| status | |
|---|---|
| master | |
| develop |
eNMS is a vendor-agnostic NMS designed for building workflow-based network automation solutions.
It encompasses the following aspects of network automation:
- Configuration Management Service: Commit / Rollback of a configuration with Napalm or Netmiko.
- Ansible Service: Sending and managing Ansible playbooks.
- ReST Service: Sending a ReST call (GET/POST/UPDATE/DELETE) with variable URL and payload.
- Custom Services: Any python script can be integrated into the web UI. If the script takes input parameters, a form will be automatically generated.
- Workflows: Services can be combined together graphically in a workflow.
- Scheduling: Services and workflows can be scheduled to start at a later time, or run periodically.
- Event-driven automation: Services and workflows can be triggered by an external event (ReST call or Syslog message).
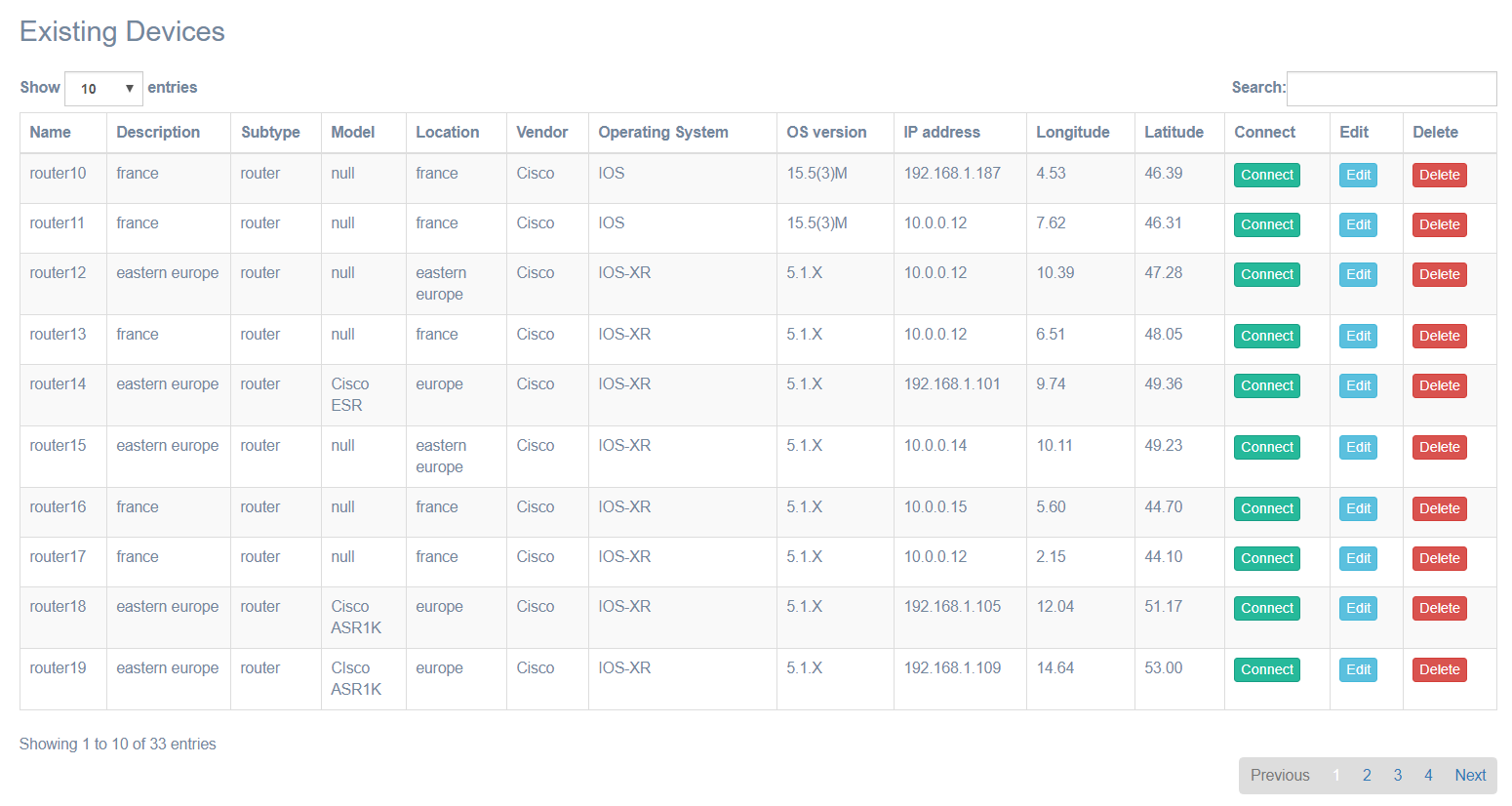
Devices and links can be created either one by one, or all at once by importing an Excel spreadsheet.
