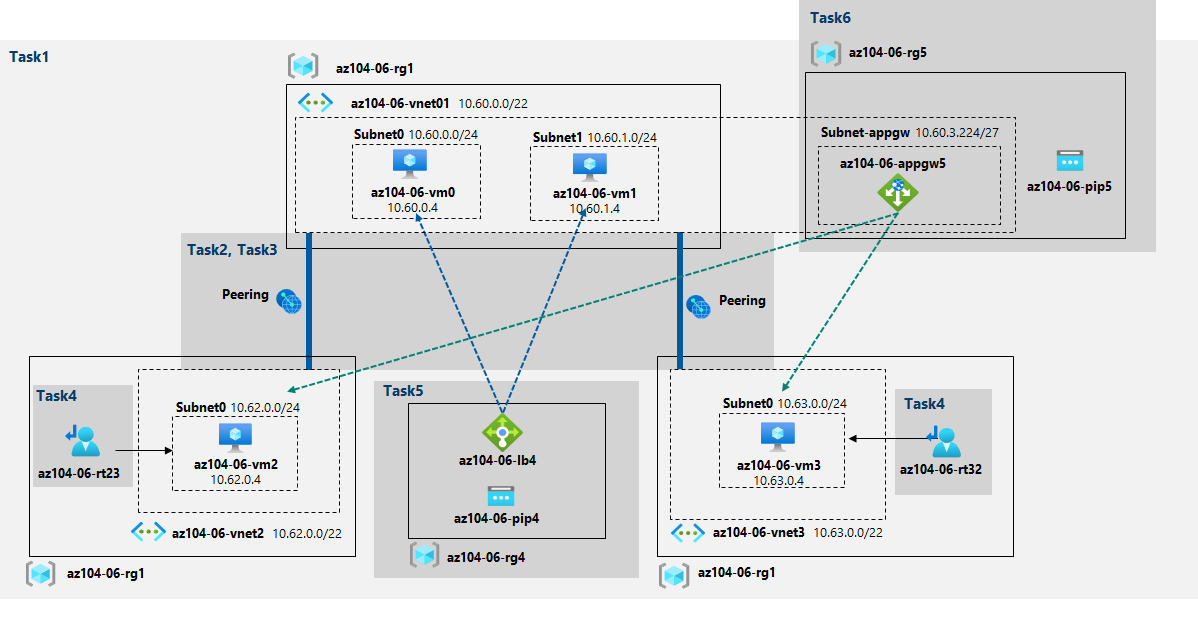
You were tasked with testing managing network traffic targeting Azure virtual machines in the hub and spoke network topology, which Contoso considers implementing in its Azure environment. This testing needs to include implementing connectivity between spokes by relying on user defined routes that force traffic to flow via the hub, as well as traffic distribution across virtual machines by using layer 4 and layer 7 load balancers. For this purpose, you intend to use Azure Load Balancer (layer 4) and Azure Application Gateway (layer 7).
In this lab, you will:
- Task 1: Provision the lab environment
- Task 2: Configure the hub and spoke network topology
- Task 3: Test transitivity of virtual network peering
- Task 4: Configure routing in the hub and spoke topology
- Task 5: Implement Azure Load Balancer
- Task 6: Implement Azure Application Gateway
In this task, you will deploy four virtual machines into the same Azure region. The first two will reside in a hub virtual network, while each of the remaining two will reside in a separate spoke virtual network.
-
Setup git and Terraform.
-
Create the rg module and resource groups.
-
Create the vnet and subnet modules and virtual networks and subnets.
-
Create the vm module and VMs.
-
Create the pip module and public ips.
-
Create the network watcher.
-
Use Network Watcher to view topology of the network.
In this task, you will configure local peering between the virtual networks you deployed in the previous tasks in order to create a hub and spoke network topology.
- Create the peering between VNet1 and VNet2, and VNet1 and VNet3.
In this task, you will test transitivity of virtual network peering by using Network Watcher.
-
In the Azure portal, search for and select Network Watcher.
-
On the Network Watcher blade, expand the listing of Azure regions and verify the service is enabled in region you are using.
-
On the Network Watcher blade, navigate to the Connection troubleshoot.