Once created, all objects are displayed in a sortable and searchable table, from which they can be edited and deleted.
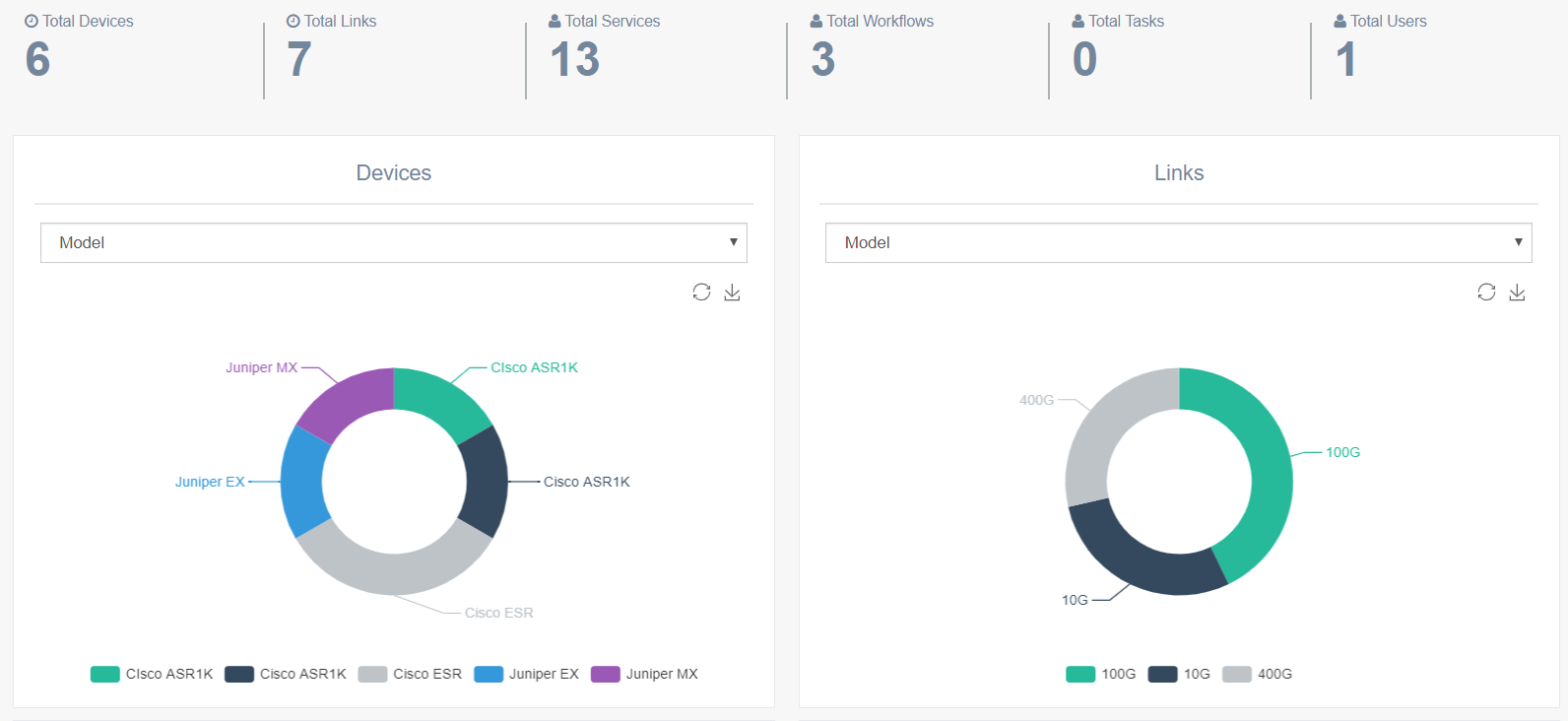
A dashboard provides a graphical overview of all objects with dynamic charts.
| Inventory | Dashboard |
|---|---|
 |
 |
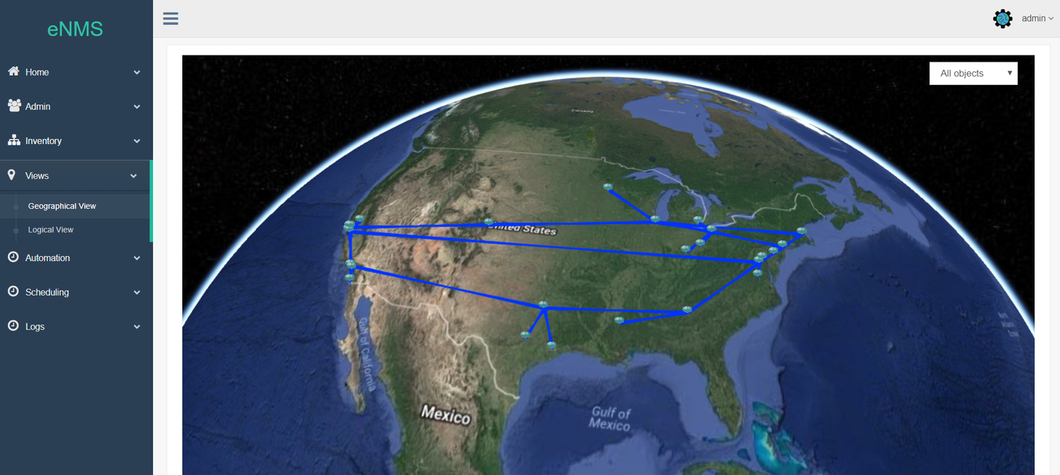
Once created, eNMS can display your network:
- geographically on a 2D or 3D world map (with the tile layer of your choice: Open Street Map, Google Map...)
- logically with a force-based algorithm (
d3.js).
You can click on a device to display its properties or start a Web SSH terminal session.
| Geographical View | Logical View |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- Online demo: Geographical View, Logical View
- Docs: Geographical View, Logical View
eNMS comes with a number of "default services" leveraging libraries such as ansible, requests, netmiko, napalm to perform simple automation tasks. However, absolutely any python script can be turned into a "service".