-
On the Network Watcher - Connection troubleshoot blade, initiate a check between vm0 and vm2.
-
Click Check and wait until results of the connectivity check are returned. Verify that the status is Reachable. Review the network path and note that the connection was direct, with no intermediate hops in between the VMs.
Note: This is expected, since the hub virtual network is peered directly with the first spoke virtual network.
-
On the Network Watcher - Connection troubleshoot blade, initiate a check between vm0 and vm3.
-
Click Check and wait until results of the connectivity check are returned. Verify that the status is Reachable. Review the network path and note that the connection was direct, with no intermediate hops in between the VMs.
Note: This is expected, since the hub virtual network is peered directly with the second spoke virtual network.
-
On the Network Watcher - Connection troubleshoot blade, initiate a check between vm2 and vm3.
-
Click Check and wait until results of the connectivity check are returned. Note that the status is Unreachable.
Note: This is expected, since the two spoke virtual networks are not peered with each other (virtual network peering is not transitive).
In this task, you will configure and test routing between the two spoke virtual networks by enabling IP forwarding on the network interface of the az104-06-vm0 virtual machine, enabling routing within its operating system, and configuring user-defined routes on the spoke virtual network.
-
In the vm module, add enable_ip_forwarding = var.ip_forwarding.
-
Set its default value as false in the variables file.
-
In the VMs.tf file override this value with true for vm0.
Note: This setting is required in order for az104-06-vm0 to function as a router, which will route traffic between two spoke virtual networks.
Note: Now you need to configure operating system of the az104-06-vm0 virtual machine to support routing.
-
In the Azure portal, navigate back to the az104-06-vm0 Azure virtual machine blade and click Overview.
-
On the az104-06-vm0 blade, in the Operations section, click Run command, and, in the list of commands, click RunPowerShellScript.
-
On the Run Command Script blade, type the following and click Run to install the Remote Access Windows Server role.
Install-WindowsFeature RemoteAccess -IncludeManagementTools
Note: Wait for the confirmation that the command completed successfully.
-
On the Run Command Script blade, type the following and click Run to install the Routing role service.
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Routing -IncludeManagementTools -IncludeAllSubFeature Install-WindowsFeature -Name "RSAT-RemoteAccess-Powershell" Install-RemoteAccess -VpnType RoutingOnly Get-NetAdapter | Set-NetIPInterface -Forwarding Enabled
Note: Wait for the confirmation that the command completed successfully.
Note: Now you need to create and configure user defined routes on the spoke virtual networks.
-
Create route tables and associations with the subnets.
-
In the Azure portal, navigate back to the Network Watcher - Connection troubleshoot blade.
-
On the Network Watcher - Connection troubleshoot blade, initiate a check between vm2 and vm3.
-
Click Check and wait until results of the connectivity check are returned. Verify that the status is Reachable. Review the network path and note that the traffic was routed via 10.60.0.4, assigned to the az104-06-nic0 network adapter. If status is Unreachable, you should stop and then start az104-06-vm0.
Note: This is expected, since the traffic between spoke virtual networks is now routed via the virtual machine located in the hub virtual network, which functions as a router.
In this task, you will implement an Azure Load Balancer in front of the two Azure virtual machines in the hub virtual network.
-
Create install_iis module and install IIS to all four VMs.
-
Create nsg module and NSGs.
-
Create the load balancer.
-
Go to the load balancer and get its public IP.
-
Open another browser tab and navigate to the IP address. Verify that the browser window displays the IIS welcome screen.
In this task, you will implement an Azure Application Gateway in front of the two Azure virtual machines in the spoke virtual networks.
-
Create the application gateway.
-
Get its public IP address.
-
Verify that the browser window displays the IIS welcome screen.
Note: Remember to remove any newly created Azure resources that you no longer use. Removing unused resources ensures you will not see unexpected charges.
Note: Don't worry if the lab resources cannot be immediately removed. Sometimes resources have dependencies and take a longer time to delete. It is a common Administrator task to monitor resource usage, so just periodically review your resources in the Portal to see how the cleanup is going.
- Use terraform destroy to clean up all resources.