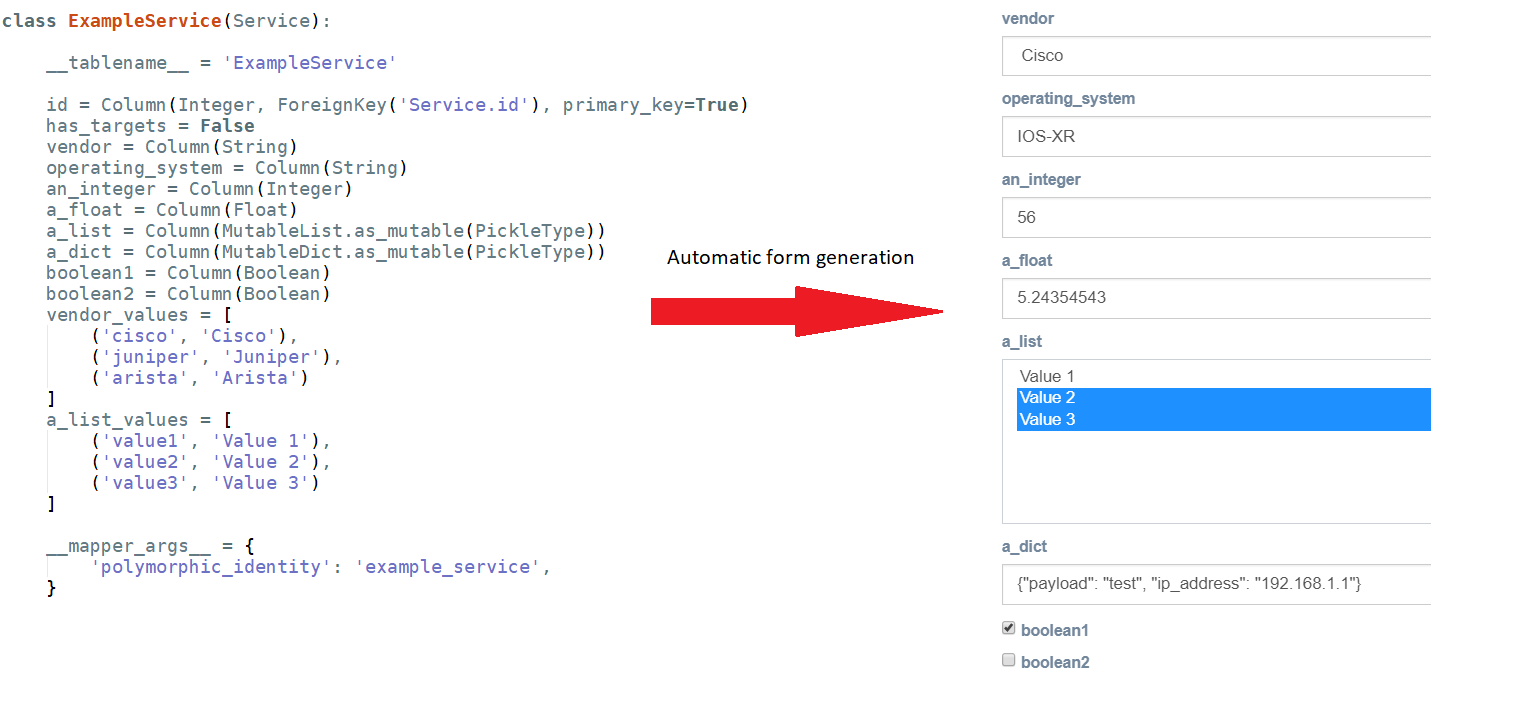
If your python script takes input parameters, eNMS will automatically generate a form in the web UI.
To generate a form that matches your service, eNMS will perform the following conversion:
- python
string-> Text box (single line or multiline) - python
list-> Drop-down list (single or multiselect). - python
bool-> Checkbox. - python
dict-> Text box expecting a dictionary.
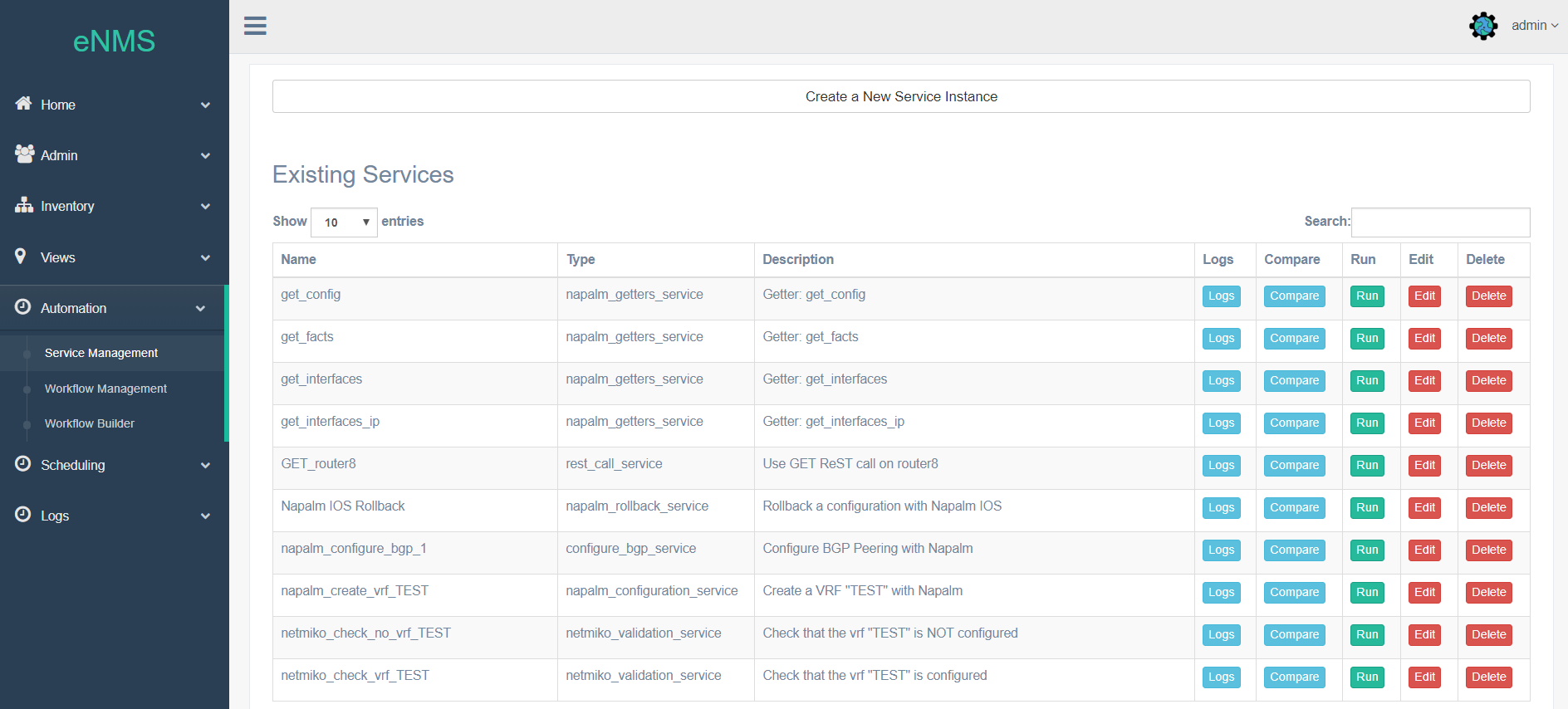
Once created, you can have as many instances of your service as you need. Service instances can be executed, edited and deleted from the web UI.
- Online demo: Services
- Docs: Services, Default Services
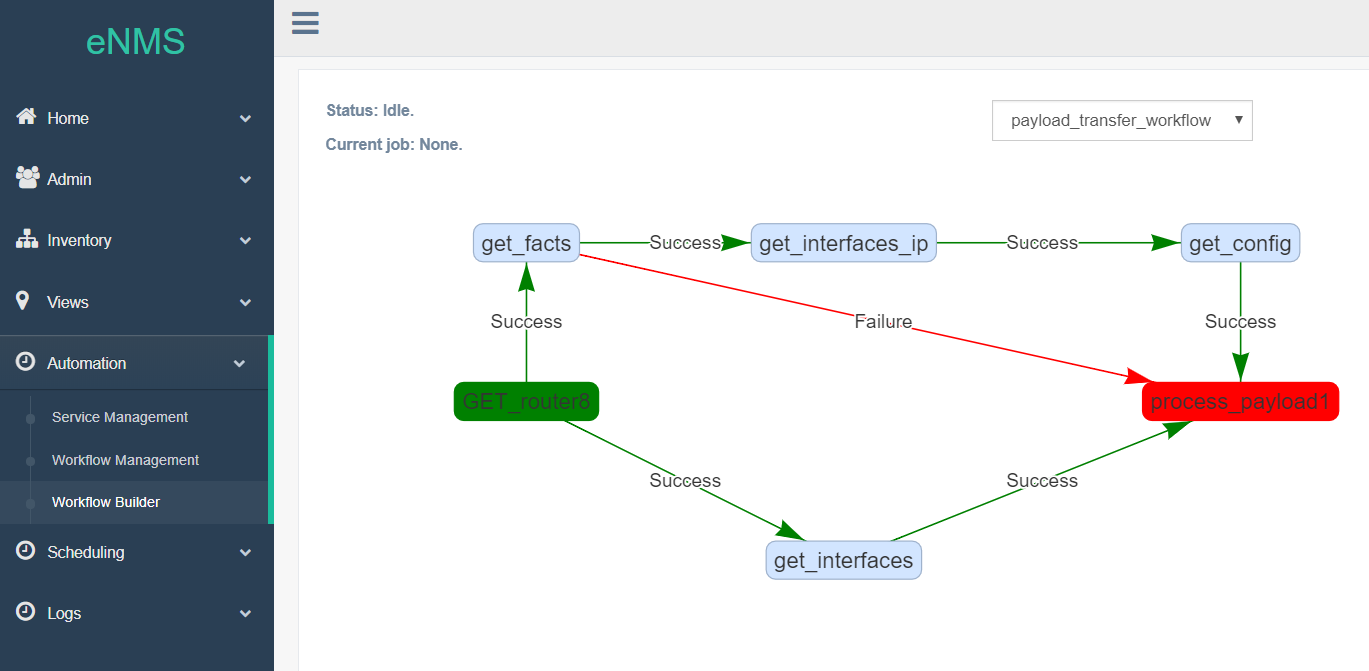
Services (and other Workflows) can be combined into a single workflow.
Within a workflow, services can be connected with two edge types: Success edge and Failure edge. The Success edge (versus Failure edge) indicates which path to follow in the graph if the source service is successfully executed (versus failed).
A workflow keeps track of a payload dictionary, such that when a service starts, it has access to the results of all previously executed services.
When a workflow is executed, its status will be updated in real-time on the web UI.
- Online demo: Workflow Builder
- Docs: Workflow System, Workflow Payload
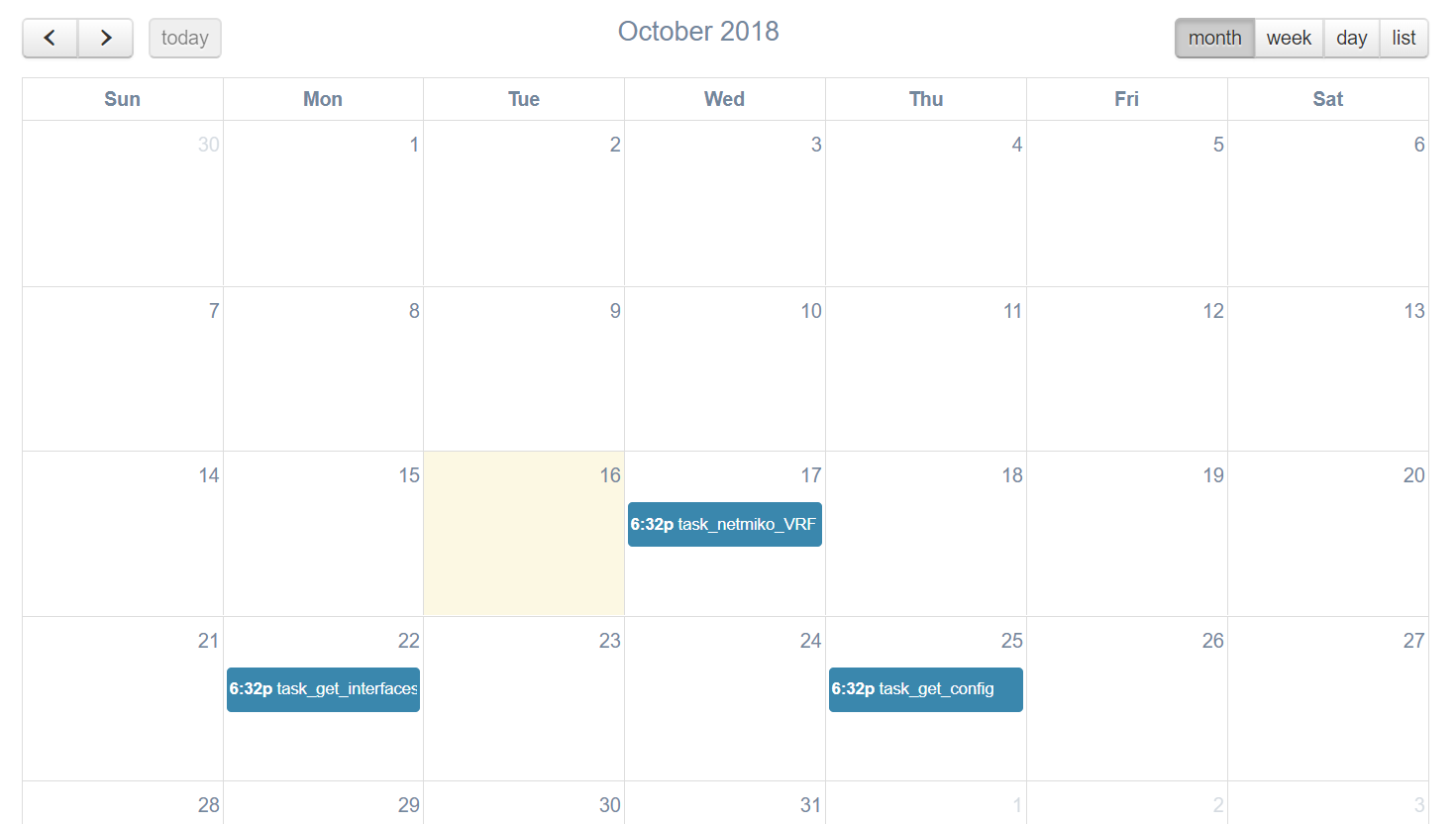
While services and workflows can be run directly and immediately from the web UI, you can also schedule them to run at a later time, or periodically by defining a frequency, a start date and an end date. All scheduled tasks are displayed in a calendar.
- Online Demo: Calendar
- Docs: Scheduling
Event-driven automation in eNMS has two aspects:
- eNMS has a ReST API that can be used to create, update and delete any type of objects (services, workflows, tasks), but also to trigger the execution of a service or a workflow with a GET request to the appropriate URL.
- eNMS can be configured as a Syslog server: all logs are stored in the database, and rules can be created to trigger the execution of a service or a workflow upon receiving a log matched by the rule.
Docs: ReST API
- eNMS supports TACACS+ authentication: upon logging in, a request will be sent to your TACACS+ server to validate the credentials and log in the user.
- Authentication with RADIUS and Active Directory are currently under development.
If you use an NSoT like OpenNMS or Netbox to document your network, eNMS can automatically import the network topology (devices and links), as well as all IP addresses and geographical coordinates.
- Networks can be exported as an Excel file.
- Networks can be exported as a
kmzfile for you to visualize your network on Google Earth.
Install python 3.5+ (earlier versions not supported)
git clone https://github.com/afourmy/eNMS.git
cd eNMS
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
export FLASK_APP=app.py (on Windows, use `set` instead of `export`)
flask run --host=0.0.0.0
Log in (default credentials: `admin`/ `admin`)
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name enms --restart always afourmy/enms
Log in (default credentials: `admin`/ `admin`)
In production, eNMS is configured to use a PostgreSQL database and a Hashicorp Vault (storage of network credentials).
Check out the Installation section of the docs: Install eNMS
For any feedback, advice, feature request, join us on the Network to Code slack, channel #enms.
- A notification system (send the results of an automation task via mail or Slack)
- Gitlab support (e.g push the logs of an automation task to gitlab)
- RADIUS + Active Directory authentication
- Flask Gentelella: The Flask/Bootstrap template eNMS is built upon.
- pyNMS: A PyQt software for network simulation and optimization.
- SWAP: A solver for the Wavelength Assignment Problem in optical networks.